graph/network-delay-time
优质
小牛编辑
138浏览
2023-12-01
Network Delay Time
描述
There are N network nodes, labelled 1 to N.
Given times, a list of travel times as directed edges times[i] = (u, v, w), where u is the source node, v is the target node, and w is the time it takes for a signal to travel from source to target.
Now, we send a signal from a certain node K. How long will it take for all nodes to receive the signal? If it is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
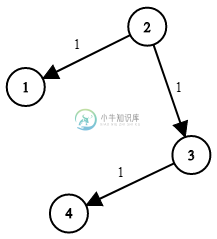
Input: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], N = 4, K = 2
Output: 2
Note:
Nwill be in the range[1, 100].Kwill be in the range[1, N].- The length of
timeswill be in the range[1, 6000]. - All edges
times[i] = (u, v, w)will have1 <= u, v <= Nand0 <= w <= 100.
分析
本题可以抽象为:给定图 G 和源顶点 v,找到从 v 至图中所有顶点的最短路径。这是经典的单源最短路径问题,用 Dijkstra 算法。时间复杂度 $O(E\log V)$,空间复杂度 $O(V+E)$,V 为顶点个数,E 为边条数。
代码
// Network Delay Time
// Dijkstra
// Time Complexity: O(ElogN), Space Complexity: O(N + E)
class Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int N, int K) {
// adjacency list, map<vertex_id, map<vertex_id, weight>>
Map<Integer, Map<Integer,Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] time : times){
graph.putIfAbsent(time[0], new HashMap<>());
graph.get(time[0]).put(time[1], time[2]);
}
Map<Integer, Integer> dist = dijkstra(graph, K);
return dist.size() == N ? Collections.max(dist.values()) : -1;
}
/** Standard Dijkstra algorithm.
*
@param graph Adjacency list, map<vertex_id, map<vertex_id, weight>>.
@param start The starting vertex ID.
@return dist, map<vertex_id, distance>.
*/
private static Map<Integer, Integer> dijkstra(Map<Integer, Map<Integer,Integer>> graph, int start) {
// map<vertex_id, distance>
Map<Integer, Integer> dist = new HashMap<>();
// vertex_id -> father_vertex_id
Map<Integer, Integer> father = new HashMap<>();
// pair<distance, vertex_id>, min heap, sorted by distance from start to vertex_id
Queue<Pair<Integer, Integer>> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.getKey() - b.getKey());
// from start to start itself
pq.offer(new Pair(0, start));
dist.put(start, 0);
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
final int u = pq.poll().getValue();
if (!graph.containsKey(u)) continue; // leaf node
for(int v : graph.get(u).keySet()){
final int w = graph.get(u).get(v);
if (!dist.containsKey(v) || dist.get(u)+ w < dist.get(v)) {
final int shorter = dist.get(u)+ w;
dist.put(v, shorter);
father.put(v, u);
pq.offer(new Pair(shorter, v));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
// TODO

