bitwise-operations/gray-code
Gray Code
描述
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
For example, given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0
01 - 1
11 - 3
10 - 2
Note:
- For a given
n, a gray code sequence is not uniquely defined. - For example,
[0,2,3,1]is also a valid gray code sequence according to the above definition. - For now, the judge is able to judge based on one instance of gray code sequence. Sorry about that.
分析
格雷码(Gray Code)的定义请参考 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gray_code
自然二进制码转换为格雷码:$$g0=b_0, g_i=b_i \oplus b{i-1}$$
保留自然二进制码的最高位作为格雷码的最高位,格雷码次高位为二进制码的高位与次高位异或,其余各位与次高位的求法类似。例如,将自然二进制码 1001,转换为格雷码的过程是:保留最高位;然后将第 1 位的 1 和第 2 位的 0 异或,得到 1,作为格雷码的第 2 位;将第 2 位的 0 和第 3 位的 0 异或,得到 0,作为格雷码的第 3 位;将第 3 位的 0 和第 4 位的 1 异或,得到 1,作为格雷码的第 4 位,最终,格雷码为 1101。
格雷码转换为自然二进制码:$$b0=g_0, b_i=g_i \oplus b{i-1}$$
保留格雷码的最高位作为自然二进制码的最高位,次高位为自然二进制高位与格雷码次高位异或,其余各位与次高位的求法类似。例如,将格雷码 1000 转换为自然二进制码的过程是:保留最高位 1,作为自然二进制码的最高位;然后将自然二进制码的第 1 位 1 和格雷码的第 2 位 0 异或,得到 1,作为自然二进制码的第 2 位;将自然二进制码的第 2 位 1 和格雷码的第 3 位 0 异或,得到 1,作为自然二进制码的第 3 位;将自然二进制码的第 3 位 1 和格雷码的第 4 位 0 异或,得到 1,作为自然二进制码的第 4 位,最终,自然二进制码为 1111。
格雷码有数学公式,整数n的格雷码是$$n \oplus (n/2)$$。
这题要求生成n比特的所有格雷码。
方法 1,最简单的方法,利用数学公式,对从 $$0\sim2^n-1$$的所有整数,转化为格雷码。
方法 2,n比特的格雷码,可以递归地从n-1比特的格雷码生成。如下图所示。
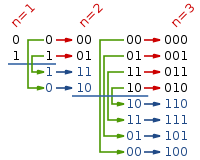
数学公式
// Gray Code
// 数学公式,时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(1)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
final int size = 1 << n; // 2^n
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
result.add(binary_to_gray(i));
return result;
}
private static int binary_to_gray(int n) {
return n ^ (n >> 1);
}
}
// Gray Code
// 数学公式,时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> grayCode(int n) {
const int size = 1 << n; // 2^n
vector<int> result;
result.reserve(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
result.push_back(binary_to_gray(i));
return result;
}
private:
static int binary_to_gray(int n) {
return n ^ (n >> 1);
}
};
Reflect-and-prefix method
// Gray Code
// reflect-and-prefix method
// 时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(1)
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
final int size = 1 << n;
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(size);
result.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
final int highest_bit = 1 << i;
for (int j = result.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) // 要反着遍历,才能对称
result.add(highest_bit | result.get(j));
}
return result;
}
}
// Gray Code
// reflect-and-prefix method
// 时间复杂度O(2^n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> grayCode(int n) {
const int size = 1 << n;
vector<int> result;
result.reserve(size);
result.push_back(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const int highest_bit = 1 << i;
for (int j = result.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) // 要反着遍历,才能对称
result.push_back(highest_bit | result[j]);
}
return result;
}
};

