类神经网路 Neural_Networks - Ex 1: Visualization of MLP weights on MNIST
优质
小牛编辑
144浏览
2023-12-01
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/neural_networks/plot_mnist_filters.html
此范例将使用MNIST dataset的训练资料集去训练MLPClassifier,资料集中每张图片都是28*28,对于第一层的每个神经元都会有28*28个特征,输出结果是将训练资料的每个像素点对于神经元的权重画成28*28的图,用来表示图片上每个像素点对于神经元的权重多寡。
(一)引入函式库与资料
1.matplotlib.pyplot:用来绘制影像
2.sklearn.datasets:引入内建的手写数字资料库
3.sklearn.neural_network:引入类神经网路的套件
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_mldatafrom sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifiermnist = fetch_mldata("MNIST original")
(二)将资料切割成训练集与测试集
# 将灰阶影像降尺度降到[0,1]X, y = mnist.data / 255., mnist.targetX_train, X_test = X[:60000], X[60000:]y_train, y_test = y[:60000], y[60000:]
(三)设定分类器参数与训练网路并画出权重矩阵
#hidden_layer_sizes=(50)此处使用1层隐藏层,只有50个神经元,max_iter=10叠代训练10次mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(50), max_iter=10, alpha=1e-4,solver='sgd', verbose=10, tol=1e-4, random_state=1,learning_rate_init=.1)mlp.fit(X_train, y_train)#画出16个神经元的权重图,黑色表示负的权重,越深色表示数值越大,白色表示正的权重,越浅色表示数值越大fig, axes = plt.subplots(4, 4)# use global min / max to ensure all weights are shown on the same scalevmin, vmax = mlp.coefs_[0].min(), mlp.coefs_[0].max()for coef, ax in zip(mlp.coefs_[0].T, axes.ravel()):ax.matshow(coef.reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.gray, vmin=.5 * vmin,vmax=.5 * vmax)ax.set_xticks(())ax.set_yticks(())plt.show()
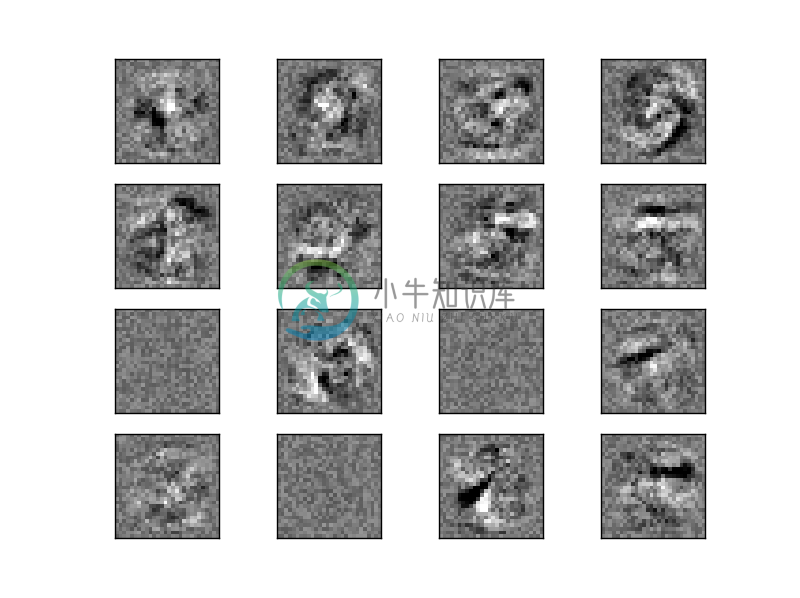
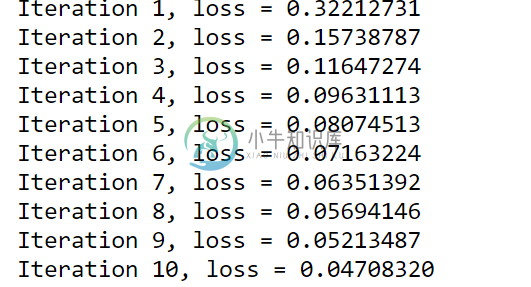
(四)完整程式码
print(__doc__)import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_mldatafrom sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifiermnist = fetch_mldata("MNIST original")X, y = mnist.data / 255., mnist.targetX_train, X_test = X[:60000], X[60000:]y_train, y_test = y[:60000], y[60000:]mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(50), max_iter=10, alpha=1e-4,solver='sgd', verbose=10, tol=1e-4, random_state=1,learning_rate_init=.1)mlp.fit(X_train, y_train)print("Training set score: %f" % mlp.score(X_train, y_train))print("Test set score: %f" % mlp.score(X_test, y_test))fig, axes = plt.subplots(4, 4)vmin, vmax = mlp.coefs_[0].min(), mlp.coefs_[0].max()for coef, ax in zip(mlp.coefs_[0].T, axes.ravel()):ax.matshow(coef.reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.gray, vmin=.5 * vmin,vmax=.5 * vmax)ax.set_xticks(())ax.set_yticks(())plt.show()

