PyTorch递归神经网络
精华
小牛编辑
245浏览
2023-03-14
递归神经网络是一种遵循顺序方法的深度学习导向算法。在神经网络中,我们总是假设每个输入和输出都独立于所有其他层。这些类型的神经网络被称为循环,因为它们以顺序方式执行数学计算,完成一个接一个的任务。
下图说明了循环神经网络的完整方法和工作 -
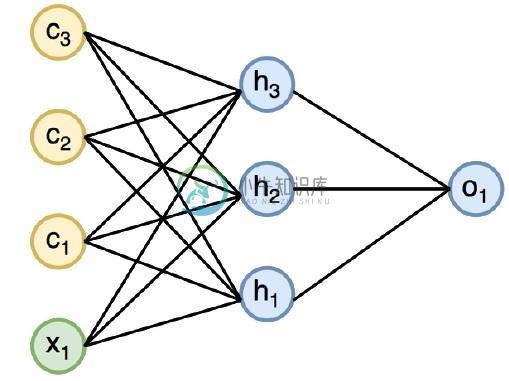
在上图中,c1,c2,c3和x1是包括一些隐藏输入值的输入,即输出o1的相应输出的h1,h2和h3。现在将专注于实现PyTorch,以在递归神经网络的帮助下创建正弦波。
在训练期间,将遵循模型的培训方法,一次只有一个数据点。输入序列x由20个数据点组成,并且目标序列与输入序列相同。
第1步
使用以下代码导入实现递归神经网络的必要包 -
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
import torch.nn.init as init
第2步
设置模型超参数,输入层的大小设置为7。将有6个上下文神经元和1个输入神经元用于创建目标序列。
dtype = torch.FloatTensor
input_size, hidden_size, output_size = 7, 6, 1
epochs = 300
seq_length = 20
lr = 0.1
data_time_steps = np.linspace(2, 10, seq_length + 1)
data = np.sin(data_time_steps)
data.resize((seq_length + 1, 1))
x = Variable(torch.Tensor(data[:-1]).type(dtype), requires_grad=False)
y = Variable(torch.Tensor(data[1:]).type(dtype), requires_grad=False)
我们将生成训练数据,其中x是输入数据序列,y是所需的目标序列。
第3步
使用具有零均值的正态分布在递归神经网络中初始化权重。W1表示接受输入变量,w2表示生成的输出,如下所示 -
w1 = torch.FloatTensor(input_size,
hidden_size).type(dtype)
init.normal(w1, 0.0, 0.4)
w1 = Variable(w1, requires_grad = True)
w2 = torch.FloatTensor(hidden_size, output_size).type(dtype)
init.normal(w2, 0.0, 0.3)
w2 = Variable(w2, requires_grad = True)
第4步
现在,创建一个唯一定义神经网络的前馈功能非常重要。
def forward(input, context_state, w1, w2):
xh = torch.cat((input, context_state), 1)
context_state = torch.tanh(xh.mm(w1))
out = context_state.mm(w2)
return (out, context_state)
第5步
下一步是开始循环神经网络正弦波实现的训练过程。外循环遍历每个循环,内循环遍历序列元素。在这里,还将计算均方误差(MSE),它有助于预测连续变量。
for i in range(epochs):
total_loss = 0
context_state = Variable(torch.zeros((1, hidden_size)).type(dtype), requires_grad = True)
for j in range(x.size(0)):
input = x[j:(j+1)]
target = y[j:(j+1)]
(pred, context_state) = forward(input, context_state, w1, w2)
loss = (pred - target).pow(2).sum()/2
total_loss += loss
loss.backward()
w1.data -= lr * w1.grad.data
w2.data -= lr * w2.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_()
w2.grad.data.zero_()
context_state = Variable(context_state.data)
if i % 10 == 0:
print("Epoch: {} loss {}".format(i, total_loss.data[0]))
context_state = Variable(torch.zeros((1, hidden_size)).type(dtype), requires_grad = False)
predictions = []
for i in range(x.size(0)):
input = x[i:i+1]
(pred, context_state) = forward(input, context_state, w1, w2)
context_state = context_state
predictions.append(pred.data.numpy().ravel()[0])
第6步
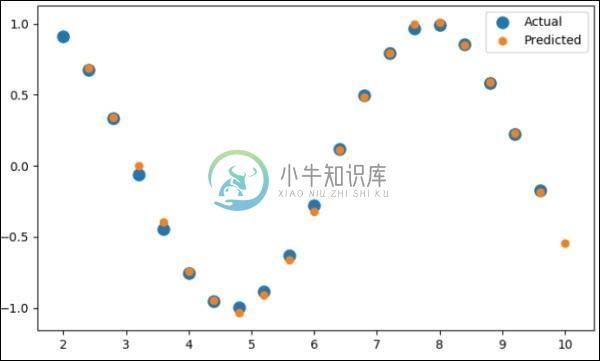
现在,以正确的方式绘制正弦波。
pl.scatter(data_time_steps[:-1], x.data.numpy(), s = 90, label = "Actual")
pl.scatter(data_time_steps[1:], predictions, label = "Predicted")
pl.legend()
pl.show()
上述过程的输出如下 -