特征选择 Feature Selection - Ex 2: Recursive Feature Elimination
特征选择/范例二: Recursive feature elimination
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/feature_selection/plot_rfe_digits.html
本范例主要目的是减少特征数量来提升机器学习之预测准确度。
主要方法是去不断去剔除与资料分类关係转少之特征,来筛选特征数目至指定数目。
- 以
load_digits取得内建的数字辨识资料 - 以
RFE叠代方式删去相对不具有目标影响力的特征.
(一)产生内建的数字辨识资料
# Load the digits datasetdigits = load_digits()X = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))y = digits.target
数位数字资料是解析度为8*8的手写数字影像,总共有1797笔资料。预设为0~9十种数字类型,亦可由n_class来设定要取得多少种数字类型。
输出的资料包含
- ‘data’, 特征资料(1797*64)
- ‘images’, 影像资料(1797*8*8)
- ‘target’, 资料标签(1797)
- ‘target_names’, 选取出的标签列表(与n_class给定的长度一样)
- ‘DESCR’, 此资料库的描述
可以参考Classification的Ex1
(二)以叠代方式计算模型
RFE以排除最不具目标影响力的特征,做特征的影响力排序。并且将训练用的特征挑选至n_features_to_select所给定的特征数。因为要看每一个特征的影响力排序,所以我们将n_features_to_select设定为1,一般会根据你所知道的具有影响力特征数目来设定该参数。而step代表每次删除较不具影响力的特征数目,因为本范例要观察每个特征的影响力排序,所以也是设定为1。若在实际应用时,特征的数目较大,可以考虑将step的参数设高一点。
# Create the RFE object and rank each pixelsvc = SVC(kernel="linear", C=1)rfe = RFE(estimator=svc, n_features_to_select=1, step=1)rfe.fit(X, y)ranking = rfe.ranking_.reshape(digits.images[0].shape)
可以用方法ranking_来看输入的特征权重关係。而方法estimator_可以取得训练好的分类机状态。比较特别的是当我们核函数是以线性来做分类时,estimator_下的方法coef_即为特征的分类权重矩阵。权重矩阵的大小会因为n_features_to_select与资料的分类类别而改变,譬如本范例是十个数字的分类,并选择以一个特征来做分类训练,就会得到45*1的係数矩阵,其中45是从分类类别所需要的判断式而来,与巴斯卡三角形的第三层数正比。
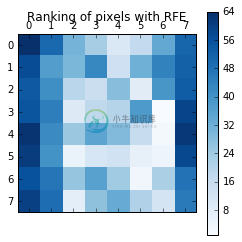
(三)画出每个像素所对应的权重顺序
取得每个像素位置对于判断数字的权重顺序后,我们把权重顺序依照颜色画在对应的位置,数值愈大代表该像素是较不重要之特征。由结果来看,不重要之特征多半位于影像之外围部份。而所有的训练影像中,外围像素多半为空白,因此较不重要。
# Plot pixel rankingplt.matshow(ranking, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)plt.colorbar()plt.title("Ranking of pixels with RFE")plt.show()
(四)原始码
Python source code: plot_rfe_digits.py
print(__doc__)from sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.datasets import load_digitsfrom sklearn.feature_selection import RFEimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Load the digits datasetdigits = load_digits()X = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))y = digits.target# Create the RFE object and rank each pixelsvc = SVC(kernel="linear", C=1)rfe = RFE(estimator=svc, n_features_to_select=1, step=1)rfe.fit(X, y)ranking = rfe.ranking_.reshape(digits.images[0].shape)# Plot pixel rankingplt.matshow(ranking, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)plt.colorbar()plt.title("Ranking of pixels with RFE")plt.show()

