Troubleshoot server-side components
General troubleshooting advice
- Verify that that your JavaScript configuration is correct for the relevant TinyMCE plugin.
- Ensure that your firewall has the appropriate ports and rules configured correctly. Be sure that the server the service is running on is accessible from the browser via the port specified in the server configuration
- Check the logs of your Java server for information. When making changes to the configuration you will need to restart the application server each time a change is made for that change to take effect. Refresh your browser window and then try the service again.
Debug server configuration
If a service does not appear to be working, this is generally caused by one of the following reasons. This guide will walk you through the debugging process to identify the specific problem and how to remedy the issue.
- The
application.conffile is incorrect. Please go back and follow the steps listed in the installation guide. This is the most common problem - often the origins are specified without the port numbers and this can cause things to fail, eg: usehttp://localhost:8080instead ofhttp://localhost. After making changes to theapplication.conffile, please restart your Java web server (e.g. Jetty or Tomcat). - The
application.conffile is correct, but something is wrong with one of the services. See the section below to debug the services. - The
application.conffile is correct, and the services are working, but the server-side component URLs that the editor uses are not quite right. Refer to the Spell Checker Pro, Image Tools, Enhanced Media Embed and Link Checker plugin pages for help. - The browser is sending a different origin than expected (and configured in
application.conf). Refer to step 6 of Using browser tooling to investigate services issues
Browser-specific issues
Internet Explorer specific troubleshooting tips
If the editor is reporting that the service cannot be found and tracing the network traffic reveals that no request is made at all, check that the server is not listed in the Trusted Sites section of Internet Explorer’s security options. If it is, remove it and try again.
Chrome specific tips
If the server is not running on a standard HTTP or HTTPS port (80 or 443) then Chrome will include the port in the Origin header that is sent to the server. Other browsers do not do this. This is why when specifying the allowed-origins config, you should use both the hostname by itself and the hostname and port in the configuration. See Additional Information Around Entering Origins for more details.
Using browser tooling to investigate services issues
- Open your browser’s Console/Network tools:
- Chrome: View menu -> Developer -> JavaScript Console. Click the Network tab (located between Elements and Sources).
- Firefox: Tools menu -> Web Developer -> Network.
- Safari: Develop -> Show Error Console. Click the Timelines link between Resources and Debugger.
- Internet Explorer: Click the cog icon on the top-right side of the browser. Select F12 Developer Tools. Click the Network link (next to the ‘Profiler’ link).
- Refresh the webpage featuring an TinyMCE configured with the spelling service. Enter a misspelled word into the editor.
- Locate the network results that match the following URLs:
http://YOUR_SERVER:YOUR_PORT/ephox-spelling/1/autocorrecthttp://YOUR_SERVER:YOUR_PORT/ephox-spelling/1/correction
- If the network response for these services is 404, try the following:
- Take the service URL displayed as erroneous (example:
http://YOUR_SERVER:YOUR_PORT/ephox-spelling/1/autocorrect). - Remove everything from the ‘1’ onwards (including the ‘1’) and replace it with /version. (example: Change
http://YOUR_SERVER:YOUR_PORT/ephox-spelling/1/correctiontohttp://YOUR_SERVER:YOUT_PORT/ephox-spelling/version). The response code should be 200 and the body should display the version number.
- Take the service URL displayed as erroneous (example:
- If the response for the version URL is still 404, it means the service has not been started or installed correctly.
- To check the “Origin” value that the browser uses, open the network tools (Chrome in this screenshot) and refresh the page. Then enter a couple of words in the editor and select one of the requests on the bottom left (‘correction’ in the screen shot) and select the ‘Headers’ section. Look for the ‘Origin’ header value.
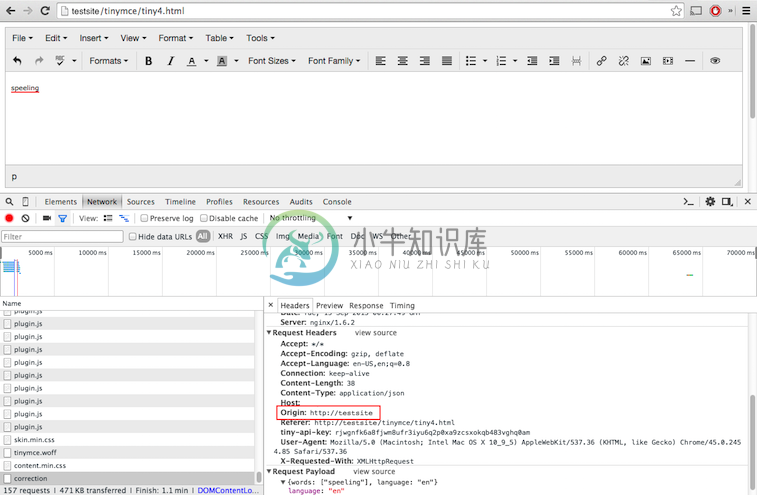
Note: The value of the Origin header sent by the must match the origin specified in the
application.confserver configuration. If it does not match, you must make the server configuration match the browser.
Windows Server specific issues
Sometimes the Origin header is never sent to the services, which results in the editor and services not working as intended. Refer to step 6 of Using browser tooling to investigate services issues and determine what the origin is - if you do not see an Origin header at all, please do the following:
- Try accessing the editor web page using your machine’s fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and keep the network tools open so you can see if the Origin header is sent back to the services. For example, if you have been testing on port 8080 on your local machine and the editor is instantiated on a page with path
tinymce/index.html, navigate tohttp://myserver.example.com:8080/tinymce/index.htmlrather thanhttp://localhost:8080/tinymce/index.html. - If you now see an Origin header being sent across, alter your
application.confand replace all instances of ‘localhost’ with the domain name of your machine. - Restart the Tomcat / Jetty service.
- Reload the browser page and all should work well.
Out of memory errors
The Java application server throws “Out of Memory” errors
Even though you may have a large amount of RAM available, the Java Virtual Machine doesn’t get to see all of that - by default it is limited to only 256Mb.
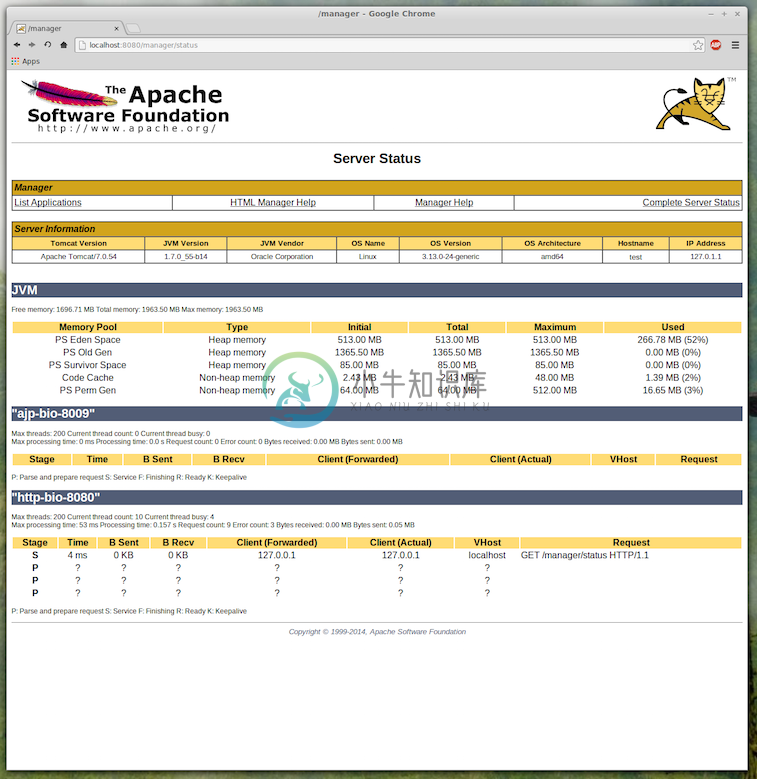
For example, if you are using Tomcat, you can view how much memory is being consumed by apps. To do this you need to have the management console enabled.
On a vanilla install this is done by editing the file /tomcat/install/directory/conf/tomcat-users.xml adding these lines in:
<role rolename="manager-gui" />
<user username="tomcat" password="password" roles="manager-gui"/>
Then, restart the server and go to a browser and open the default tomcat page http://localhost:8080. On the top right hand side are three buttons, the first of which should be “Server Status”. Click that link, login with the details you set above and you should be able to see the memory consumption (see the figure below for an example).
To increase the amount of memory
Tomcat
Edit the setenv.sh (Unix) or setenv.bat (Windows) to read as follows:
On Windows, please prefix each line with ‘set’ and remove the quotes . So the configuration would look like:
set CATALINA_OPTS= -Dephox.config.file=/config/file/location/application.conf
set JAVA_OPTS= -Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -XX:PermSize=64m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m -Dfile.encoding=utf-8 -Djava.awt.headless-true -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100
CATALINA_OPTS=" -Dephox.config.file=/config/file/location/application.conf
JAVA_OPTS=" -Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -XX:PermSize=64m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m -Dfile.encoding=utf-8 -Djava.awt.headless-true -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100"
Jetty
Edit the start.ini file to read as follows:
#===========================================================
# Jetty start.jar arguments
# Each line of this file is prepended to the command line
# arguments # of a call to:
# java -jar start.jar [arg...]
#===========================================================
-Xms2048m -Xmx2048m -XX:PermSize=64m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m -Dephox.config.file=/config/file/location/application.conf
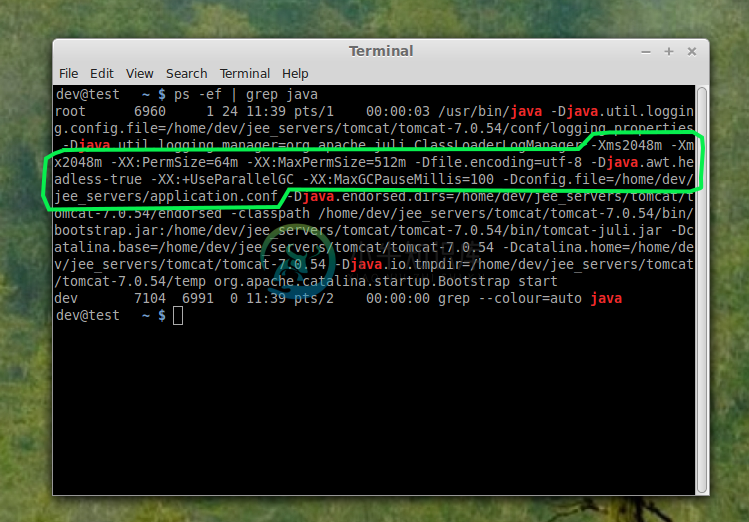
Restart the service and confirm the settings have been applied like so:
Troubleshooting tools: curl
Installing curl on Mac
curl is installed by default on all MacOS X installations. Open the “terminal” application to use it.
Installing curl on Linux
Use your distribution package manager to install curl. See your distribution documentation for details.
Installing curl (or equivalent package) on Windows
Download and install the curl package based on your environment:
x64: http://curl.haxx.se/dlwiz/?type=bin&os=Win64&flav=MinGW64
x86: http://curl.haxx.se/dlwiz/?type=bin&os=Win32&flav=-&ver=2000%2FXP and select either of the curl version: 7.39.0 - SSL enabled SSH enabled packages
Once downloaded:
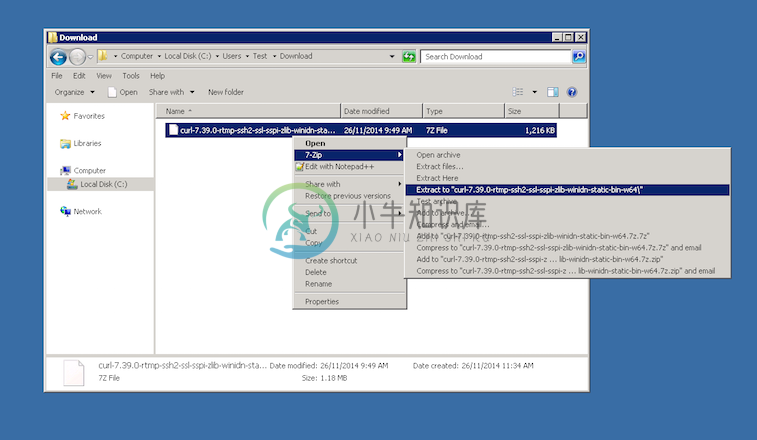
Unzip the package like so:
Copy the path of the folder to where the ‘curl.exe’ is in:
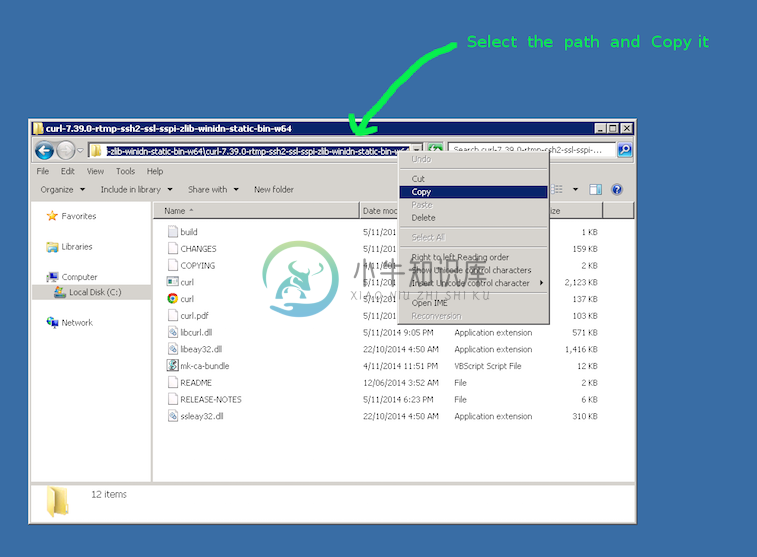
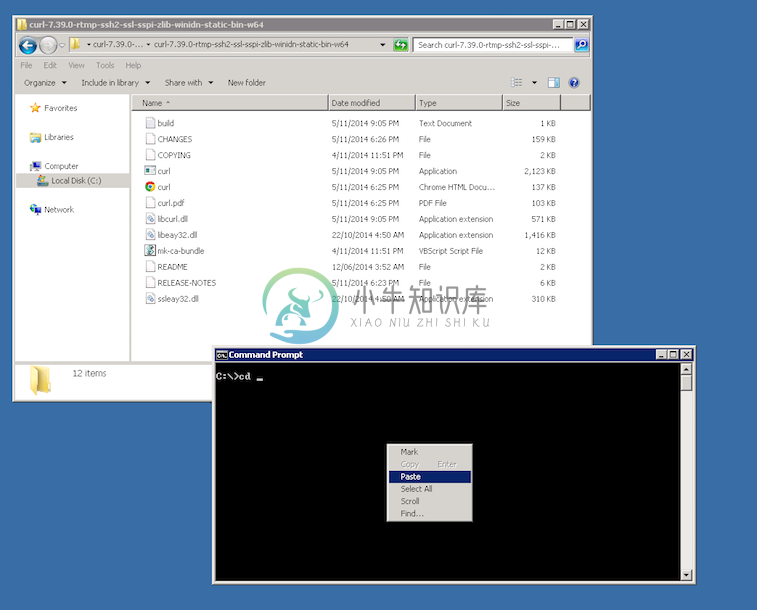
Open a cmd prompt. Start -> Programs -> Accessories -> cmd (or command prompt). Then change to that directory to the folder where the ‘curl.exe’ is found.Enter ‘cd’ (without quotes) and then paste in the path from step 2.
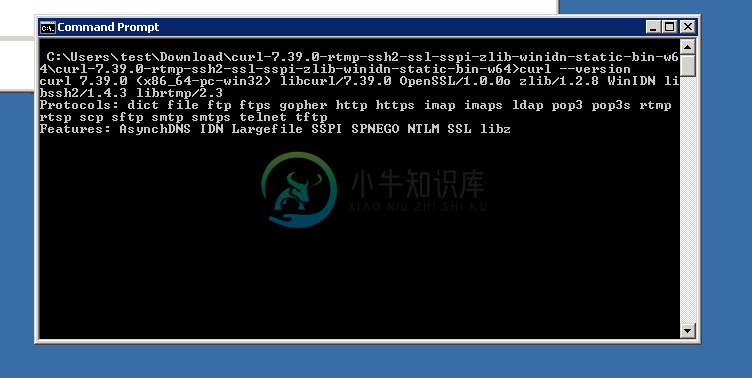
Once in the folder enter ‘curl –version’ (without quotes) and ensure you get a valid version
Need more help?
If you are still experiencing problems, please contact Tiny Support.

