哈希表(Hash Table)
优质
小牛编辑
144浏览
2023-12-01
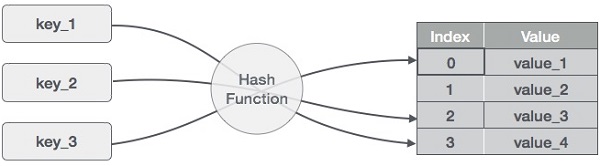
哈希表是以关联方式存储数据的数据结构。 在散列表中,数据以数组格式存储,其中每个数据值都有自己唯一的索引值。 如果我们知道所需数据的索引,则访问数据会变得非常快。
因此,它成为一种数据结构,其中插入和搜索操作非常快,而与数据的大小无关。 散列表使用数组作为存储介质,并使用散列技术生成索引,其中要插入元素或将要定位元素。
Hashing
散列是一种将一系列键值转换为数组索引范围的技术。 我们将使用模运算符来获取一系列键值。 考虑大小为20的哈希表的示例,并且要存储以下项目。 项目采用(键,值)格式。
- (1,20)
- (2,70)
- (42,80)
- (4,25)
- (12,44)
- (14,32)
- (17,11)
- (13,78)
- (37,98)
| Sr.No. | 键 | 哈希 | 数组索引 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1%20 = 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2%20 = 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 42 | 42%20 = 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 | 4%20 = 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 12 | 12%20 = 12 | 12 |
| 6 | 14 | 14%20 = 14 | 14 |
| 7 | 17 | 17%20 = 17 | 17 |
| 8 | 13 | 13%20 = 13 | 13 |
| 9 | 37 | 37%20 = 17 | 17 |
线性探测
我们可以看到,可能会发生散列技术用于创建已使用的数组索引。 在这种情况下,我们可以通过查看下一个单元格来搜索数组中的下一个空位置,直到找到一个空单元格。 这种技术称为线性探测。
| Sr.No. | 键 | 哈希 | 数组索引 | 线性探测后,阵列索引 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1%20 = 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2%20 = 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 42 | 42%20 = 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 | 4%20 = 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 12 | 12%20 = 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 6 | 14 | 14%20 = 14 | 14 | 14 |
| 7 | 17 | 17%20 = 17 | 17 | 17 |
| 8 | 13 | 13%20 = 13 | 13 | 13 |
| 9 | 37 | 37%20 = 17 | 17 | 18 |
基本操作 (Basic Operations)
以下是哈希表的基本主要操作。
Search - 搜索哈希表中的元素。
Insert - 在哈希表中插入元素。
delete - 从哈希表中删除元素。
DataItem
定义具有一些数据和密钥的数据项,基于该数据项在哈希表中进行搜索。
struct DataItem {
int data;
int key;
};
哈希方法
定义散列方法以计算数据项的键的散列码。
int hashCode(int key){
return key % SIZE;
}
搜索操作 (Search Operation)
每当要搜索元素时,计算传递的密钥的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位元素。 如果在计算的哈希码中找不到元素,则使用线性探测来获取元素。
例子 (Example)
struct DataItem *search(int key) {
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
插入操作 (Insert Operation)
每当要插入元素时,计算传递的密钥的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。 如果在计算的哈希码处找到元素,则对空位置使用线性探测。
例子 (Example)
void insert(int key,int data) {
struct DataItem *item = (struct DataItem*) malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
item->data = data;
item->key = key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty or deleted cell
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL && hashArray[hashIndex]->key != -1) {
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
删除操作 (Delete Operation)
每当要删除元素时,计算传递的密钥的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。 如果在计算的哈希码中找不到元素,则使用线性探测来获取元素。 找到后,在那里存储一个虚拟项目,以保持哈希表的性能不变。
例子 (Example)
struct DataItem* delete(struct DataItem* item) {
int key = item->key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] !=NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
struct DataItem* temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
//assign a dummy item at deleted position
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
要了解C编程语言中的哈希实现,请单击此处 。

