三种方式遍历树
优质
小牛编辑
139浏览
2023-12-01
遍历是访问树的所有节点的过程,也可以打印它们的值。 因为所有节点都是通过边(链接)连接的,所以我们总是从根(头)节点开始。 也就是说,我们不能随机访问树中的节点。 我们使用三种方式遍历树 -
- 有序遍历
- Pre-order Traversal
- Post-order Traversal
我们现在将使用以下二叉树来查看C编程语言中树遍历的实现 -
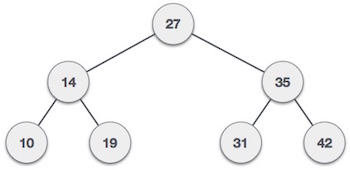
用C实现 (Implementation in C)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data) {
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
} //go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data) {
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}
//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
return current;
}
void <b>pre_order_traversal</b>(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void <b>inorder_traversal</b>(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void <b>post_order_traversal</b>(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main() {
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
i = 31;
struct node * temp = search(i);
if(temp != NULL) {
printf("[%d] Element found.", temp->data);
printf("\n");
}else {
printf("[ x ] Element not found (%d).\n", i);
}
i = 15;
temp = search(i);
if(temp != NULL) {
printf("[%d] Element found.", temp->data);
printf("\n");
}else {
printf("[ x ] Element not found (%d).\n", i);
}
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
如果我们编译并运行上面的程序,它将产生以下结果 -
输出 (Output)
Visiting elements: 27 35 [31] Element found.
Visiting elements: 27 14 19 [ x ] Element not found (15).
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42
Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42
Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27

