数据结构与算法 - 链表
优质
小牛编辑
146浏览
2023-12-01
链表的概念
逻辑结构上一个挨一个的数据,在实际存储时,并没有像顺序表(数组)那样也相互紧挨着。恰恰相反,数据随机分布在内存中的各个位置,这种存储结构称为线性表的链式存储。
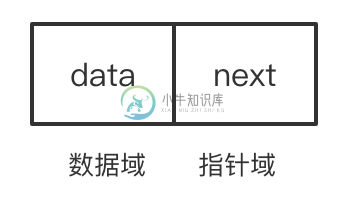
每个元素本身由两部分组成:
- 本身的信息,称为 数据域
指向直接后继的指针,称为 指针域
内存分布
数据是连续存储的,一个挨着一个,连续的。链表是存储单元不一定是连续的, 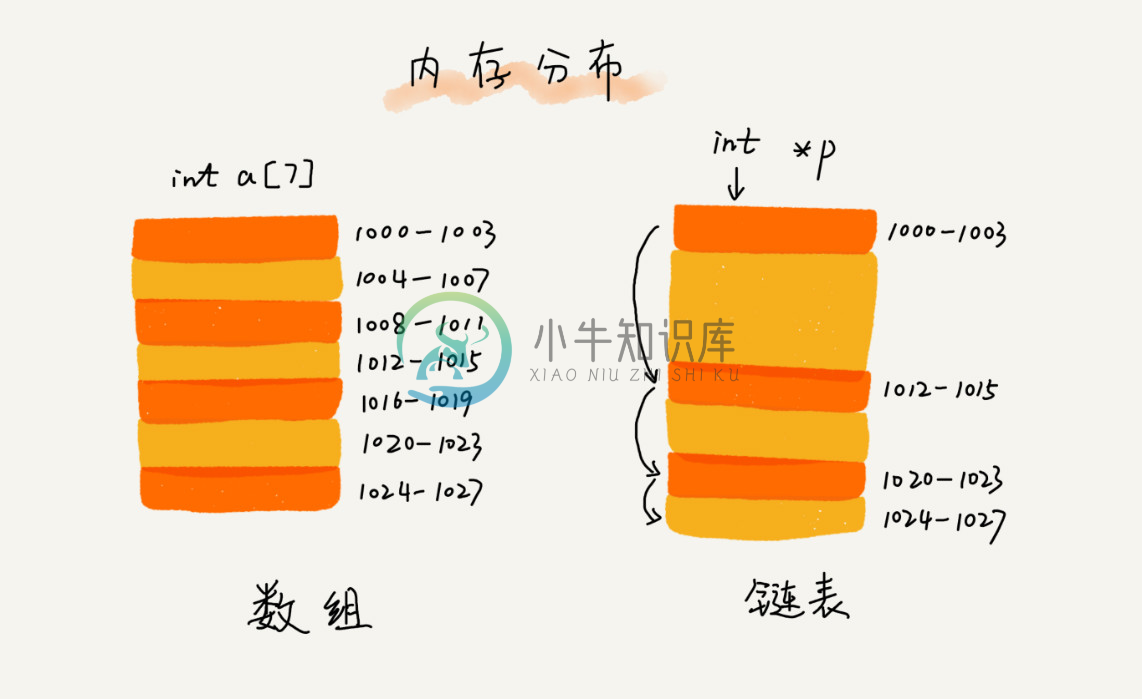
主要分类
- 单向链表
- 循环链表
- 双向链表
- 双向循环链表
单向链表
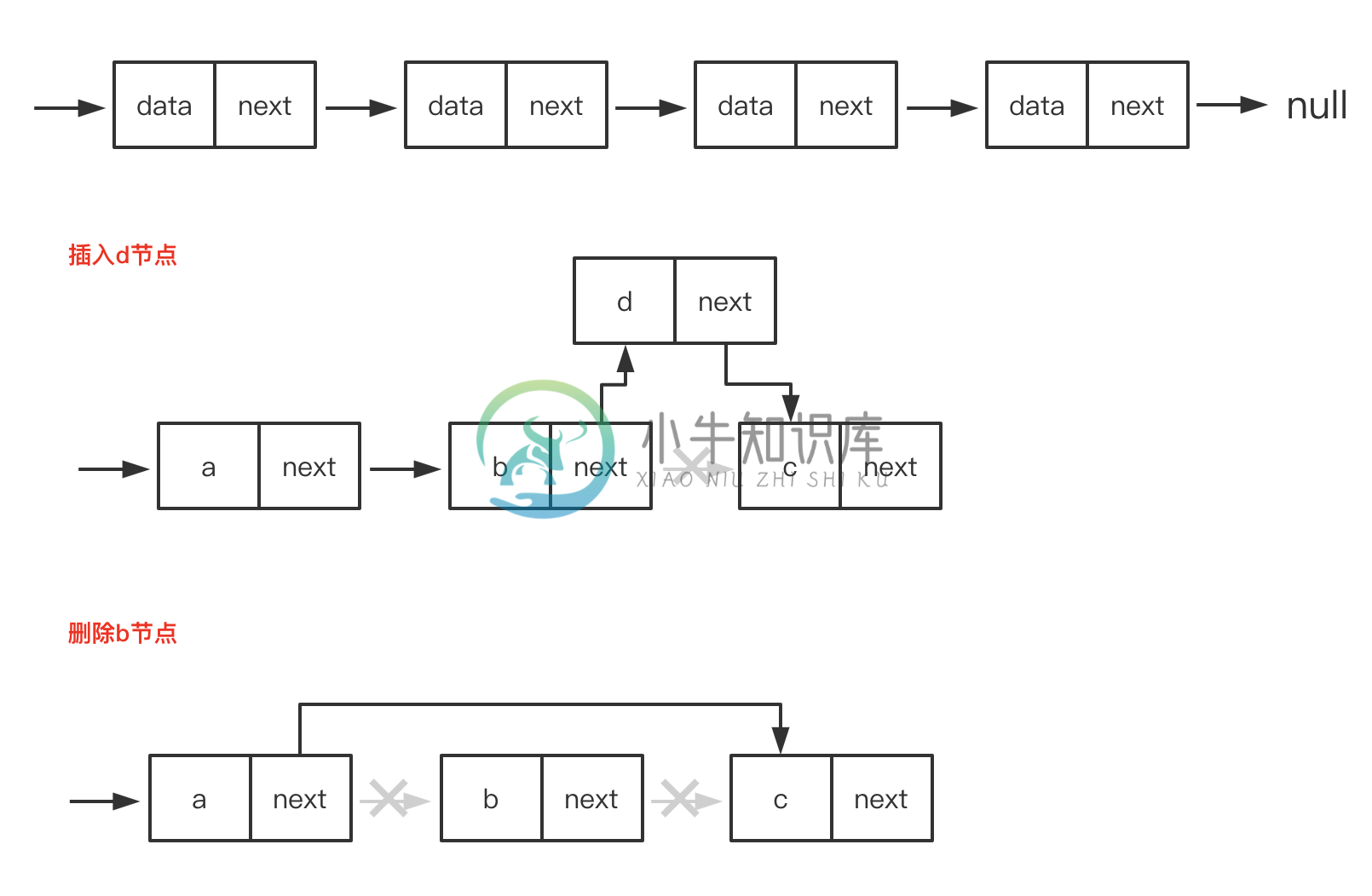
循环链表
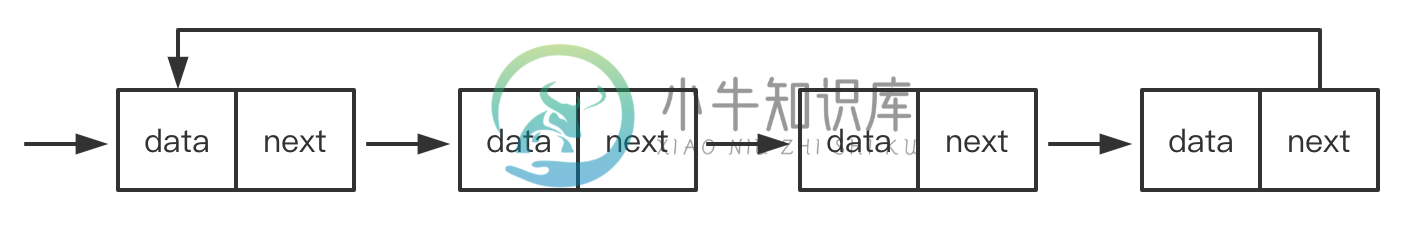
双向链表

双向循环链表
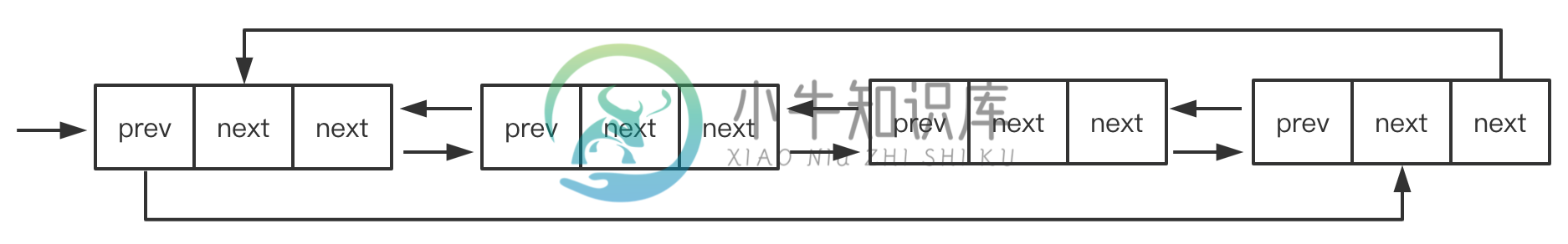
链表和数组的区别
两者的区别
- 数组静态分配内存,链表动态分配内存。
- 数组在内存中是连续的,链表是不连续的。
- 数组利用下标定位,查找的时间复杂度是O(1),链表通过遍历定位元素,查找的时间复杂度是O(N)。
- 数组插入和删除需要移动其他元素,时间复杂度是O(N),链表的插入或删除不需要移动其他元素,时间复杂度是O(1)。
数组的优点
- 随机访问性比较强,可以通过下标进行快速定位。随机访问性比较强
- 查找速度快
数组的缺点
- 插入和删除的效率低,需要移动其他元素。
- 会造成内存的浪费,因为内存是连续的,所以在申请数组的时候就必须规定七内存的大小,如果不合适,就会造成内存的浪费。
- 内存空间要求高,创建一个数组,必须要有足够的连续内存空间。
- 数组的大小是固定的,在创建数组的时候就已经规定好,不能动态拓展。
链表的优点和缺点
- 链表是通过指针将零散的内存块串连起来的。 所以链表不支持 随机访问,如果要找特定的项,只能从头开始遍历,直到找到某个项。 所以访问的时间复杂度为 O(n)。查找的效率低,因为链表是从第一个节点向后遍历查找。
- 高效的插入和删除。 链表中插入或者删除一个数据,我们并不需要为了保持内存的连续性而搬移结点,因为链表的存储空间本身就不是连续的,只需要考虑相邻结点的指针改变。 所以,在链表中插入和删除一个数据是非常快速的,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
- 内存利用率高,不会浪费内存,可以使用内存中细小的不连续的空间,只有在需要的时候才去创建空间。
- 大小不固定,拓展很灵活。
实现
单链表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
/**
单向链表
append(element):向链表尾部添加新项
insert(position, element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项
remove(element):从链表中移除一项
indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返回-1
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0,返回false
size():返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似
getHead():返回链表的第一个元素
toString():由于链表使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的toString()方法,让其只输出元素的值
print():打印链表的所有元素
*/
class Node {
constructor(element = null, next = null) {
this.element = element
this.next = next
}
}
class SinglyList {
constructor() {
// 头指针
this.head = null
// 尾指针
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
/**
* 尾插法 插入元素
* @param element
*/
append(element) {
let newNode = new Node(element)
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
// let curNode = this.head
// while (curNode.next) {
// curNode = curNode.next
// }
//
// // 找到最后一个节点
// curNode.next = newNode
this.tail.next = newNode
this.tail = newNode
}
this.length++
}
/**
* 头插法 插入元素
* @param value
* @returns {SinglyList}
*/
prepend(value) {
// Make new node to be a head.
const newNode = new Node(value, this.head)
this.head = newNode
// If there is no tail yet let's make new node a tail.
if (!this.tail) {
this.tail = newNode
}
this.length++
return this
}
/**
* 向单向链表中插入某个元素
* @param {Number} position 插入的位置
* @param {Any} element 插入的元素
* @return {Boolean} 成功返回true,失败返回false
*/
insert(position, element) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return false
}
let newNode = new Node(element)
let curNode = this.head
let index = 0
let preNode = null
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = curNode
this.head = newNode
} else {
// 排除不需要插入的节点
while (index++ < position) {
preNode = curNode // 保存上一节点
curNode = curNode.next // 保存当前节点
}
// 找到节点
newNode.next = curNode
preNode.next = newNode
}
this.length++
return true
}
removeAt(postion) {
if (postion <= -1 || postion > this.length) return null
let curNode = this.head
let prvNode
let index = 0
if (postion === 0) {
// 因为之前head指向第一个元素,现在把head修改为指向第二个元素。
// 核心概念在于链表前后全靠指针链接,而非数组一般。
// 所以只需要改变head的元素。
this.head = curNode.next
} else {
// 跟插入操作类似处理
while (index++ < postion) {
prvNode = curNode
curNode = curNode.next
}
prvNode.next = curNode.next
}
this.length--
return curNode.data
}
/**
* 移除给定的元素
* @param {Any} element 要移除的元素
* @return {Number} 返回值>=0表示移除成功
*/
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element)
if (index > -1) {
return this.removeAt(index)
} else {
return null
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0
}
size() {
return this.length
}
getHead() {
if (!this.isEmpty()) {
return this.head
}
}
toString() {
let curNode = this.head
let str = ''
while (curNode) {
str += ' ' + curNode.data
curNode = curNode.next
}
// 删除前面第一个空格slice(1)
return str.slice(1)
}
/**
* 单向连表
* 已知一个单链表的头结点,找到该链表中,倒数第 K 个结点。
* @param k
* @returns {*}
*/
//
theKthNode(k) {
if (k < 0) {
return null;
}
let fast = this.head
let slow = this.head
let i = k;
// fast 指针,先走 K 步
for (; i > 0 && fast != null; i--) {
fast = fast.next
}
if (i > 0) {
// 链表长度,小于 K
return null;
}
// fast、slow 同步走
while (fast != null){
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
}
return slow
}
toArray() {
let list = []
let current = this.head
while (current) {
list.push(current.element)
current = current.next
}
return list
}
/**
* @return {LinkedListNode}
*/
deleteTail() {
const deletedTail = this.tail;
if (this.head === this.tail) {
// There is only one node in linked list.
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
return deletedTail;
}
// If there are many nodes in linked list...
// Rewind to the last node and delete "next" link for the node before the last one.
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode.next) {
if (!currentNode.next.next) {
currentNode.next = null;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
this.tail = currentNode;
return deletedTail;
}
/**
* @return {LinkedListNode}
*/
deleteHead() {
if (!this.head) {
return null
}
const deletedHead = this.head
if (this.head.next) {
this.head = this.head.next
} else {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
}
return deletedHead
}
find({value = undefined, callback = undefined}) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
// callback返回值为 false 就一直查找
if (callback && callback(currentNode.element)) {
return currentNode;
}
// If value is specified then try to compare by value..
if (value !== undefined && currentNode.element === value) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return null;
}
delete(value) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let deletedNode = null;
// If the head must be deleted then make next node that is differ
// from the head to be a new head.
while (this.head && this.head.element.key === value) {
deletedNode = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
}
let currentNode = this.head;
if (currentNode !== null) {
// If next node must be deleted then make next node to be a next next one.
while (currentNode.next) {
if (currentNode.next.element.key === value) {
deletedNode = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next = currentNode.next.next
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.next
}
}
}
// Check if tail must be deleted.
if (this.tail.element.key === value) {
this.tail = currentNode;
}
this.length --
return deletedNode;
}
}
window.singly = new SinglyLinkedList()
singly.append('A')
singly.append('B')
singly.append('D')
let node = singly.theKthNode(2)
console.log(node)
</script>
</body>
</html>
双向链表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
/**
双向链表提供了两种迭代列表的方法:
从头到尾
从尾到头。
我们可以访问一个特定节点的下一个或前一个元素。
在单向链表中,如果迭代链表时错过了要找的元素,就需要回到链表起点,重新开始迭代。
在双向链表中,可以从任一节点,向前或向后迭代,这是双向链表的一个优点。
*/
class Node {
constructor(data = null, next = null, prev = null) {
this.element = data
this.next = next
this.prev = prev
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
append(element) {
let newNode = new Node(element)
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode // 将队尾元素next指向插入的元素
newNode.prev = this.tail // 插入的新元素上一级指向原来的队尾元素素
this.tail = newNode // 新元素成为队尾
}
this.length++
return this
}
// 正向遍历的方法
forwardString() {
let curNode = this.head
let str = ''
while (curNode) {
str += ' ' + curNode.element
curNode = curNode.next
}
return str.slice(1)
}
// 反向遍历的方法
reverseString() {
let curNode = this.tail
let str = ''
while (curNode) {
str += ' ' + curNode.element
curNode = curNode.prev
}
return str.slice(1)
}
toString() {
return this.forwardString()
}
getHead() {
return this.head.element
}
getTail() {
return this.tail.element
}
/**
* 向单向链表中插入某个元素
* @param {Number} position 要插入的位置
* @param {Any} element 要插入的元素
* @return {Boolean} 插入成功返回true,失败返回false
*/
insert(position, element) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return false
}
let newNode = new LinkedListNode(element)
let curNode = this.head
let index = 0
let preNode = null
if (position === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.head.prev = newNode
newNode.next = this.head
this.head = newNode
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
this.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = newNode
} else {
// 不需要插入的节点
while (index++ < position) {
preNode = curNode // 保存上一节点
curNode = curNode.next // 保存当前节点
}
// 找到节点
newNode.next = curNode
newNode.prev = preNode
curNode.prev = newNode
preNode.next = newNode
}
this.length++
return true
}
/**
* 寻找某个元素在单向链表中的位置
* @param {Any} element 要寻找的元素
* @return {Number} 返回值>=0则代表找到相应位置
*/
indexOf(elemnt) {
let curNode = this.head
let index = 0
while (curNode) {
// 找到
if (curNode.element === elemnt) {
return index
}
//继续找
index++
curNode = curNode.next
}
// 没有找到
return -1
}
find({value = undefined, callback = undefined}) {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
// callback返回值为 false 就一直查找
if (callback && callback(currentNode.element)) {
return currentNode;
}
// If value is specified then try to compare by value..
if (value !== undefined && currentNode.element === value) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 移除指定位置的元素
* @param postion
* @returns {*}
*/
removeAt(postion) {
if (postion <= -1 || postion > this.length) return null
let curNode = this.head
let prvNode
let index = 0
if (postion === 0) {
// 因为之前head指向第一个元素,现在把head修改为指向第二个元素。
// 核心概念在于链表前后全靠指针链接,而非数组一般。
// 所以只需要改变head的元素。
this.head = curNode.next
} else {
// 跟插入操作类似处理
while (index++ < postion) {
prvNode = curNode
curNode = curNode.next
}
prvNode.next = curNode.next
}
this.length--
return curNode.element
}
/**
* 移除给定的元素
* @param {Any} element 要移除的元素
* @return {Number} 返回值>=0表示移除成功
*/
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element)
if (index > -1) {
return this.removeAt(index)
} else {
return null
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0
}
size() {
return this.length
}
clear () {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
toArray() {
let list = []
let current = this.head
while (current) {
list.push(current.element)
current = current.next
}
return list
}
/**
* 反转链表
* @returns {LinkedList}
*/
reverse() {
let currNode = this.head
let prevNode = null
let nextNode = null
while (currNode) {
// Store next node.
nextNode = currNode.next
// Change next node of the current node so it would link to previous node.
currNode.next = prevNode
// Move prevNode and currNode nodes one step forward.
prevNode = currNode
currNode = nextNode
}
// Reset head and tail.
this.tail = this.head
this.head = prevNode
// 返回当前实例对象
return this
}
fromArray (values) {
if (!Array.isArray(values)) return false
values.forEach(value => this.append(value))
return this
}
}
let list = new DoublyLinkedList()
list.append('A')
list.append('B')
list.append('D')
list.append({ value: 1, key: 'test1' })
.append({ value: 2, key: 'test2' })
.append({ value: 3, key: 'test3' })
let node = list.find({
callback: (value) => {
return value.key === 'test1'
}
})
console.log(node)
</script>
</body>
</html>
链表操作摘要
- 单链表反转
- 单链表反转从位置 m 到 n 的部分
- 链表中环的检测
- 合并两个有序的链表
- 合并K个排序链表
- 删除链表倒数第n个节点
- 求链表的中间结点
- 求链表环的入口节点
- 两两交换链表中的节点
- K 个一组翻转链表

