数据结构与算法 - 哈希表
哈希表也叫散列表,是一种非常重要的数据结构,应用场景及其丰富,许多缓存技术核心就是在内存中维护着一张巨大的哈希表。
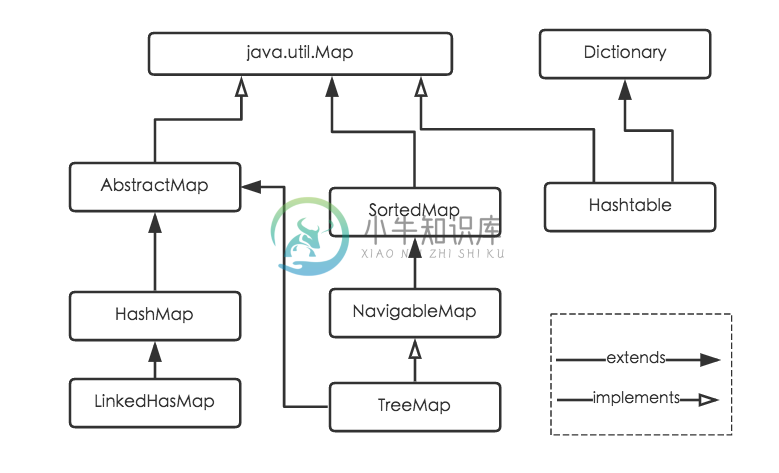
学过Java对这个应该很熟悉,Java为数据结构中的映射定义了一个接口java.util.Map,此接口主要有四个常用的实现类,分别是 HashMap 、 Hashtable 、 LinkedHashMap 和 TreeMap ,类继承关系如下图所示:
 HashMap是Java程序员使用频率最高的用于映射(键值对)处理的数据类型。
HashMap是Java程序员使用频率最高的用于映射(键值对)处理的数据类型。
ES6中并没有提供HashMap这样类。ES6 提供了 Map类就是一种完善的 Hash 结构实现,网上搜到一个 "利用HashMap开发Emoji表情库" 的案例。
存储结构
从结构实现来讲,HashMap是 数组+链表+红黑树(JDK1.8增加了红黑树部分)实现的,如下如所示。 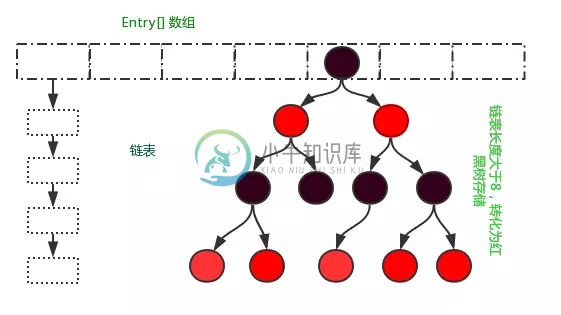
HashMap
调用键对象上的hashCode方法,并将返回的哈希值应用于其自己的静态哈希函数,以找到存储区的存储区,在该存储区中,键和值以称为Entry(Map.Entry)的嵌套类的形式存储。HashMap的内存分配如下图: 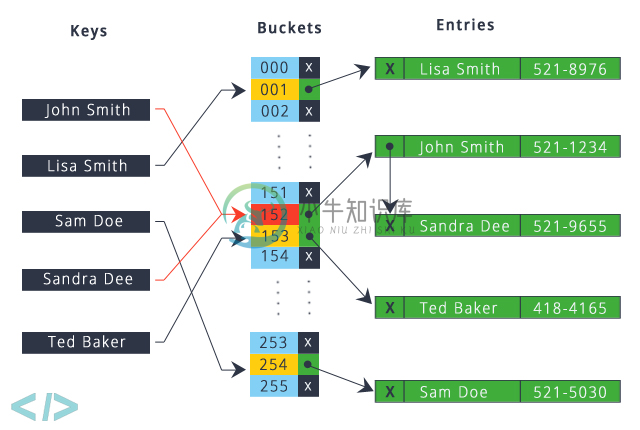
图中John Smith 和 Sandra Dee 有哈希冲突,同时为152,采用链表的形式存储。
HashTable
使用 哈希函数 计算存储 桶或插槽数组的索引,从中可以找到所需的值。哈希表的内存分配如下图: 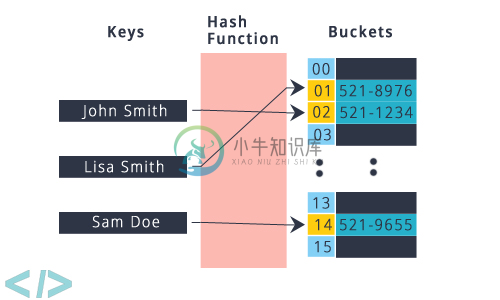
为什么要有 Hash
我们通常使用 数组 或者 链表 来存储元素,一旦存储的内容数量特别多,需要占用很大的空间,而且在查找某个元素是否存在的过程中,数组和链表都需要挨个循环比较,而通过 哈希 计算,可以大大减少比较次数。
举个栗子:
现在有 4 个数 {2, 5, 9, 13},需要查找 13 是否存在。Java里并没有JSj里的indexOf方法。
1.使用数组存储
需要新建个数组 new int[]{2,5,9,13},然后需要写个循环遍历查找
int[] numbers = new int[]{2,5,9,13};
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (numbers[i] == 13){
System.out.println("find it!");
return;
}
}
这样需要遍历 4 次才能找到,时间复杂度为 O(n)。
2.使用哈希函数
而假如存储时先使用哈希函数进行计算,这里我随便用个函数
H[key] = key % 3;
四个数 {2, 5, 9, 13} 对应的哈希值为:
H[2] = 2 % 3 = 2;
H[5] = 5 % 3 = 2;
H[9] = 9 % 3 = 0;
H[13] = 13 % 3 = 1;
然后把它们存储到对应的位置。 当要查找 13 时,只要先使用哈希函数计算它的位置,然后去那个位置查看是否存在就好了,本例中只需查找一次,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
因此可以发现,哈希 其实是随机存储的一种优化,先进行分类,然后查找时按照这个对象的分类去找。
HashTable
根据 HashTable 上图 我们要实现一个Hash Function。 这里我们设计了两个哈希函数 djb2HashCode() 和 loseloseHashCode()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
class HashTable {
constructor(props) {
this.items = []
}
/**
* 哈希函数
* key -> number -> itmes[numer]
* abc => a:97 b:98 c:99
* @returns {number}
*/
loseloseHashCode(key){
let hash = 0
for(var i = 0 ; i < key.length ; i++){
hash += key[i].charCodeAt()
}
return hash % 37
}
/**
* 哈希函数
* @param key
* @returns {number}
*/
djb2HashCode(key) {
let hash = 5381
for(var i = 0 ; i < key.length ; i++){
hash = hash * 33 + key[i].charCodeAt()
}
return hash % 1013
}
put(key,value){
let position = this.djb2HashCode(key)
console.log(position + ' - ' + value)
this.items[position] = value
}
remove(key){
this.items[this.djb2HashCode(key)] = undefined
}
get(key){
return this.items[this.djb2HashCode(key)]
}
getItems(){
return this.items
}
}
let ht = new HashTable
ht.put('Donnie','Donie@qq.com')
ht.put('Ana','Ana@qq.com')
</script>
</body>
</html>
打印结果 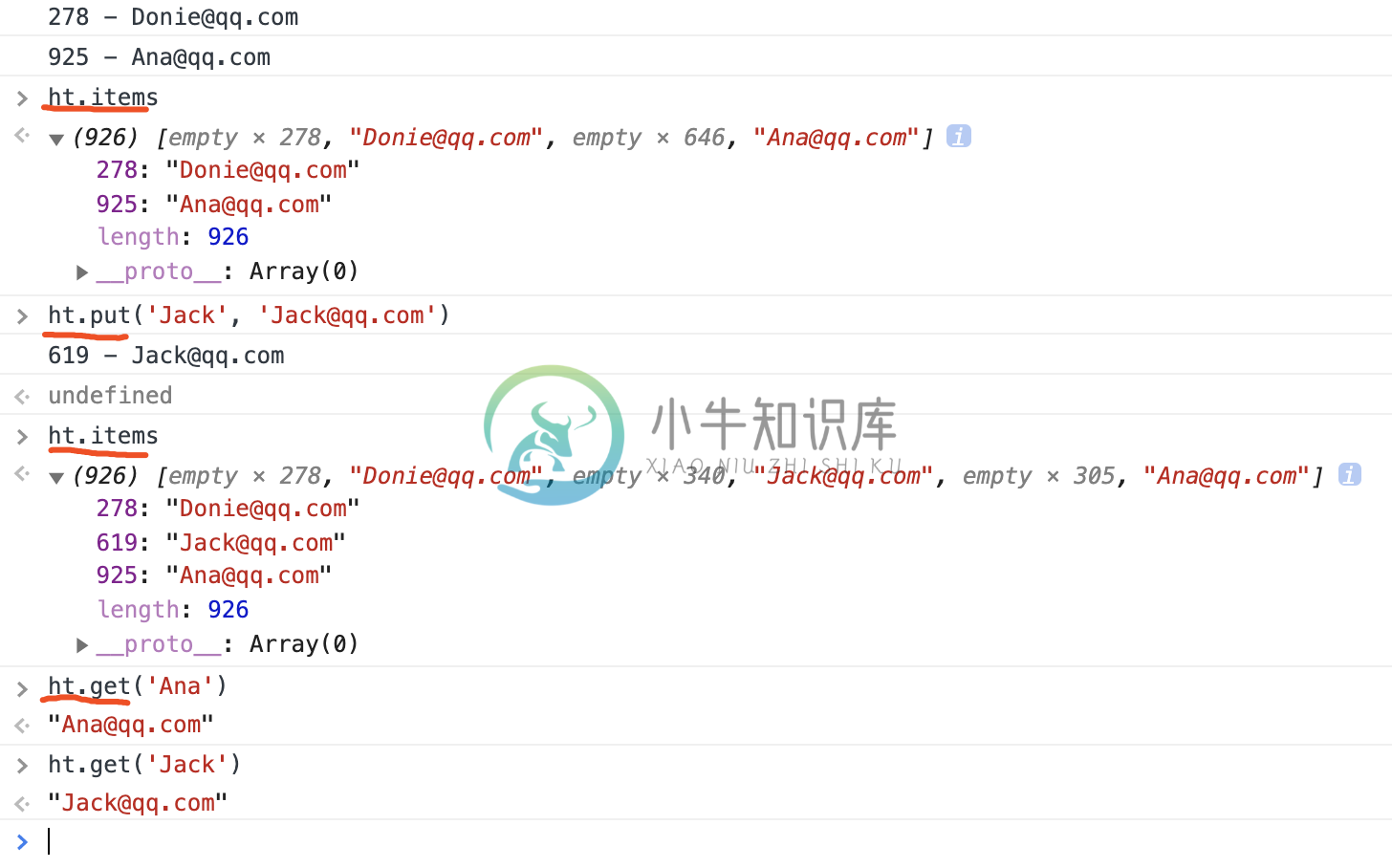
但是如果我们设计的哈希函数,不同的key,产生的值是一样的怎么办?如果我们把上面代码调用 djb2HashCode() 全部改成 loseloseHashCode() 方法,会产生怎样的效果呢? 我们可以试下打印结果
 从结果里可以看到key: Donnie 和 key: Ana 通过哈希计算返回的结果是一样的13,Ana直接覆盖掉Donnie。 这就是产生哈希冲突。
从结果里可以看到key: Donnie 和 key: Ana 通过哈希计算返回的结果是一样的13,Ana直接覆盖掉Donnie。 这就是产生哈希冲突。
构造哈希函数的方法很多,实际工作中要根据不同的情况选择合适的方法,总的原则是尽可能少的产生冲突。 通常考虑的因素有关键字的长度和分布情况、哈希值的范围等。 如:当关键字是整数类型时就可以用除留余数法;如果关键字是小数类型,选择随机数法会比较好。
哈希冲突的解决
选用哈希函数计算哈希值时,可能不同的 key 会得到相同的结果,一个地址怎么存放多个数据呢?这就是冲突。 常用的主要有两种方法解决冲突:
- 分离链接法
- 线性探测法
分离链接法
含义
其做法就是将散列到同一个值的所有元素保存到一个链表中。如下图: 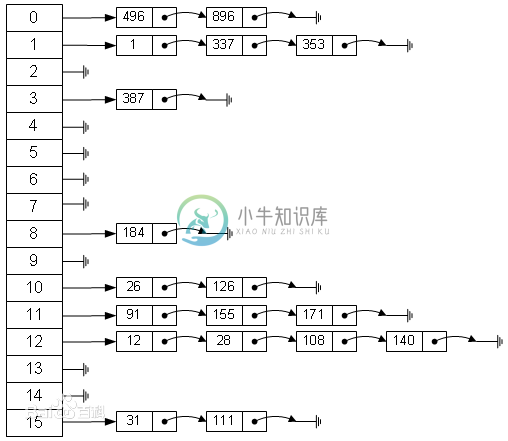
实现
这里代码重新设计了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
/**
fill()方法的作用是使用 一个固定值来 替换 数组中的元素。该固定值可以是字母、数字、字符串、数组等等。
fill()方法还有两个可选参数,表示填充的起始位置和结束位置。
let arr = [12,23,34,45,56];
arr.fill("hello");
console.log(arr3) // ["hello", "hello", "hello", "hello", "hello"]
*/
import SinglyLinkedList from './SinglyLinkedList.js'
class HashTable {
constructor(hashTabsize = 5) {
this.buckets = Array(hashTabsize).fill(null).map(() => new SinglyLinkedList())
this.keys = {}
}
hash(key) {
const hash = Array.from(key).reduce((hashAccumulator, keySymbol) => (hashAccumulator + keySymbol.charCodeAt(0)), 0,)
return hash % this.buckets.length
}
put(key, value) {
const keyHash = this.hash(key)
this.keys[key] = keyHash
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash]
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key})
if (!node) {
// Insert new node.
bucketLinkedList.append({key, value});
} else {
// Update value of existing node.
node.element.value = value;
}
return this
}
delete(key) {
const keyHash = this.hash(key)
delete this.keys[key]
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash]
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key})
if (node) {
return bucketLinkedList.delete(node.element.key)
}
return null
}
get(key) {
const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)]
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key})
return node ? node.element.value : undefined
}
has(key) {
return Object.hasOwnProperty.call(this.keys, key)
}
getKeys() {
return Object.keys(this.keys)
}
getBuckets(){
return this.buckets
}
}
let ht = new HashTable()
window.ht = ht
ht.put('Donnie','Donie@qq.com')
ht.put('Ana','Ana@qq.com')
ht.put('Jack','Jack@qq.com')
</script>
</body>
</html>
打印结果,可以看到Ana和Jack产生了一样的值为2。 我们可以试试把HashTbale里构造函数中hashTabsize改成32看看效果会是什么样。 
线性探测法
在开放定址算法里,线性探测法是散列解决冲突的一种方法,当hash一个关键字时,发现没有冲突,就保存关键字, 如果出现冲突,则就探测冲突地址下一个地址,依次按照线性查找,直到发现有空地址为止,从而解决冲突。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 辅助类
class Node {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key
this.value = value
}
}
//线性探查
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.buckets = []
}
/**
* 哈希函数
* key -> number -> itmes[numer]
* abc => a:97 b:98 c:99
* @returns {number}
*/
loseloseHashCode(key) {
let hash = 0
for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key[i].charCodeAt()
}
return hash % 37
}
put(key, value) {
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
if (this.buckets[position] === undefined) {
this.buckets[position] = new Node(key, value)
} else {
// 位置被占用
var index = position + 1
while (this.buckets[index] !== undefined) {
index++
}
this.buckets[index] = new Node(key, value)
}
}
remove(key) {
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
this.buckets[position] = undefined
}
get(key) {
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
return this.buckets[position].value
}
}
var ht = new HashTable()
ht.put('Donnie', 'Donie@qq.com')
ht.put('Ana', 'Ana@qq.com')
ht.put('Jack', 'Ana@qq.com')
console.log(ht)
</script>
</body>
</html>
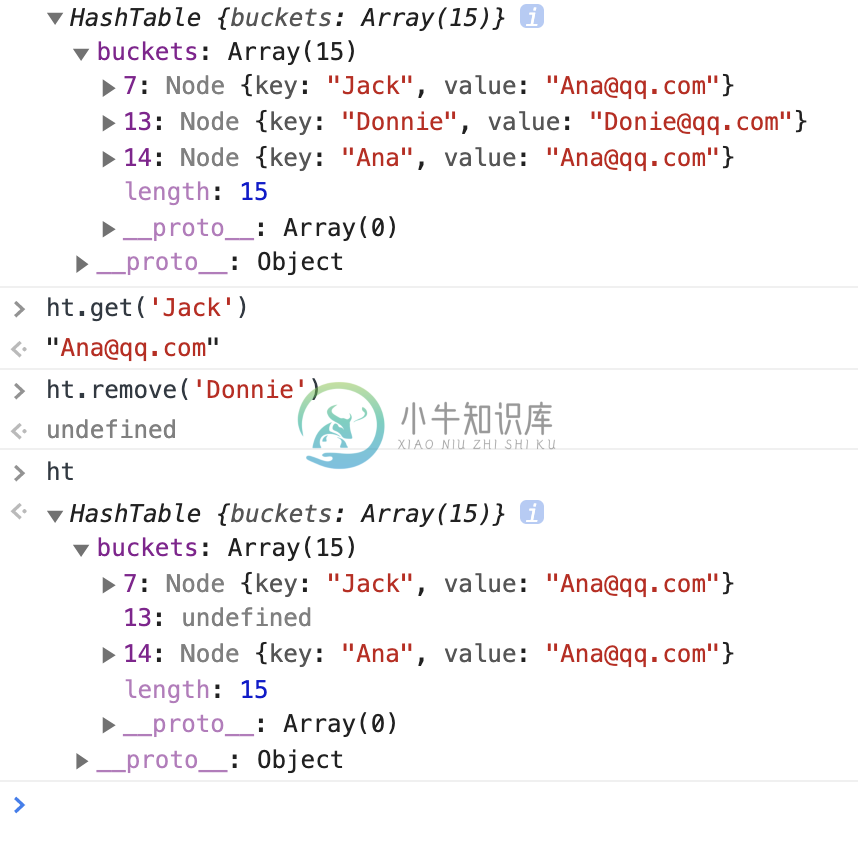 最后来张图:
最后来张图:
HashMap和Hashtable之间的区别 (英文) Java 容器 × HashMap[JDK 1.8]源码学习 Java 8系列之重新认识HashMap

