Regularized Linear Regression
优质
小牛编辑
138浏览
2023-12-01
#!/usr/bin/env python
# h(x)=b+wx
%matplotlib inline
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def model(X, w, b):
return tf.mul(X, w) + b
trX = np.linspace(-1, 1, 101).astype(np.float32)
# create a y value which is approximately linear but with some random noise
trY = 2 * trX + np.random.randn(*trX.shape) * 0.33 + 10
# create a shared variable (like theano.shared) for the weight matrix
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1], -1.0, 1.0))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
# choose Regularization Parameter to 0.05
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(trY-model(trX, w, b)) + 0.05*np.sum(w))
# construct an optimizer to minimize cost and fit line to my data
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cost)
# Launch the graph in a session
with tf.Session() as sess:
# you need to initialize variables (in this case just variable W)
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_op)
print(sess.run(w)) # It should be something around 2
print(sess.run(b)) # It should be something around 10
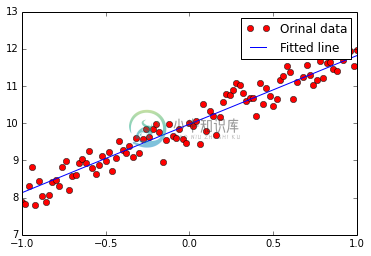
plt.plot(trX, trY, "ro", label="Orinal data")
plt.plot(trX, sess.run(w)*trX + sess.run(b), label="Fitted line")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
[ 1.84230614]
[ 9.97495556]
Regularized Multi-variable Linear Regression
%matplotlib inline
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def model(X, w, b):
return tf.mul(w, X) + b
trX = np.mgrid[-1:1:0.01, -10:10:0.1].reshape(2, -1).T
trW = np.array([3, 5])
trY = trW*trX + np.random.randn(*trX.shape) + [20, 100]
w = tf.Variable(np.array([1., 1.]).astype(np.float32))
b = tf.Variable(np.array([[1., 1.]]).astype(np.float32))
# Choose Regularization Parameter to 0.05
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(trY-model(trX, w, b)) + 0.05*np.sum(w))
# construct an optimizer to minimize cost and fit line to my data
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.05).minimize(cost)
# Launch the graph in a session
with tf.Session() as sess:
# you need to initialize variables (in this case just variable W)
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_op)
print "w should be something around [3, 5]: ", sess.run(w)
print "b should be something around [20,100]:", sess.run(b)
w should be something around [3, 5]: [ 2.92737865 4.99970579] b should be something around [20,100]: [[ 20.01066017 100.00799561]]

