4.4 Huffman Compression
优质
小牛编辑
140浏览
2023-12-01
主要思想:放弃文本文件的普通保存方式:不再使用7位或8位二进制数表示每一个字符,而是用较少的比特表示出现频率最高的字符,用较多的比特表示出现频率低的字符。
使用变长编码来表示字符串,势必会导致编解码时码字的唯一性问题,因此需要一种编解码方式唯一的前缀码,而表示前缀码的一种简单方式就是使用单词查找树,其中最优前缀码即为Huffman首创。
以符号F, O, R, G, E, T为例,其出现的频次如以下表格所示。
| Symbol | F | O | R | G | E | T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequence | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 |
| Code | 000 | 001 | 100 | 101 | 01 | 11 |
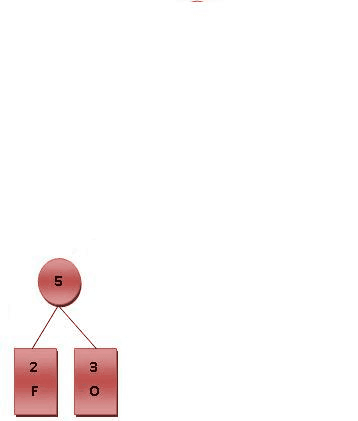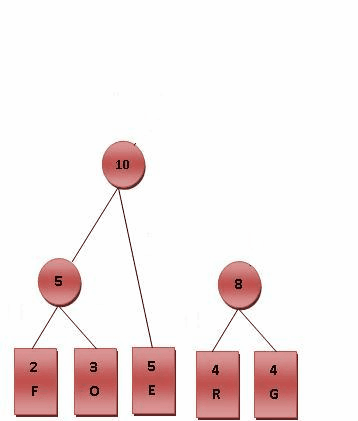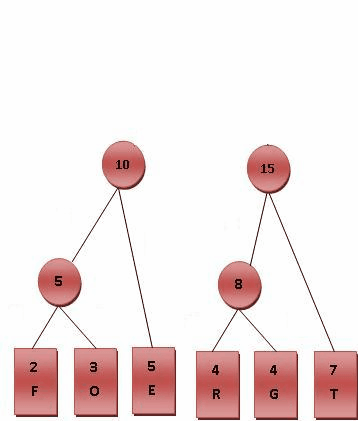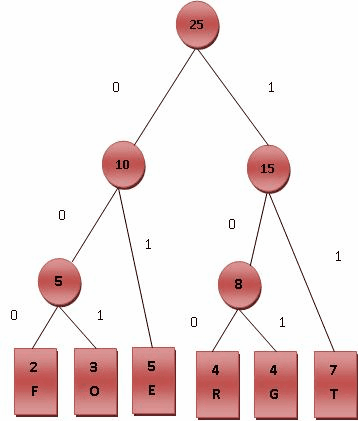
则对各符号进行霍夫曼编码的动态演示如下图所示。基本步骤是将出现频率由小到大排列,组成子树后频率相加作为整体再和其他未加入二叉树中的节点频率比较。加权路径长为节点的频率乘以树的深度。
Python 实现
"""
Use serveral ways to compress string `everyday is awesome!`
1. use simple bits to replace ASCII value
2. use huffman coding
"""
import heapq
import collections
def get_rate(compressed_binary, uncompressed_bits):
return len(compressed_binary) * 100 / uncompressed_bits
class SimpleCompression:
def __init__(self, string):
self.symbols = set(string)
self.bit_len = 1
while 2**self.bit_len < len(self.symbols):
self.bit_len += 1
self.string = string
self.s2b = {}
self.b2s = {}
i = 0
for s in self.symbols:
b = bin(i)[2:]
if len(b) < self.bit_len:
b = (self.bit_len - len(b)) * '0' + b
self.s2b[s] = b
self.b2s[b] = s
i += 1
def compress(self):
bits = ''
for s in self.string:
bits += self.s2b[s]
return bits
def uncompress(self, bits):
string = ''
for i in range(0, len(bits), self.bit_len):
string += self.b2s[bits[i:i + self.bit_len]]
return string
class HuffmanCompression:
class Trie:
def __init__(self, val, char=''):
self.val = val
self.char = char
self.coding = ''
self.left = self.right = None
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.val == other.val
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.val < other.val
def __gt__(self, other):
return self.val > other.val
def __init__(self, string):
self.string = string
counter = collections.Counter(string)
heap = []
for char, cnt in counter.items():
heapq.heappush(heap, HuffmanCompression.Trie(cnt, char))
while len(heap) != 1:
left = heapq.heappop(heap)
right = heapq.heappop(heap)
trie = HuffmanCompression.Trie(left.val + right.val)
trie.left, trie.right = left, right
heapq.heappush(heap, trie)
self.root = heap[0]
self.s2b = {}
self.bfs_encode(self.root, self.s2b)
def bfs_encode(self, root, s2b):
queue = collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node.char:
s2b[node.char] = node.coding
continue
if node.left:
node.left.coding = node.coding + '0'
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
node.right.coding = node.coding + '1'
queue.append(node.right)
def compress(self):
bits = ''
for char in self.string:
bits += self.s2b[char]
return bits
def uncompress(self, bits):
string = ''
root = self.root
for bit in bits:
if bit == '0':
root = root.left
else:
root = root.right
if root.char:
string += root.char
root = self.root
return string
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = 'everyday is awesome!'
# ASCII
bits = len(s) * 8
print('Total bits: %d' % bits)
# simple compression
sc = SimpleCompression(s)
compressed = sc.compress()
print('Compressed binary: ' + compressed)
print('Uncompressed: ' + sc.uncompress(compressed))
print(sc.s2b)
print('Simple Compression-compress rate: %d%%' % get_rate(compressed, bits))
print('===================')
# huffman compression
hc = HuffmanCompression(s)
compressed = hc.compress()
print('Compressed binary: ' + compressed)
print('Uncompressed: ' + hc.uncompress(compressed))
print(hc.s2b)
print('Huffman Compression-compress rate: %d%%' % get_rate(compressed, bits))
"""
Total bits: 160
Compressed binary: 00101011001010001100001100001100000101000111000100001010001001110110010100101001
Uncompressed: everyday is awesome!
{'a': '0000', ' ': '0001', 'e': '0010', 'd': '0011', 'i': '0100', 'm': '0101', 'o': '0110', 's': '0111', 'r': '1000', '!': '1001', 'w': '1010', 'v': '1011', 'y': '1100'}
Simple Compression-compress rate: 50%
===================
Compressed binary: 011001011011110011010111111000010000111000111111010011110100011011010001
Uncompressed: everyday is awesome!
{'!': '0001', ' ': '001', 'e': '01', 'd': '11010', 'i': '0000', 'm': '11011', 'o': '1000', 's': '1110', 'r': '1011', 'a': '1111', 'w': '1010', 'v': '1001', 'y': '1100'}
Huffman Compression-compress rate: 45%
"""
源码分析
简单压缩: 根据字符串出现的字符,将ASCII替换成更短的表示形式 霍夫曼压缩: 根据字符串出现频率,构建Trie树, 对每个tree node进行定义,使得频率越高的字符离root节点越近
有关霍夫曼编码的具体步骤可参考 Huffman 编码压缩算法 | 酷 壳 - CoolShell.cn 和 霍夫曼编码 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书,清晰易懂。

