VUE-learn-state
优质
小牛编辑
135浏览
2023-12-01
简单状态管理
简单的store模式:
var store = {
debug: true,
state: {
message: 'Hello!'
},
setMessageAction (newValue) {
if (this.debug) console.log('setMessageAction triggered with', newValue)
this.state.message = newValue
},
clearMessageAction () {
if (this.debug) console.log('clearMessageAction triggered')
this.state.message = ''
}
}
需要注意,所有 store 中 state 的改变,都放置在 store 自身的 action 中去管理。这种集中式状态管理能够被更容易地理解哪种类型的 mutation 将会发生,以及它们是如何被触发。当错误出现时,我们现在也会有一个 log 记录 bug 之前发生了什么。
此外,每个实例/组件仍然可以拥有和管理自己的私有状态:
var vmA = new Vue({
data: {
privateState: {},
sharedState: store.state
}
})
var vmB = new Vue({
data: {
privateState: {},
sharedState: store.state
}
})
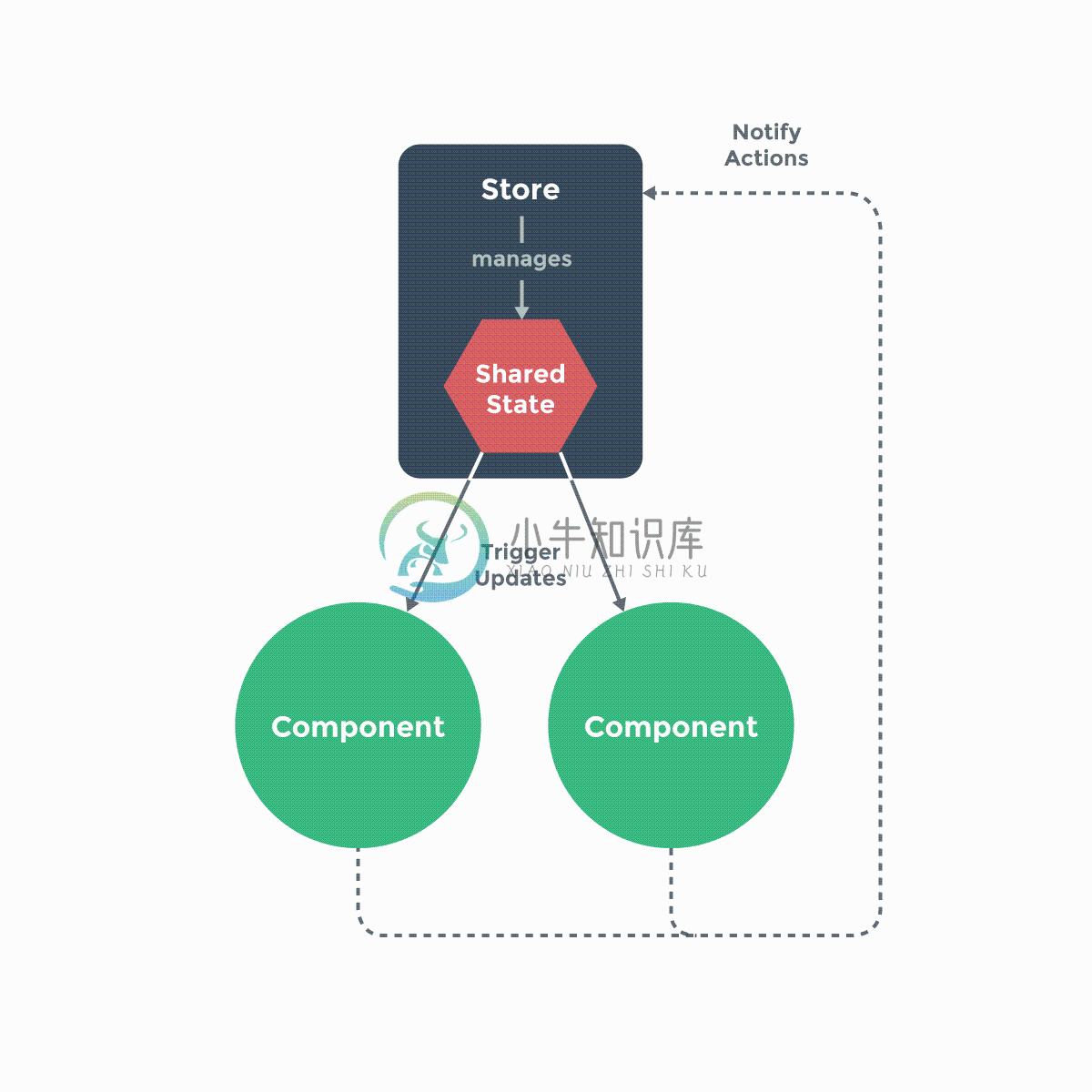
重要的是,注意你不应该在 action 中 替换原始的状态对象 - 组件和 store 需要引用同一个共享对象,mutation 才能够被观察
组件不允许直接修改属于 store 实例的 state,而应执行 action 来分发 (dispatch) 事件通知 store 去改变,我们最终达成了 Flux 架构。
Vuex
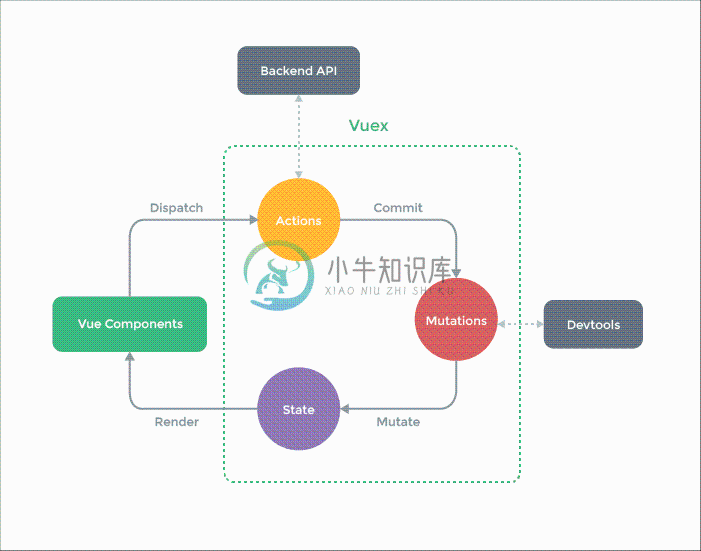
Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同:
Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是
显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
Vuex 使用单一状态树
Vuex 通过 store 选项,提供了一种机制将状态从根组件“注入”到每一个子组件中(需调用 Vue.use(Vuex)):
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 把 store 对象提供给 “store” 选项,这可以把 store 的实例注入所有的子组件
store,
components: { Counter },
template: `
<div class="app">
<counter></counter>
</div>
`
})
通过在根实例中注册 store 选项,该 store 实例会注入到根组件下的所有子组件中,且子组件能通过 this.$store 访问到。

