6.3 完整的例子
优质
小牛编辑
135浏览
2023-12-01
本节我们将使用一个弹球的例子来完整地学习使用动画效果。
首先,我们把通用的框架部分写好,按照4.1节的方法实现动画重绘函数,并按6.2节的方法加入stat.js库:
var requestAnimationFrame = window.requestAnimationFrame
|| window.mozRequestAnimationFrame
|| window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame
|| window.msRequestAnimationFrame;
window.requestAnimationFrame = requestAnimationFrame;
var scene = null;
var camera = null;
var renderer = null;
var id = null;
var stat = null;
function init() {
stat = new Stats();
stat.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stat.domElement.style.right = '0px';
stat.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.body.appendChild(stat.domElement);
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas: document.getElementById('mainCanvas')
});
scene = new THREE.Scene();
id = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
}
function draw() {
stat.begin();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
id = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
stat.end();
}
function stop() {
if (id !== null) {
cancelAnimationFrame(id);
id = null;
}
}
然后,为了实现弹球弹动的效果,我们创建一个球体作为弹球模型,创建一个平面作为弹球反弹的平面。为了在draw函数中改变弹球的位置,我们可以声明一个全局变量ballMesh,以及弹球半径ballRadius。
var ballMesh = null;
var ballRadius = 0.5;
在init函数中添加球体和平面,使弹球位于平面上,平面采用棋盘格图像作材质:
// ball
ballMesh = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.SphereGeometry(ballRadius, 16, 8),
new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0xffff00
}));
ballMesh.position.y = ballRadius;
scene.add(ballMesh);
// plane
var texture = THREE.ImageUtils.loadTexture('../img/chess.png', {}, function() {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
});
texture.wrapS = texture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;
texture.repeat.set(4, 4);
var plane = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.PlaneGeometry(5, 5),
new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({map: texture}));
plane.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
scene.add(plane);
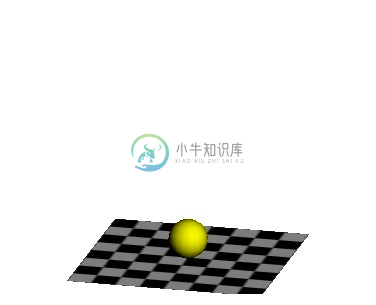
现在,每帧绘制的都是相同的效果:
为了记录弹球的状态,我们至少需要位置、速度、加速度三个矢量,为了简单起见,这里弹球只做竖直方向上的自由落体运动,因此位置、速度、加速度只要各用一个变量表示。其中,位置就是ballMesh.position.y,不需要额外的变量,因此我们在全局声明速度v和加速度a:
var v = 0;
var a = -0.1;
这里,a = -0.1代表每帧小球向y方向负方向移动0.1个单位。
一开始,弹球从高度为maxHeight处自由下落,掉落到平面上时会反弹,并且速度有损耗。当速度很小的时候,弹球会在平面上作振幅微小的抖动,所以,当速度足够小时,我们需要让弹球停止跳动。因此,定义一个全局变量表示是否在运动,初始值为false:
var isMoving = false;
在HTML中定义一个按钮,点击按钮时,弹球从最高处下落:
function drop() {
isMoving = true;
ballMesh.position.y = maxHeight;
v = 0;
}
下面就是最关键的函数了,在draw函数中,需要判断当前的isMoving值,并且更新小球的速度和位置:
function draw() {
stat.begin();
if (isMoving) {
ballMesh.position.y += v;
v += a;
if (ballMesh.position.y <= ballRadius) {
// hit plane
v = -v * 0.9;
}
if (Math.abs(v) < 0.001) {
// stop moving
isMoving = false;
ballMesh.position.y = ballRadius;
}
}
renderer.render(scene, camera);
id = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
stat.end();
}
这样就实现小球的弹动效果了。最终的代码为:
var requestAnimationFrame = window.requestAnimationFrame
|| window.mozRequestAnimationFrame
|| window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame
|| window.msRequestAnimationFrame;
window.requestAnimationFrame = requestAnimationFrame;
var scene = null;
var camera = null;
var renderer = null;
var id = null;
var stat = null;
var ballMesh = null;
var ballRadius = 0.5;
var isMoving = false;
var maxHeight = 5;
var v = 0;
var a = -0.01;
function init() {
stat = new Stats();
stat.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
stat.domElement.style.right = '0px';
stat.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.body.appendChild(stat.domElement);
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas: document.getElementById('mainCanvas')
});
scene = new THREE.Scene();
camera = new THREE.OrthographicCamera(-5, 5, 3.75, -3.75, 0.1, 100);
camera.position.set(5, 10, 20);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0, 3, 0));
scene.add(camera);
// ball
ballMesh = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.SphereGeometry(ballRadius, 16, 8),
new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0xffff00
}));
ballMesh.position.y = ballRadius;
scene.add(ballMesh);
// plane
var texture = THREE.ImageUtils.loadTexture('../img/chess.png', {}, function() {
renderer.render(scene, camera);
});
texture.wrapS = texture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;
texture.repeat.set(4, 4);
var plane = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.PlaneGeometry(5, 5),
new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({map: texture}));
plane.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
scene.add(plane);
var light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff);
light.position.set(10, 10, 15);
scene.add(light);
id = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
}
function draw() {
stat.begin();
if (isMoving) {
ballMesh.position.y += v;
v += a;
if (ballMesh.position.y <= ballRadius) {
// hit plane
v = -v * 0.9;
}
if (Math.abs(v) < 0.001) {
// stop moving
isMoving = false;
ballMesh.position.y = ballRadius;
}
}
renderer.render(scene, camera);
id = requestAnimationFrame(draw);
stat.end();
}
function stop() {
if (id !== null) {
cancelAnimationFrame(id);
id = null;
}
}
function drop() {
isMoving = true;
ballMesh.position.y = maxHeight;
v = 0;
}

