3D 基础知识(3D Basics)
优质
小牛编辑
134浏览
2023-12-01
在前面的章节中,我们已经了解了如何创建2D对象,对其应用效果以及转换对象。 本章将教您如何绘制具有第三维和某些形状的线。
让我们用z轴画一条简单的线,看看2D和3D线之间的区别。 首先绘制一条简单的线,然后将第二条线3个单位绘制到窗口中。
让我们通过该程序绘制3D线 -
import javax.media.opengl.GL2;
import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable;
import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities;
import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener;
import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile;
import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas;
import javax.media.opengl.glu.GLU;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Line3d implements GLEventListener {
private GLU glu = new GLU();
@Override
public void display( GLAutoDrawable drawable ) {
final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
gl.glTranslatef( 0f, 0f, -2.5f );
gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES );
gl.glVertex3f( -0.75f,0f,0 );
gl.glVertex3f( 0f,-0.75f, 0 );
gl.glEnd();
//3d line
gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES );
gl.glVertex3f( -0.75f,0f,3f );// 3 units into the window
gl.glVertex3f( 0f,-0.75f,3f );
gl.glEnd();
}
@Override
public void dispose( GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) {
//method body
}
@Override
public void init( GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) {
// method body
}
@Override
public void reshape( GLAutoDrawable drawable, int x, int y, int width, int height ) {
GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
if( height <= 0 )
height = 1;
final float h = ( float ) width/( float ) height;
gl.glViewport( 0, 0, width, height );
gl.glMatrixMode( GL2.GL_PROJECTION );
gl.glLoadIdentity();
glu.gluPerspective( 45.0f, h, 1.0, 20.0 );
gl.glMatrixMode( GL2.GL_MODELVIEW );
gl.glLoadIdentity();
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
//getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile
final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get( GLProfile.GL2 );
GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile);
// The canvas
final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas( capabilities );
Line3d line3d = new Line3d();
glcanvas.addGLEventListener( line3d );
glcanvas.setSize( 400, 400 );
//creating frame
final JFrame frame = new JFrame (" 3d line");
//adding canvas to it
frame.getContentPane().add( glcanvas );
frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize() );
frame.setVisible( true );
}//end of main
}//end of class
编译并执行上述程序时,会生成以下输出 -
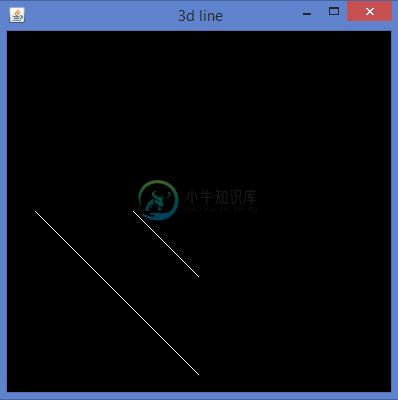
可以通过给glVertex3f()方法的z象限赋予非零值来绘制3D形状,从而生成上述视图。 现在加入剩余的线将导致3D边缘。
现在以同样的方式让我们开发出第三维的优势。
import javax.media.opengl.GL2;
import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable;
import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities;
import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener;
import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile;
import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas;
import javax.media.opengl.glu.GLU;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Edge1 implements GLEventListener {
private GLU glu = new GLU();
@Override
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, -2.5f);
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glEnd();
//3d line
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
//3 units in to the window
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
//top
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
//bottom
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
}
@Override
public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable arg0) {
//method body
}
@Override
public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0) {
// method body
}
@Override
public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable drawable, int x, int y, int width, int height) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stubfinal
GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
if(height <= 0)
height = 1;
final float h = (float) width/(float) height;
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_PROJECTION);
gl.glLoadIdentity();
glu.gluPerspective(45.0f, h, 1.0, 20.0);
gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_MODELVIEW);
gl.glLoadIdentity();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile
final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get(GLProfile.GL2);
GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile);
// The canvas
final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas(capabilities);
Edge1 b = new Edge1();
glcanvas.addGLEventListener(b);
glcanvas.setSize(400, 400);
//creating frame
final JFrame frame = new JFrame (" 3d edge");
//adding canvas to it
frame.getContentPane().add(glcanvas);
frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize());
frame.setVisible(true);
}//end of main
}//end of class
编译并执行上述程序时,会生成以下输出 -
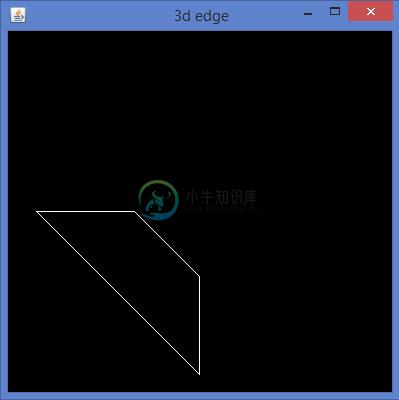
以同样的方式,通过将3D边缘开发到任何2D四边形的相应边并连接相邻顶点,您可以获得3D四边形。
下面给出了一个使用JOGL绘制菱形的程序。
import javax.media.opengl.GL2;
import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable;
import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities;
import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener;
import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile;
import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas;
import javax.media.opengl.glu.GLU;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Rhombus implements GLEventListener {
private GLU glu = new GLU();
@Override
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) {
final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, -2.5f);
//drawing edge1.....
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f); // 3 units into the window
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
//top
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
// bottom
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
// edge 2....
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 0);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 3f);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f, 3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 3f);
gl.glEnd();
//Edge 3.............
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,3f);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0);
gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
//final edge
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f, 0);
gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_LINES);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0);
gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,3f);
gl.glEnd();
}
@Override
public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable arg0) {
//method body
}
@Override
public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0) {
// method body
}
@Override
public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable drawable, int x, int y, int width, int height) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub final
GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
if(height lt;= 0)
height = 1;
final float h = (float) width/(float) height;
gl.glViewport(3, 6, width, height);
gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_PROJECTION);
gl.glLoadIdentity();
glu.gluPerspective(45.0f, h, 1.0, 20.0);
gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_MODELVIEW);
gl.glLoadIdentity();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile
final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get(GLProfile.GL2);
GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile);
// The canvas
final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas(capabilities);
Rhombus b = new Rhombus();
glcanvas.addGLEventListener(b);
glcanvas.setSize(400, 400);
//creating frame
final JFrame frame = new JFrame (" Rhombus 3d");
//adding canvas to it
frame.getContentPane().add(glcanvas);
frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize());
frame.setVisible(true);
}//end of main
}//end of classimport javax.media.opengl.GL2;
编译并执行上述程序时,将生成以下输出。 它显示使用3D线条绘制的菱形。
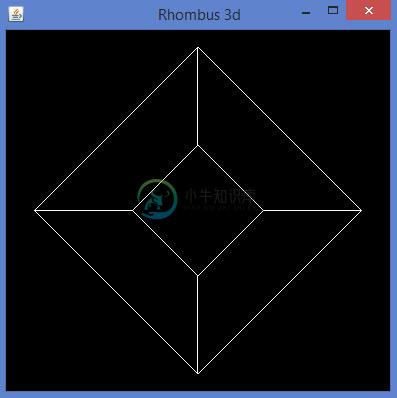
glBegin()方法的预定义参数可用于绘制3D形状。

