剑指 Offer 题解 - 20~29
优质
小牛编辑
154浏览
2023-12-01
- 20. 表示数值的字符串
- 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
- 22. 链表中倒数第 K 个结点
- 23. 链表中环的入口结点
- 24. 反转链表
- 25. 合并两个排序的链表
- 26. 树的子结构
- 27. 二叉树的镜像
- 28 对称的二叉树
- 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
20. 表示数值的字符串
题目描述
// true "+100" "5e2" "-123" "3.1416" "-1E-16"
// false "12e" "1a3.14" "1.2.3" "+-5" "12e+4.3"
解题思路
使用正则表达式进行匹配。
// html [] : 字符集合 () : 分组 ? : 重复 0 ~ 1 次 + : 重复 1 ~ n 次 * : 重复 0 ~ n 次 . : 任意字符 \\. : 转义后的 . \\d : 数字
// java
public boolean isNumeric(char[] str) {
if (str == null || str.length == 0)
return false;
return new String(str).matches("[+-]?\\d*(\\.\\d+)?([eE][+-]?\\d+)?");
}
21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目描述
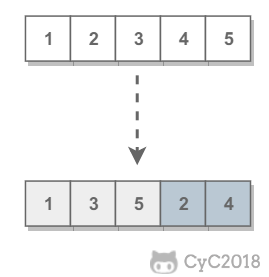
需要保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变,这和书本不太一样。
解题思路
方法一:创建一个新数组,时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度 O(N)。
// java
public void reOrderArray(int[] nums) {
// 奇数个数
int oddCnt = 0;
for (int x : nums)
if (!isEven(x))
oddCnt++;
int[] copy = nums.clone();
int i = 0, j = oddCnt;
for (int num : copy) {
if (num % 2 == 1)
nums[i++] = num;
else
nums[j++] = num;
}
}
private boolean isEven(int x) {
return x % 2 == 0;
}
方法二:使用冒泡思想,每次都当前偶数上浮到当前最右边。时间复杂度 O(N2),空间复杂度 O(1),时间换空间。
// java
public void reOrderArray(int[] nums) {
int N = nums.length;
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (isEven(nums[j]) && !isEven(nums[j + 1])) {
swap(nums, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
private boolean isEven(int x) {
return x % 2 == 0;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
22. 链表中倒数第 K 个结点
解题思路
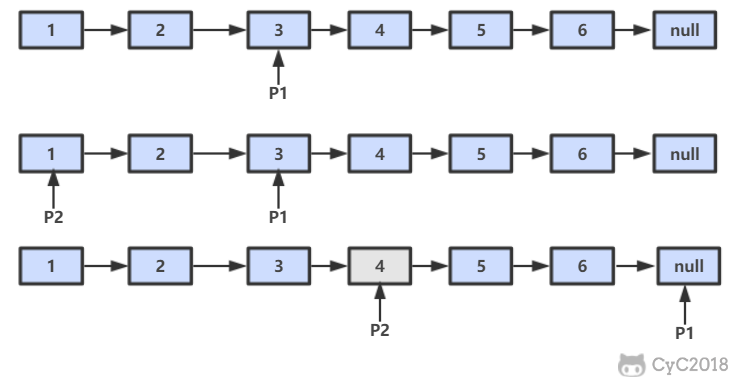
设链表的长度为 N。设置两个指针 P1 和 P2,先让 P1 移动 K 个节点,则还有 N - K 个节点可以移动。此时让 P1 和 P2 同时移动,可以知道当 P1 移动到链表结尾时,P2 移动到第 N - K 个节点处,该位置就是倒数第 K 个节点。
// java
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return null;
ListNode P1 = head;
while (P1 != null && k-- > 0)
P1 = P1.next;
if (k > 0)
return null;
ListNode P2 = head;
while (P1 != null) {
P1 = P1.next;
P2 = P2.next;
}
return P2;
}
23. 链表中环的入口结点
题目描述
一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点。要求不能使用额外的空间。
解题思路
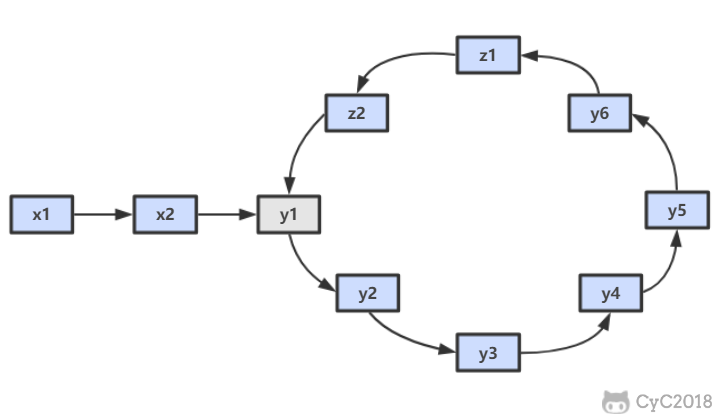
使用双指针,一个指针 fast 每次移动两个节点,一个指针 slow 每次移动一个节点。因为存在环,所以两个指针必定相遇在环中的某个节点上。假设相遇点在下图的 z1 位置,此时 fast 移动的节点数为 x+2y+z,slow 为 x+y,由于 fast 速度比 slow 快一倍,因此 x+2y+z=2(x+y),得到 x=z。
在相遇点,slow 要到环的入口点还需要移动 z 个节点,如果让 fast 重新从头开始移动,并且速度变为每次移动一个节点,那么它到环入口点还需要移动 x 个节点。在上面已经推导出 x=z,因此 fast 和 slow 将在环入口点相遇。
// java
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return null;
ListNode slow = pHead, fast = pHead;
do {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
} while (slow != fast);
fast = pHead;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
24. 反转链表
解题思路
递归
// java
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
迭代
使用头插法。
// java
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newList = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newList.next;
newList.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
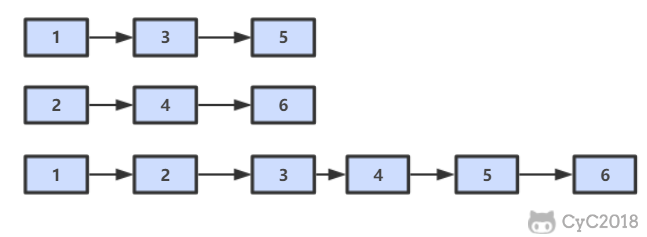
25. 合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
解题思路
递归
// java
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
if (list2 == null)
return list1;
if (list1.val <= list2.val)="" {="" list1.next="Merge(list1.next," list2);="" return="" list1;="" }="" else="" list2.next="Merge(list1," list2.next);="" list2;=""
迭代
// java
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = head;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val)="" {="" cur.next="list1;" list1="list1.next;" }="" else="" list2="list2.next;" cur="cur.next;" if="" (list1="" !="null)" (list2="" return="" head.next;=""
26. 树的子结构
题目描述
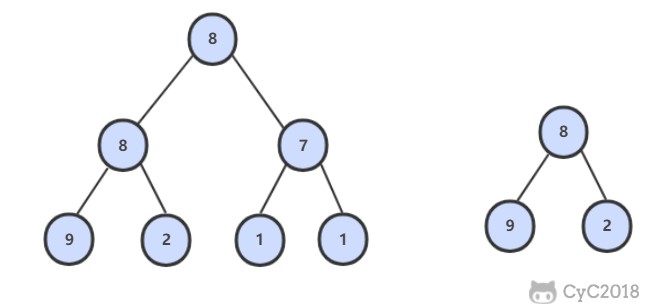
解题思路
// java
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null || root2 == null)
return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(root1, root2) || HasSubtree(root1.left, root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
}
private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root2 == null)
return true;
if (root1 == null)
return false;
if (root1.val != root2.val)
return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(root1.left, root2.left) && isSubtreeWithRoot(root1.right, root2.right);
}
27. 二叉树的镜像
题目描述
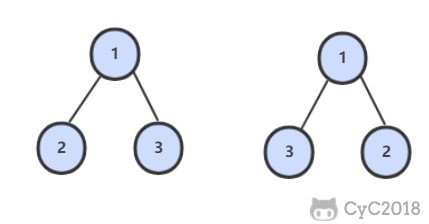
解题思路
// java
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
swap(root);
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
private void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode t = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = t;
}
28 对称的二叉树
题目描述
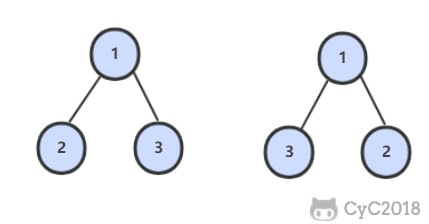
解题思路
// java
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if (pRoot == null)
return true;
return isSymmetrical(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);
}
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null)
return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null)
return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val)
return false;
return isSymmetrical(t1.left, t2.right) && isSymmetrical(t1.right, t2.left);
}
29. 顺时针打印矩阵
题目描述
下图的矩阵顺时针打印结果为:1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10
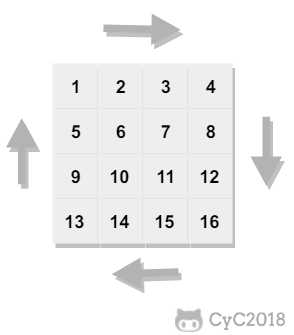
解题思路
// java
public ArrayList printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2="" &&="" c1="" = c1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[r2][i]);
if (c1 != c2)
for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[i][c1]);
r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;
}
return ret;
}

