SkylarkOS GPIO 使用指南
大部分外设的驱动开发都和GPIO的操作相关,因此,熟悉我们平台的GPIO使用是非常重要的
PD1开头的port对应ck域的port
PD2开头的port对应A7域的port
PD2PORT0 - PD2PORT31 对应 gpa0 组
PD2PORT32 - PD2PORT51 对应 gpa1 组
PD1PORT0 - PD1PORT31 对应ck_gpa0 组
在VSP代码上使用GPIO
VSP控制我们芯片内的一个独立的ck-mcu芯片
CK域的GPIO支持拉高,拉低,中断,PMW操作
每一个GPIO都支持中断使能,共支持8路PMW输出
使用参考 vsp/mcu/drivers/gpio
在linux上使用GPIO
arm上可以操作CK域的GPIO,除了中断操作不能。但是ck-mcu不能操作arm上的GPIO
要正常操作GPIO,首先要和硬件工程师确认,哪些管脚允许复用为GPIO。在这个基础上,在这个基础上,需要在ck的代码上和uboot的代码上,把管脚复用修改正确。
如果一个GPIO是要在linux上来操作的,并且该GPIO也可以被ck-mcu控制,那么必须保证ck-mcu的代码不会操作到它,否则两方都去操作,会导致异常。
ck-mcu上的管脚复用,请参考这里
uboot上修改管脚复用:
假设对应的开发板是8009,进入uboot/board/nationalchip/leo_gx8009_ssd/pinmux.c 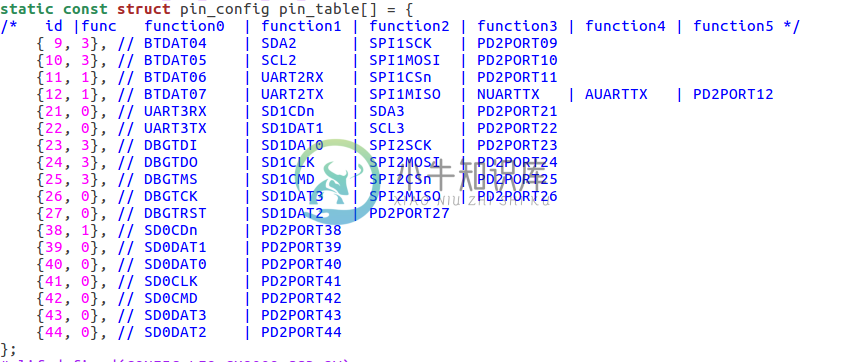
我们看这行:{ 9, 3}, // BTDAT04 | SDA2 | SPI1SCK | PD2PORT09
管脚9支持四种功能BTDAT04,SDA2,SPI1SCK ,PD2PORT09。
- BTDAT04功能索引是0
- SDA2功能索引是1
- SPI1SCK功能索引是2
- PD2PORT09功能索引是3
这里可以看出,管脚9被配置为GPIO功能了,名字是:PD2PORT09
在linux上操作GPIO有三种方法:
- 通过shell来操作
- 通过应用设备读写操作
- 通过linux驱动操作
通过shell操作如下: echo 进 export 的数字有一个换算关系: A7域的port echo 进 export 的数字就是PD1PORTXX的数字
ck域的port echo 进 export 的数字是PD1PORTXX的数字加上64
例子: 控制PD2PORT09脚 cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 9 > export
cd gpio9
echo out > direction //设置管脚为输出
echo 1 > value //设置管脚为高电平
例子: 控制PD2PORT09脚为中断模式,边缘上升触发中断 cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 9 > export
cd gpio9
echo rising > edge //中断模式,边缘上升触发中断
例子: 控制PD1PORT10脚 cd /sys/class/gpio
echo 74 > export
cd gpio74 echo out > direction //设置管脚为输出
echo 1 > value //设置管脚为高电平
通过应用设备读写操作:
我们假设GPIO9已经通过shell的方式进入了中断模式,边缘上升触发中断
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <poll.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int f;
struct pollfd poll_fds[1];
int ret;
char value[4];
int n;
f = open("/sys/class/gpio/gpio9/value", O_RDONLY);
if(f == -1)
{
perror("can not open gpio");
return 1;
}
poll_fds[0].fd = f;
poll_fds[0].events = POLLPRI | POLLERR;
while(1)
{
printf("waiting\n");
ret = poll(poll_fds, 1, -1);
if(ret > 0)
{
n = read(f, &value, sizeof(value));
printf("button pressed: read %d bytes, value = %c\n", n, value[0]);
lseek(f,0,SEEK_SET);
}
}
return 0;
}
通过linux驱动操作: port换算关系: port 的数字就是PDXPORTXX的数字 % 32
控制PD2PORT1脚
设备树节点
test:test{
compatible = "nationalchip,LEO_A7-test";
test1-gpio = ;
};
控制PD2PORT42脚
设备树节点
test:test{
compatible = "nationalchip,LEO_A7-test";
test1-gpio = ;
};
控制PD1PORT10脚
设备树节点
test:test{
compatible = "nationalchip,LEO_A7-test";
test1-gpio = ;
};
驱动代码
desc = devm_gpiod_get(&pdev->dev, "test1", GPIOD_OUT_LOW); //申请test1-gpio这个属性对应的GPIO口描述符,并设置为输出模式,输出低电平 gpiod_direction_input(desc); //设置desc描述符对应的GPIO口为输入模式 gpiod_to_irq(desc) //获取此gpio对应的中断号,中断号要注意检查,大于0为有效的 gpiod_direction_output(desc,1); //设置desc描述符对应的GPIO口为输出模式,输出高电平 gpiod_set_value(desc,0); //设置desc描述符对应的GPIO口输出值为0 gpio_level = gpiod_get_value(desc); //得到desc描述符对应的GPIO口的电平 devm_gpiod_put(&test_pdev->dev, desc); //释放desc描述符对应的GPIO口,这样别人才能申请这个GPIO口
通过linux驱动操作中断的例子
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/input-polldev.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/freezer.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/pm_runtime.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <linux/of_device.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/dmi.h>
#include <linux/idr.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/gpio/driver.h>
#include <linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/devcoredump.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#define D_STPE_DEBUG 1
#if (D_STPE_DEBUG)
#define dprintk(fmt, arg...) printk("STPE:"fmt, ##arg)
#else
#define dprintk(fmt, arg...)
#endif
typedef struct stpe_dev {
struct gpio_desc *l_gpio_desc;
struct gpio_desc *r_gpio_desc;
struct device *dev;
}stpe_dev_t;
static stpe_dev_t *stpe_pdev;
/**
*
* interrupts isr
*
*/
static irqreturn_t stpe_isr(int irq, void *dev_id) {
struct platform_device *pdev = (struct platform_device *)dev_id;
dprintk("======irq:%d======\n", irq);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/***
*
* probe
*/
static int stpe_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int l_irq, r_irq, ret;
stpe_pdev = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*stpe_pdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if(!stpe_pdev)
{
dprintk("devm_kzalloc stpe_pdev error.\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
stpe_pdev->dev = &pdev->dev;
if(!pdev->dev.of_node)
{
dprintk("device tree node not found.\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
stpe_pdev->l_gpio_desc = devm_gpiod_get(&pdev->dev, "cts", GPIOD_IN);
if (IS_ERR(stpe_pdev->l_gpio_desc)) {
printk("failed to gpiod get.\n");
return -1;
}
stpe_pdev->r_gpio_desc = devm_gpiod_get(&pdev->dev, "rts", GPIOD_IN);
if (IS_ERR(stpe_pdev->r_gpio_desc)) {
printk("failed to gpiod get.\n");
return -1;
}
l_irq = gpiod_to_irq(stpe_pdev->l_gpio_desc);
if ( l_irq < 0) {
printk("%s get l_irq error.\n", pdev->name);
}
printk("%d %s get l_irq.\n", l_irq, pdev->name);
r_irq = gpiod_to_irq(stpe_pdev->r_gpio_desc);
if ( r_irq < 0 ) {
printk("%s get r_irq error.\n", pdev->name);
}
printk("%d %s get r_irq.\n", r_irq, pdev->name);
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, l_irq, stpe_isr,IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "cts", pdev);
if (ret) {
printk("failed to devm_request_irq l_irq error:%d\n", ret);
}
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, r_irq, stpe_isr,IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "rts", pdev);
if (ret) {
printk("failed to devm_request_irq r_irq error:%d\n", ret);
}
return 0;
}
static int int_demo_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("%s enter.\n", __func__);
//devm_gpiod_put(&pdev->dev,stpe_pdev->l_gpio_desc);
//devm_gpiod_put(&stpe_pdev->dev,stpe_pdev->r_gpio_desc);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id stpe_of_match[] = {
{.compatible = "nationalchip,LEO_uart_control"},
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, stpe_of_match);
static struct platform_driver stpe_device_driver = {
.probe = stpe_probe,
.remove = int_demo_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "stpe-driver",
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(stpe_of_match),
}
};
static int __init stpe_init(void)
{
int error = -1;
dprintk("%s:%d\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return platform_driver_register(&stpe_device_driver);
}
static void __exit stpe_exit(void)
{
dprintk("%s:%d --- \n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
devm_gpiod_put(stpe_pdev->dev,stpe_pdev->l_gpio_desc);
devm_gpiod_put(stpe_pdev->dev,stpe_pdev->r_gpio_desc);
platform_driver_unregister(&stpe_device_driver);
}
module_init(stpe_init);
module_exit(stpe_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("test gpio driver");
MODULE_ALIAS("gpio driver");
MODULE_VERSION("V1.0.0");
MODULE_AUTHOR("yanfq@nationalchip.com");
PWM使用
在kernel里只提供A7gpio的pwm功能,ck的gpio不支持(硬件上是支持的,但是ck 的 pwm 会有 ck 可能会配寄存器,如果 A7 配的话可能会互相冲掉值)
pwm0对应gpa0组,pwm1对应gpa1组 port换算关系: port 的数字就是PDXPORTXX的数字 % 32 接口
struct pwm_device *devm_pwm_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id) //获取pwm句柄 int pwm_config(struct pwm_device *pwm, int duty_ns, int period_ns) //配置pwn int pwm_enable(struct pwm_device *pwm) //开启pwm void pwm_disable(struct pwm_device *pwm) //关闭pwm
例子:
控制PD2PORT26脚
设备树节点
test:test{
compatible = "nationalchip,LEO_A7-test";
pwms = ;
}
应用层: pwmchip0 对应gpa0组 pwmchip32对应gpa1组
控制PD2PORT26脚 echo 26 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export cd /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm26 echo 0 > enable //关闭此port的pwm echo 100000 > period //周期设置为100 us echo 50000 > duty_cycle //高电平持续时间设置为 50 us echo 1 > enable
控制PD2PORT33脚 echo 1 > /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip32/export cd /sys/class/pwm/pwmchip32/pwm1 echo 0 > enable //关闭此port的pwm echo 100000 > period //周期设置为100 us echo 50000 > duty_cycle //高电平持续时间设置为 50 us echo 1 > enable

