Flyweight 模式( Flyweight Pattern)
优质
小牛编辑
140浏览
2023-12-01
Flyweight模式主要用于减少创建的对象数量,减少内存占用并提高性能。 这种类型的设计模式属于结构模式,因为该模式提供了减少对象数量的方法,从而改善了应用程序的对象结构。
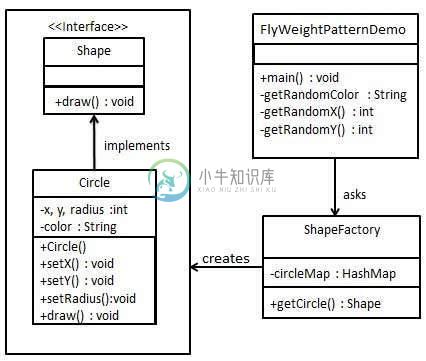
Flyweight模式尝试通过存储它们来重用已存在的类似对象,并在找不到匹配对象时创建新对象。 我们将通过绘制20个不同位置的圆圈来演示此模式,但我们将只创建5个对象。 只有5种颜色可用,因此颜色属性用于检查现有的Circle对象。
实现 (Implementation)
我们将创建一个Shape接口和实现Shape接口的具体类Circle 。 工厂类ShapeFactory被定义为下一步。
ShapeFactory有一个Circle的HashMap ,其键作为Circle对象的颜色。 每当请求为ShapeFactory创建一个特定颜色的圆圈时,它会检查其HashMap的圆形对象,如果找到Circle对象,则返回该对象,否则创建一个新对象,存储在hashmap中供将来使用,并返回到客户。
我们的演示类ShapeFactory将使用ShapeFactory来获取Shape对象。 它会将信息( red/green/blue/ black/white )传递给ShapeFactory以获得所需颜色的圆圈。
Step 1
创建一个界面。
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
Step 2
创建实现相同接口的具体类。
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color + ", x : " + x + ", y :" + y + ", radius :" + radius);
}
}
Step 3
根据给定的信息创建工厂以生成具体类的对象。
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
// Uncomment the compiler directive line and
// javac *.java will compile properly.
// @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static final HashMap circleMap = new HashMap();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}
Step 4
通过传递颜色等信息,使用工厂获取具体类的对象。
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] = { "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle = (Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}
Step 5
验证输出。
Creating circle of color : Black
Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Green
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100
Creating circle of color : White
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Red
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Blue
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100

