seaborn.FacetGrid
class seaborn.FacetGrid(data, row=None, col=None, hue=None, col_wrap=None, sharex=True, sharey=True, height=3, aspect=1, palette=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, hue_order=None, hue_kws=None, dropna=True, legend_out=True, despine=True, margin_titles=False, xlim=None, ylim=None, subplot_kws=None, gridspec_kws=None, size=None)
用于绘制条件关系的多图网格。
__init__(data, row=None, col=None, hue=None, col_wrap=None, sharex=True, sharey=True, height=3, aspect=1, palette=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, hue_order=None, hue_kws=None, dropna=True, legend_out=True, despine=True, margin_titles=False, xlim=None, ylim=None, subplot_kws=None, gridspec_kws=None, size=None)
初始化matplotlib画布和FacetGrid对象。
该类将数据集映射到由行和列组成的网格中的多个轴上,这些轴与数据集中变量的级别对应。它产生的图通常被称为“lattice”,“trellis”或“small-multiple”图形。
它还可以用hue参数表示第三个变量的级别,该参数绘制不同颜色的不同数据子集。它使用颜色来解析第三维度上的元素,但是只绘制相互重叠的子集,并且不会像接受“hue”的坐标轴级函数那样为特定的可视化定制“hue”参数。
当使用从数据集推断语义映射的seaborn函数时,必须注意在各个方面之间同步这些映射。在大多数情况下,使用图形级函数(例如relplot()或catplot())比直接使用FacetGrid更好。
基本工作流程是使用数据集和用于构造网格的变量初始化FacetGrid对象。然后,通过调用FacetGrid.map()或FacetGrid.map_dataframe(),可以将一个或多个绘图函数应用于每个子集。最后,可以使用其他方法调整绘图,以执行更改轴标签、使用不同刻度或添加图例等操作。有关详细信息,请参阅下面的详细代码示例。
更多相关信息请参阅color_palette()可以解释的参数,或者是将色调级别映射到matplotlib颜色的字典。
{row,col,hue}_order:列表,可选参数。
对所给命令级别进行排序。默认情况下,这将是在数据中显示的级别,或者,如果变量是pandas分类,则为类别顺序。
hue_kws:参数-列表值的映射字典
插入到绘图调用中的其他关键字参数,使得其他绘图属性在色调变量的级别上有所不同(例如散点图中的标记)。
legend_out:布尔值,可选参数。
如果为True,则图形尺寸将被扩展,图例将绘制在中间右侧的图形之外。
despine:布尔值,可选参数。
从图中移除顶部和右侧边缘框架。
margin_titles:布尔值,可选参数。
如果为True,则行变量的标题将绘制在最后一列的右侧。此选项是实验性的,可能无法在所有情况下使用。
{x, y}lim:元组,可选参数。
每个图片上每个轴的限制(仅当share {x,y}为True时才相关)。
subplot_kws:字典,可选参数。
传递给matplotlib subplot(s)方法的关键字参数字典。
gridspec_kws:字典,可选参数。
传递给matplotlib的
gridspec模块(通过plt.subplots)的关键字参数字典。需要matplotlib> = 1.4,如果col_wrap不是None,则忽略它。
另请参见
用于绘制成对关系的子图网格。
结合关系图和FacetGrid。
结合分类图和FacetGrid。
结合回归图和FacetGrid。
范例
使用tips数据集初始化2x2网格图:
>>> import seaborn as sns; sns.set(style="ticks", color_codes=True)
>>> tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
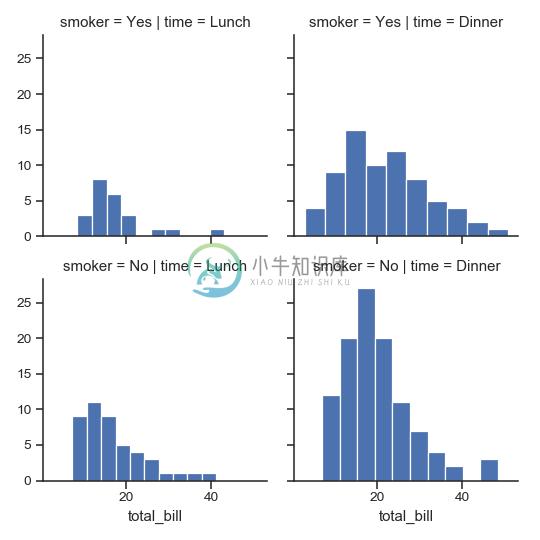
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time", row="smoker")
在每个子图绘制一个单变量图:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time", row="smoker")
>>> g = g.map(plt.hist, "total_bill")
(注意,没有必要重新捕获返回的变量;它是相同的对象,但在示例中这样做使得处理doctests更加方便)。
将其他关键字参数传递给映射函数:
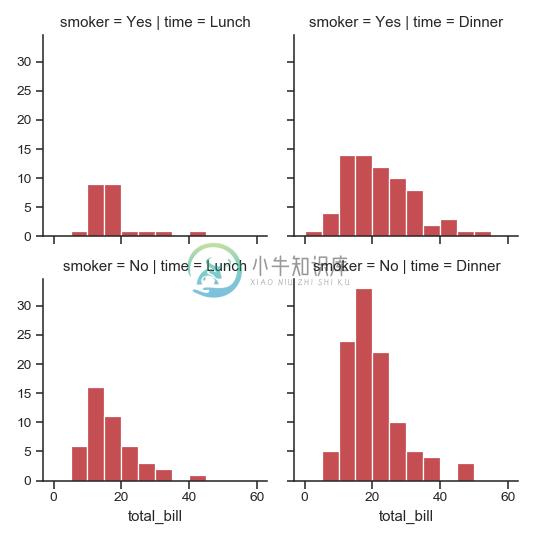
>>> import numpy as np
>>> bins = np.arange(0, 65, 5)
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time", row="smoker")
>>> g = g.map(plt.hist, "total_bill", bins=bins, color="r")
在每个子图绘制一个双变量函数:
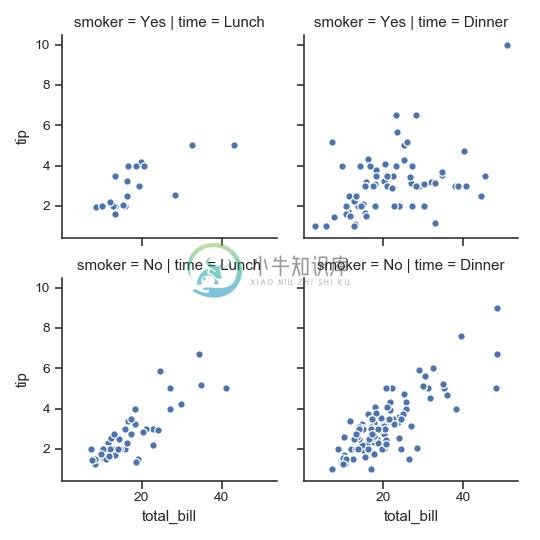
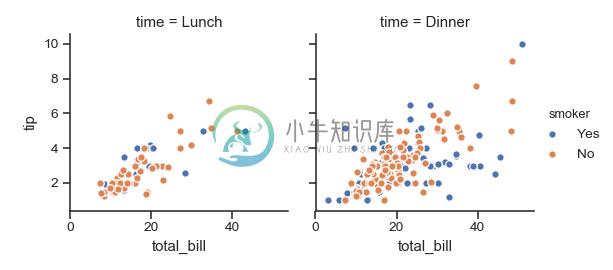
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time", row="smoker")
>>> g = g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", edgecolor="w")
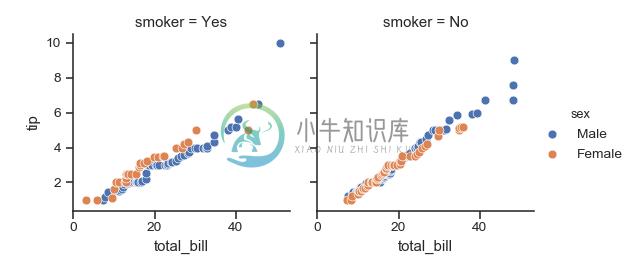
将其中一个变量分配给绘图元素的颜色:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time", hue="smoker")
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", edgecolor="w")
... .add_legend())
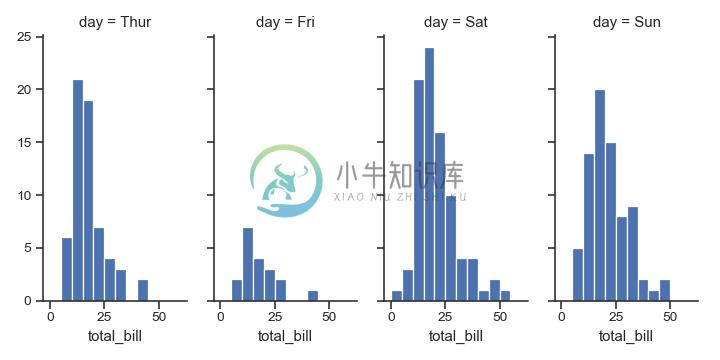
更改每个子图的高度和纵横比:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="day", height=4, aspect=.5)
>>> g = g.map(plt.hist, "total_bill", bins=bins)
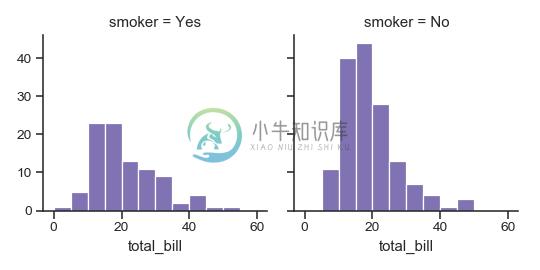
指定绘图元素的顺序:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="smoker", col_order=["Yes", "No"])
>>> g = g.map(plt.hist, "total_bill", bins=bins, color="m")
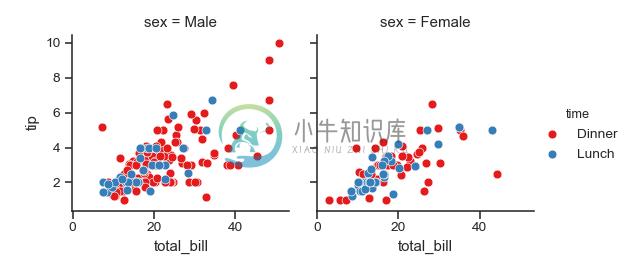
使用不同的调色板:
>>> kws = dict(s=50, linewidth=.5, edgecolor="w")
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="sex", hue="time", palette="Set1",
... hue_order=["Dinner", "Lunch"])
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", **kws)
... .add_legend())
使用字典将色调级别映射到颜色:
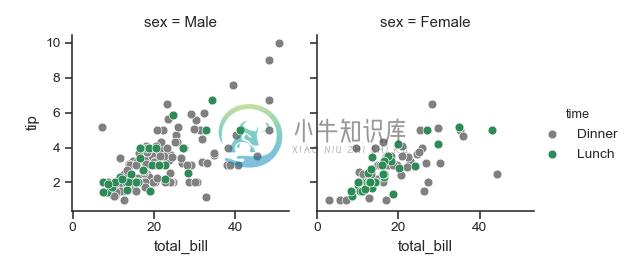
>>> pal = dict(Lunch="seagreen", Dinner="gray")
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="sex", hue="time", palette=pal,
... hue_order=["Dinner", "Lunch"])
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", **kws)
... .add_legend())
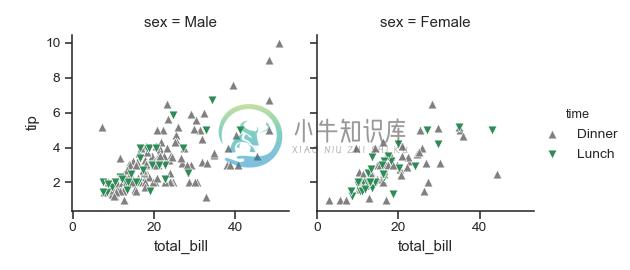
另外,为色调级别使用不同的标记:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="sex", hue="time", palette=pal,
... hue_order=["Dinner", "Lunch"],
... hue_kws=dict(marker=["^", "v"]))
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", **kws)
... .add_legend())
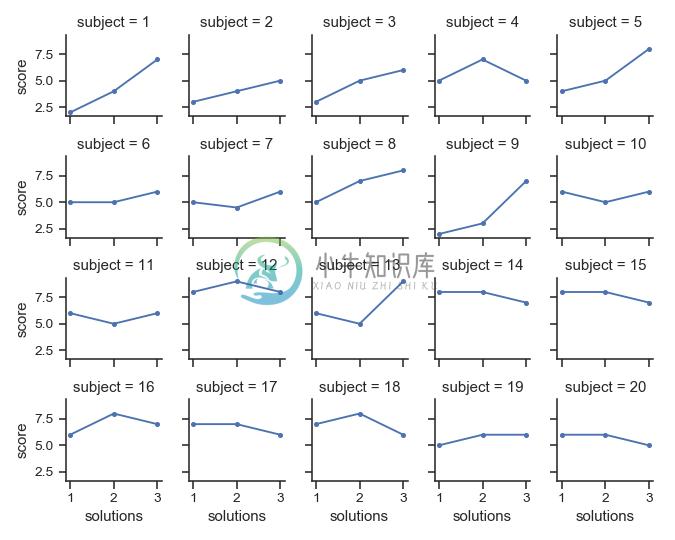
将包含多个级别的列变量“换行”到行中:
>>> att = sns.load_dataset("attention")
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(att, col="subject", col_wrap=5, height=1.5)
>>> g = g.map(plt.plot, "solutions", "score", marker=".")
定义一个自定义双变量函数来映射到网格:
>>> from scipy import stats
>>> def qqplot(x, y, **kwargs):
... _, xr = stats.probplot(x, fit=False)
... _, yr = stats.probplot(y, fit=False)
... plt.scatter(xr, yr, **kwargs)
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="smoker", hue="sex")
>>> g = (g.map(qqplot, "total_bill", "tip", **kws)
... .add_legend())
定义一个使用DataFrame对象的自定义函数,并接受列名作为位置变量:
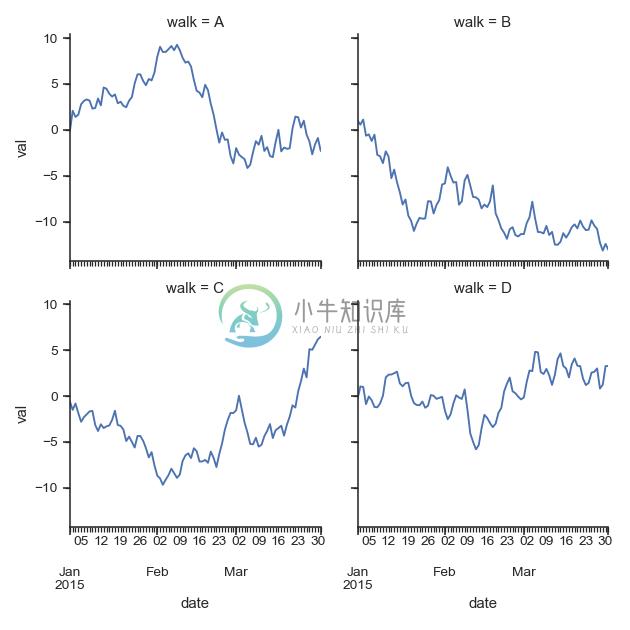
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(
... data=np.random.randn(90, 4),
... columns=pd.Series(list("ABCD"), name="walk"),
... index=pd.date_range("2015-01-01", "2015-03-31",
... name="date"))
>>> df = df.cumsum(axis=0).stack().reset_index(name="val")
>>> def dateplot(x, y, **kwargs):
... ax = plt.gca()
... data = kwargs.pop("data")
... data.plot(x=x, y=y, ax=ax, grid=False, **kwargs)
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(df, col="walk", col_wrap=2, height=3.5)
>>> g = g.map_dataframe(dateplot, "date", "val")
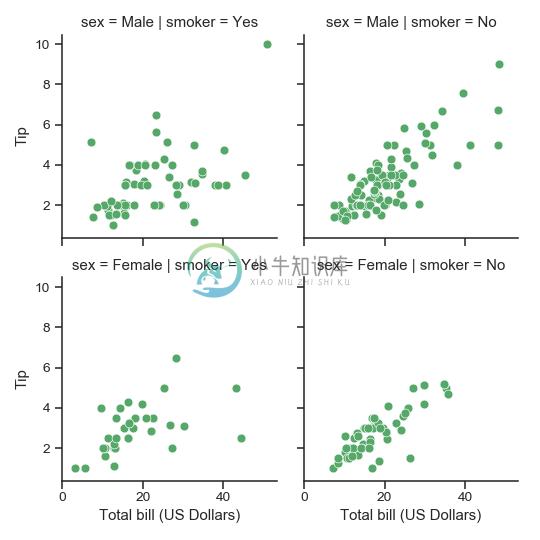
绘图后使用不同的轴标签:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="smoker", row="sex")
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", color="g", **kws)
... .set_axis_labels("Total bill (US Dollars)", "Tip"))
设置每个子图共享的其他属性:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="smoker", row="sex")
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", color="r", **kws)
... .set(xlim=(0, 60), ylim=(0, 12),
... xticks=[10, 30, 50], yticks=[2, 6, 10]))
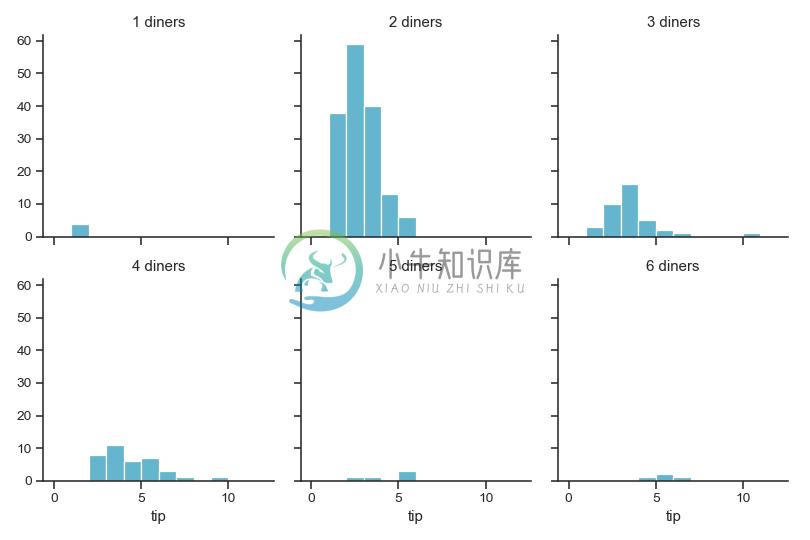
为子图标题使用不同的模板:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="size", col_wrap=3)
>>> g = (g.map(plt.hist, "tip", bins=np.arange(0, 13), color="c")
... .set_titles("{col_name} diners"))
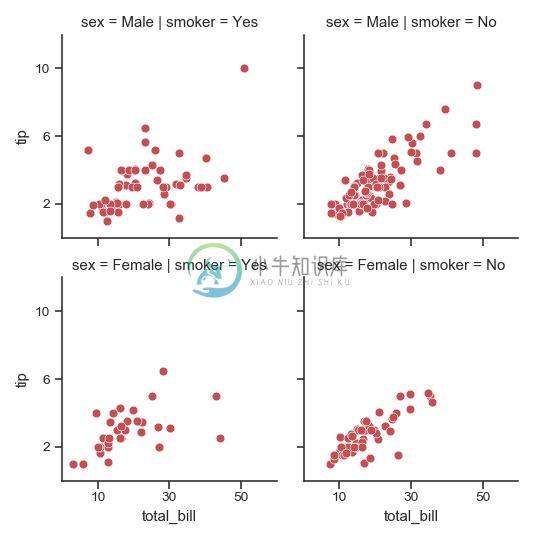
收紧每个子图:
>>> g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="smoker", row="sex",
... margin_titles=True)
>>> g = (g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", color="m", **kws)
... .set(xlim=(0, 60), ylim=(0, 12),
... xticks=[10, 30, 50], yticks=[2, 6, 10])
... .fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=.05, hspace=.05))
方法
| __init__(data[, row, col, hue, col_wrap, …]) | 初始化matplotlib画布和FacetGrid对象。 |
| add_legend([legend_data, title, label_order]) | 绘制一个图例,可能将其放在轴外并调整图形大小。|
| despine(**kwargs) | 从子图中移除轴的边缘框架。 |
| facet_axis(row_i, col_j) | 使这些索引识别的轴处于活动状态并返回。 |
| facet_data() | 用于每个子图的名称索引和数据子集的生成器。 |
| map(func, *args, **kwargs) | 将绘图功能应用于每个子图的数据子集。 |
| map_dataframe(func, *args, **kwargs) | 像.map一样,但是将args作为字符串传递并在kwargs中插入数据。 |
| savefig(*args, **kwargs) | 保存图片。 |
| set(**kwargs) | 在每个子图集坐标轴上设置属性。|
| set_axis_labels([x_var, y_var]) | 在网格的左列和底行设置轴标签。 |
| set_titles([template, row_template, …]) | 在每个子图上方或网格边缘绘制标题。 |
| set_xlabels([label]) | 在网格的底行标记x轴。 |
| set_xticklabels([labels, step]) | 在网格的底行设置x轴刻度标签。 |
| set_ylabels([label]) | 在网格的左列标记y轴。 |
| set_yticklabels([labels]) | 在网格的左列上设置y轴刻度标签。 |
属性
| ax | 轻松访问单个坐标轴。 |