Python Chart Styling
优质
小牛编辑
147浏览
2023-12-01
在python中创建的图表可以通过使用用于图表的库中的一些适当方法来进一步设置样式。 在本课中,我们将看到Annotation,图例和图表背景的实现。 我们将继续使用上一章中的代码并对其进行修改,以将这些样式添加到图表中。
添加注释
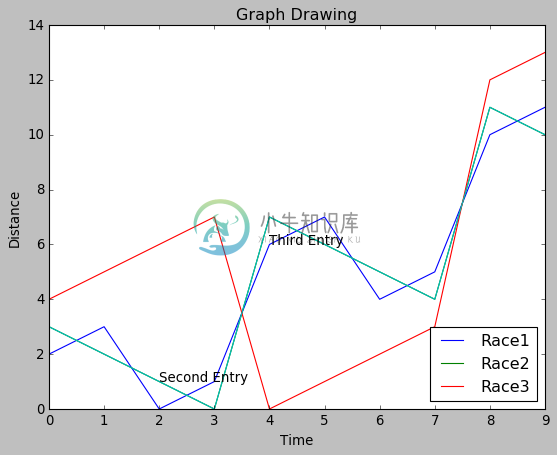
很多时候,我们需要通过突出显示图表的特定位置来注释图表。 在下面的示例中,我们通过在这些点添加注释来指示图表中值的急剧变化。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0,10)
y = x ^ 2
z = x ^ 3
t = x ^ 4
# Labeling the Axes and Title
plt.title("Graph Drawing")
plt.xlabel("Time")
plt.ylabel("Distance")
plt.plot(x,y)
#Annotate
plt.annotate(xy=[2,1], s='Second Entry')
plt.annotate(xy=[4,6], s='Third Entry')
其output如下 -
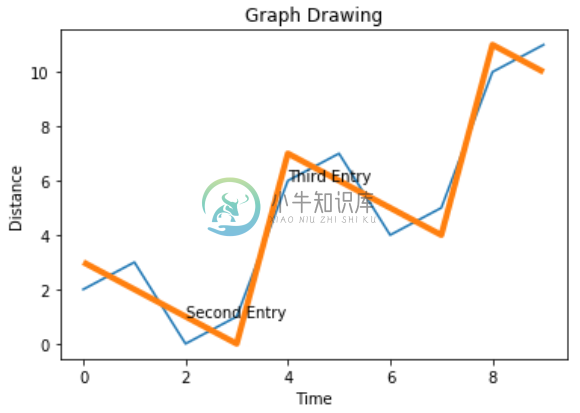
添加传说
我们有时需要绘制多行的图表。 使用图例表示与每行相关的含义。 在下面的图表中,我们有3行具有适当的图例。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0,10)
y = x ^ 2
z = x ^ 3
t = x ^ 4
# Labeling the Axes and Title
plt.title("Graph Drawing")
plt.xlabel("Time")
plt.ylabel("Distance")
plt.plot(x,y)
#Annotate
plt.annotate(xy=[2,1], s='Second Entry')
plt.annotate(xy=[4,6], s='Third Entry')
# Adding Legends
plt.plot(x,z)
plt.plot(x,t)
plt.legend(['Race1', 'Race2','Race3'], loc=4)
其output如下 -
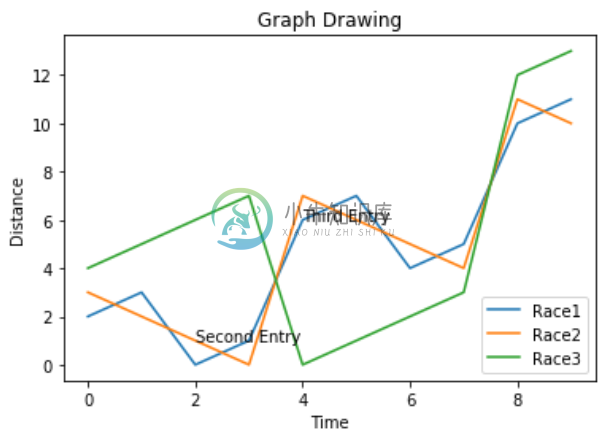
图表演示风格
我们可以使用样式包中的不同方法来修改图表的呈现样式。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0,10)
y = x ^ 2
z = x ^ 3
t = x ^ 4
# Labeling the Axes and Title
plt.title("Graph Drawing")
plt.xlabel("Time")
plt.ylabel("Distance")
plt.plot(x,y)
#Annotate
plt.annotate(xy=[2,1], s='Second Entry')
plt.annotate(xy=[4,6], s='Third Entry')
# Adding Legends
plt.plot(x,z)
plt.plot(x,t)
plt.legend(['Race1', 'Race2','Race3'], loc=4)
#Style the background
plt.style.use('fast')
plt.plot(x,z)
其output如下 -