Chameleon 两阶段聚类算法
参考文献:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangchaoyang/articles/2182752.html(用了很多的图和思想)
博客园(华夏35度) 作者:Orisun
数据挖掘算法-Chameleon算法.百度文库
我的算法库:https://github.com/linyiqun/lyq-algorithms-lib(里面可能有你正想要的算法)
算法介绍
本篇文章讲述的还是聚类算法,也是属于层次聚类算法领域的,不过与上篇文章讲述的分裂实现聚类的方式不同,这次所讲的Chameleon算法是合并形成最终的聚类,恰巧相反。Chamelon的英文单词的意思是变色龙,所以这个算法又称之为变色龙算法,变色龙算法的过程如标题所描绘的那样,是分为2个主要阶段的,不过他可不是像BIRCH算法那样,是树的形式。继续看下面的原理介绍。
算法原理
先来张图来大致了解整个算法的过程。
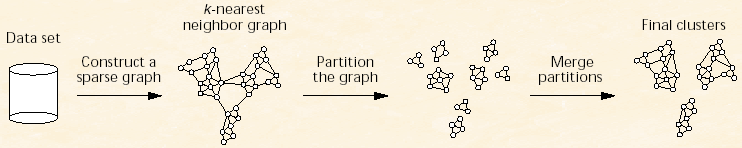
上面图的显示过程虽然说有3个阶段,但是这其中概况起来就是两个阶段,第一个是形成小簇集的过程就是从Data Set 到k最近邻图到分裂成小聚餐,第二个阶段是合并这些小聚簇形成最终的结果聚簇。理解了算法的大致过程,下面看看里面定义的一些概念,还不少的样子。
为了引出变色龙算法的一些定义,这里先说一下以往的一些聚类算法的不足之处。
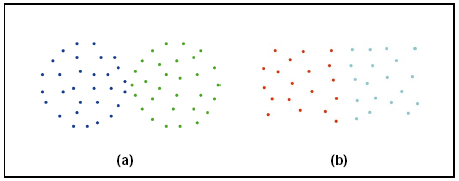
1、忽略簇与簇之间的互连性。就会导致最终的结果形成如下:
2、忽略簇与簇之间的近似性。就会导致最终的聚类结果变成这样“:
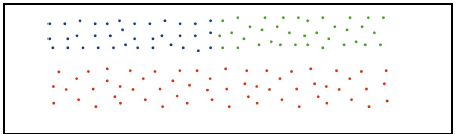
为什么提这些呢,因为Chameleon算法正好弥补了这2点要求,兼具互连性和近似性。在Chameleon算法中定义了相对互连性,RI表示和相对近似性,RC表示,最后通过一个度量函数:
function value = RI( Ci, Cj)× RC( Ci, Cj)α,α在这里表示的多少次方的意思,不是乘法。
来作为2个簇是否能够合并的标准,其实这些都是第二阶段做的事情了。
在第一阶段,所做的一件关键的事情就是形成小簇集,由零星的几个数据点连成小簇,官方的作法是用hMetic算法根据最小化截断的边的权重和来分割k-最近邻图,然后我网上找了一些资料,没有确切的hMetic算法,借鉴了网上其他人的一些办法,于是用了一个很简单的思路,就是给定一个点,把他离他最近的k个点连接起来,就算是最小簇了。事实证明,效果也不会太差,最近的点的换一个意思就是与其最大权重的边,采用距离的倒数最为权重的大小。因为后面的计算,用到的会是权重而不是距离。
我们再回过头来细说第二阶段所做的事情,首先是2个略复杂的公式(直接采用截图的方式):
相对互连性RI=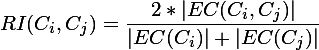
相对近似性RC=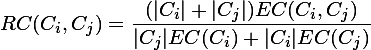
Ci,Cj表示的是i,j聚簇内的数据点的个数,EC(Ci)表示的Ci聚簇内的边的权重和,EC(Ci,Cj)表示的是连接2个聚簇的边的权重和。
后来我在查阅书籍和一些文库的时候发现,这个公式还不是那么的标准,因为他对分母,分子进行了部分的改变,但是大意上还是一致的,标准公式上用到的是平均权重,而这里用的是和的形式,差别不大,所以就用这个公式了。
那么合并的过程如下:
1、给定度量函数如下minMetric,
2、访问每个簇,计算他与邻近的每个簇的RC和RI,通过度量函数公式计算出值tempMetric。
3、找到最大的tempMetric,如果最大的tempMetric超过阈值minMetric,将簇与此值对应的簇合并
4、如果找到的最大的tempMetric没有超过阈值,则表明此聚簇已合并完成,移除聚簇列表,加入到结果聚簇中。
4、递归步骤2,直到待合并聚簇列表最终大小为空。
算法的实现
算法的输入依旧采用的是坐标点的形式graphData.txt:
0 2 2
1 3 1
2 3 4
3 3 14
4 5 3
5 8 3
6 8 6
7 9 8
8 10 4
9 10 7
10 10 10
11 10 14
12 11 13
13 12 8
14 12 15
15 14 7
16 14 9
17 14 15
18 15 8
package DataMining_Chameleon;
/**
* 坐标点类
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Point{
//坐标点id号,id号唯一
int id;
//坐标横坐标
Integer x;
//坐标纵坐标
Integer y;
//是否已经被访问过
boolean isVisited;
public Point(String id, String x, String y){
this.id = Integer.parseInt(id);
this.x = Integer.parseInt(x);
this.y = Integer.parseInt(y);
}
/**
* 计算当前点与制定点之间的欧式距离
*
* @param p
* 待计算聚类的p点
* @return
*/
public double ouDistance(Point p) {
double distance = 0;
distance = (this.x - p.x) * (this.x - p.x) + (this.y - p.y)
* (this.y - p.y);
distance = Math.sqrt(distance);
return distance;
}
/**
* 判断2个坐标点是否为用个坐标点
*
* @param p
* 待比较坐标点
* @return
*/
public boolean isTheSame(Point p) {
boolean isSamed = false;
if (this.x == p.x && this.y == p.y) {
isSamed = true;
}
return isSamed;
}
}
簇类Cluster.java:
package DataMining_Chameleon;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 聚簇类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Cluster implements Cloneable{
//簇唯一id标识号
int id;
// 聚簇内的坐标点集合
ArrayList<Point> points;
// 聚簇内的所有边的权重和
double weightSum = 0;
public Cluster(int id, ArrayList<Point> points) {
this.id = id;
this.points = points;
}
/**
* 计算聚簇的内部的边权重和
*
* @return
*/
public double calEC() {
int id1 = 0;
int id2 = 0;
weightSum = 0;
for (Point p1 : points) {
for (Point p2 : points) {
id1 = p1.id;
id2 = p2.id;
// 为了避免重复计算,取id1小的对应大的
if (id1 < id2 && ChameleonTool.edges[id1][id2] == 1) {
weightSum += ChameleonTool.weights[id1][id2];
}
}
}
return weightSum;
}
/**
* 计算2个簇之间最近的n条边
*
* @param otherCluster
* 待比较的簇
* @param n
* 最近的边的数目
* @return
*/
public ArrayList<int[]> calNearestEdge(Cluster otherCluster, int n){
int count = 0;
double distance = 0;
double minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Point point1 = null;
Point point2 = null;
ArrayList<int[]> edgeList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Point> pointList1 = (ArrayList<Point>) points.clone();
ArrayList<Point> pointList2 = null;
Cluster c2 = null;
try {
c2 = (Cluster) otherCluster.clone();
pointList2 = c2.points;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
int[] tempEdge;
// 循环计算出每次的最近距离
while (count < n) {
tempEdge = new int[2];
minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (Point p1 : pointList1) {
for (Point p2 : pointList2) {
distance = p1.ouDistance(p2);
if (distance < minDistance) {
point1 = p1;
point2 = p2;
tempEdge[0] = p1.id;
tempEdge[1] = p2.id;
minDistance = distance;
}
}
}
pointList1.remove(point1);
pointList2.remove(point2);
edgeList.add(tempEdge);
count++;
}
return edgeList;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//引用需要再次复制,实现深拷贝
ArrayList<Point> pointList = (ArrayList<Point>) this.points.clone();
Cluster cluster = new Cluster(id, pointList);
return cluster;
}
}
算法工具类Chameleon.java:
package DataMining_Chameleon;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Chameleon 两阶段聚类算法工具类
*
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class ChameleonTool {
// 测试数据点文件地址
private String filePath;
// 第一阶段的k近邻的k大小
private int k;
// 簇度量函数阈值
private double minMetric;
// 总的坐标点的个数
private int pointNum;
// 总的连接矩阵的情况,括号表示的是坐标点的id号
public static int[][] edges;
// 点与点之间的边的权重
public static double[][] weights;
// 原始坐标点数据
private ArrayList<Point> totalPoints;
// 第一阶段产生的所有的连通子图作为最初始的聚类
private ArrayList<Cluster> initClusters;
// 结果簇结合
private ArrayList<Cluster> resultClusters;
public ChameleonTool(String filePath, int k, double minMetric) {
this.filePath = filePath;
this.k = k;
this.minMetric = minMetric;
readDataFile();
}
/**
* 从文件中读取数据
*/
private void readDataFile() {
File file = new File(filePath);
ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String str;
String[] tempArray;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
tempArray = str.split(" ");
dataArray.add(tempArray);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
Point p;
totalPoints = new ArrayList<>();
for (String[] array : dataArray) {
p = new Point(array[0], array[1], array[2]);
totalPoints.add(p);
}
pointNum = totalPoints.size();
}
/**
* 递归的合并小聚簇
*/
private void combineSubClusters() {
Cluster cluster = null;
resultClusters = new ArrayList<>();
// 当最后的聚簇只剩下一个的时候,则退出循环
while (initClusters.size() > 1) {
cluster = initClusters.get(0);
combineAndRemove(cluster, initClusters);
}
}
/**
* 递归的合并聚簇和移除聚簇
*
* @param clusterList
*/
private ArrayList<Cluster> combineAndRemove(Cluster cluster,
ArrayList<Cluster> clusterList) {
ArrayList<Cluster> remainClusters;
double metric = 0;
double maxMetric = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Cluster cluster1 = null;
Cluster cluster2 = null;
for (Cluster c2 : clusterList) {
if (cluster.id == c2.id) {
continue;
}
metric = calMetricfunction(cluster, c2, 1);
if (metric > maxMetric) {
maxMetric = metric;
cluster1 = cluster;
cluster2 = c2;
}
}
// 如果度量函数值超过阈值,则进行合并,继续搜寻可以合并的簇
if (maxMetric > minMetric) {
clusterList.remove(cluster2);
// 将边进行连接
connectClusterToCluster(cluster1, cluster2);
// 将簇1和簇2合并
cluster1.points.addAll(cluster2.points);
remainClusters = combineAndRemove(cluster1, clusterList);
} else {
clusterList.remove(cluster);
remainClusters = clusterList;
resultClusters.add(cluster);
}
return remainClusters;
}
/**
* 将2个簇进行边的连接
*
* @param c1
* 聚簇1
* @param c2
* 聚簇2
*/
private void connectClusterToCluster(Cluster c1, Cluster c2) {
ArrayList<int[]> connectedEdges;
connectedEdges = c1.calNearestEdge(c2, 2);
for (int[] array : connectedEdges) {
edges[array[0]][array[1]] = 1;
edges[array[1]][array[0]] = 1;
}
}
/**
* 算法第一阶段形成局部的连通图
*/
private void connectedGraph() {
double distance = 0;
Point p1;
Point p2;
// 初始化权重矩阵和连接矩阵
weights = new double[pointNum][pointNum];
edges = new int[pointNum][pointNum];
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pointNum; j++) {
p1 = totalPoints.get(i);
p2 = totalPoints.get(j);
distance = p1.ouDistance(p2);
if (distance == 0) {
// 如果点为自身的话,则权重设置为0
weights[i][j] = 0;
} else {
// 边的权重采用的值为距离的倒数,距离越近,权重越大
weights[i][j] = 1.0 / distance;
}
}
}
double[] tempWeight;
int[] ids;
int id1 = 0;
int id2 = 0;
// 对每个id坐标点,取其权重前k个最大的点进行相连
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {
tempWeight = weights[i];
// 进行排序
ids = sortWeightArray(tempWeight);
// 取出前k个权重最大的边进行连接
for (int j = 0; j < ids.length; j++) {
if (j < k) {
id1 = i;
id2 = ids[j];
edges[id1][id2] = 1;
edges[id2][id1] = 1;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 权重的冒泡算法排序
*
* @param array
* 待排序数组
*/
private int[] sortWeightArray(double[] array) {
double[] copyArray = array.clone();
int[] ids = null;
int k = 0;
double maxWeight = -1;
ids = new int[pointNum];
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {
maxWeight = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < copyArray.length; j++) {
if (copyArray[j] > maxWeight) {
maxWeight = copyArray[j];
k = j;
}
}
ids[i] = k;
// 将当前找到的最大的值重置为-1代表已经找到过了
copyArray[k] = -1;
}
return ids;
}
/**
* 根据边的连通性去深度优先搜索所有的小聚簇
*/
private void searchSmallCluster() {
int currentId = 0;
Point p;
Cluster cluster;
initClusters = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Point> pointList = null;
// 以id的方式逐个去dfs搜索
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {
p = totalPoints.get(i);
if (p.isVisited) {
continue;
}
pointList = new ArrayList<>();
pointList.add(p);
recusiveDfsSearch(p, -1, pointList);
cluster = new Cluster(currentId, pointList);
initClusters.add(cluster);
currentId++;
}
}
/**
* 深度优先的方式找到边所连接着的所有坐标点
*
* @param p
* 当前搜索的起点
* @param lastId
* 此点的父坐标点
* @param pList
* 坐标点列表
*/
private void recusiveDfsSearch(Point p, int parentId, ArrayList<Point> pList) {
int id1 = 0;
int id2 = 0;
Point newPoint;
if (p.isVisited) {
return;
}
p.isVisited = true;
for (int j = 0; j < pointNum; j++) {
id1 = p.id;
id2 = j;
if (edges[id1][id2] == 1 && id2 != parentId) {
newPoint = totalPoints.get(j);
pList.add(newPoint);
// 以此点为起点,继续递归搜索
recusiveDfsSearch(newPoint, id1, pList);
}
}
}
/**
* 计算连接2个簇的边的权重
*
* @param c1
* 聚簇1
* @param c2
* 聚簇2
* @return
*/
private double calEC(Cluster c1, Cluster c2) {
double resultEC = 0;
ArrayList<int[]> connectedEdges = null;
connectedEdges = c1.calNearestEdge(c2, 2);
// 计算连接2部分的边的权重和
for (int[] array : connectedEdges) {
resultEC += weights[array[0]][array[1]];
}
return resultEC;
}
/**
* 计算2个簇的相对互连性
*
* @param c1
* @param c2
* @return
*/
private double calRI(Cluster c1, Cluster c2) {
double RI = 0;
double EC1 = 0;
double EC2 = 0;
double EC1To2 = 0;
EC1 = c1.calEC();
EC2 = c2.calEC();
EC1To2 = calEC(c1, c2);
RI = 2 * EC1To2 / (EC1 + EC2);
return RI;
}
/**
* 计算簇的相对近似度
*
* @param c1
* 簇1
* @param c2
* 簇2
* @return
*/
private double calRC(Cluster c1, Cluster c2) {
double RC = 0;
double EC1 = 0;
double EC2 = 0;
double EC1To2 = 0;
int pNum1 = c1.points.size();
int pNum2 = c2.points.size();
EC1 = c1.calEC();
EC2 = c2.calEC();
EC1To2 = calEC(c1, c2);
RC = EC1To2 * (pNum1 + pNum2) / (pNum2 * EC1 + pNum1 * EC2);
return RC;
}
/**
* 计算度量函数的值
*
* @param c1
* 簇1
* @param c2
* 簇2
* @param alpha
* 幂的参数值
* @return
*/
private double calMetricfunction(Cluster c1, Cluster c2, int alpha) {
// 度量函数值
double metricValue = 0;
double RI = 0;
double RC = 0;
RI = calRI(c1, c2);
RC = calRC(c1, c2);
// 如果alpha大于1,则更重视相对近似性,如果alpha逍遥于1,注重相对互连性
metricValue = RI * Math.pow(RC, alpha);
return metricValue;
}
/**
* 输出聚簇列
*
* @param clusterList
* 输出聚簇列
*/
private void printClusters(ArrayList<Cluster> clusterList) {
int i = 1;
for (Cluster cluster : clusterList) {
System.out.print("聚簇" + i + ":");
for (Point p : cluster.points) {
System.out.print(MessageFormat.format("({0}, {1}) ", p.x, p.y));
}
System.out.println();
i++;
}
}
/**
* 创建聚簇
*/
public void buildCluster() {
// 第一阶段形成小聚簇
connectedGraph();
searchSmallCluster();
System.out.println("第一阶段形成的小簇集合:");
printClusters(initClusters);
// 第二阶段根据RI和RC的值合并小聚簇形成最终结果聚簇
combineSubClusters();
System.out.println("最终的聚簇集合:");
printClusters(resultClusters);
}
}
调用类Client.java:
package DataMining_Chameleon;
/**
* Chameleon(变色龙)两阶段聚类算法
* @author lyq
*
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
String filePath = "C:\\Users\\lyq\\Desktop\\icon\\graphData.txt";
//k-近邻的k设置
int k = 1;
//度量函数阈值
double minMetric = 0.1;
ChameleonTool tool = new ChameleonTool(filePath, k, minMetric);
tool.buildCluster();
}
}算法输出如下:
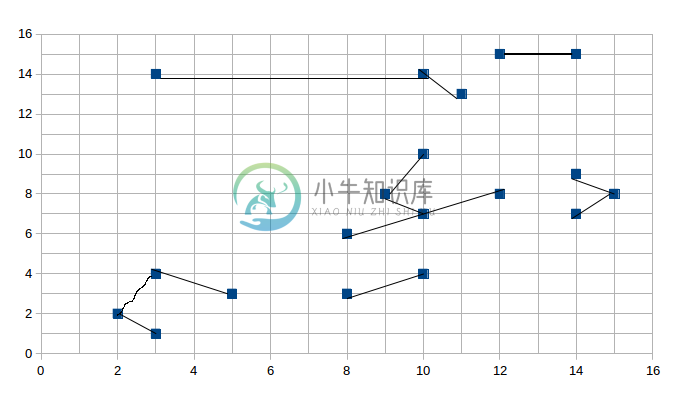
第一阶段形成的小簇集合:
聚簇1:(2, 2) (3, 1) (3, 4) (5, 3)
聚簇2:(3, 14) (10, 14) (11, 13)
聚簇3:(8, 3) (10, 4)
聚簇4:(8, 6) (9, 8) (10, 7) (12, 8) (10, 10)
聚簇5:(12, 15) (14, 15)
聚簇6:(14, 7) (15, 8) (14, 9)
最终的聚簇集合:
聚簇1:(2, 2) (3, 1) (3, 4) (5, 3) (8, 3) (10, 4)
聚簇2:(3, 14) (10, 14) (11, 13) (12, 15) (14, 15)
聚簇3:(8, 6) (9, 8) (10, 7) (12, 8) (10, 10) (14, 7) (15, 8) (14, 9) 图形展示情况如下:
首先是第一阶段形成小簇集的结果:
然后是第二阶段合并的结果:
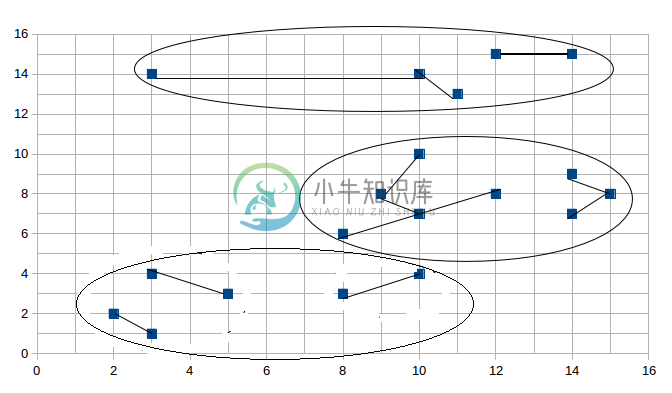
与结果相对应,请读者细细比较。
算法总结
在算法的实现过程中遇到一个比较大的困惑点在于2个簇近和并的时候,合并边的选取,我是直接采用的是最近的2对顶点进行连接,显然这是不合理的,当簇与簇规模比较大的时候,这个连接边需要变多,我有想过做一个计算函数,帮我计算估计要连接几条边。这里再提几点变色龙算法的优缺点,首先是这个算法将互连性和近似性都考虑了进来,其次他能发现高质量的任意形状的簇,问题有,第一与KNN算法一样,这个k的取值永远是一个痛,时间复杂度高,有可能会达到O(n*n)的程度,细心的博友一定能观察到我好多地方用到了双次循环的操作了。

