继承(Inheritance)
继承可以定义为一个类获取另一个类的属性(方法和字段)的过程。 通过使用继承,可以按层次顺序管理信息。
继承其他属性的类称为子类(派生类,子类),其属性被继承的类称为超类(基类,父类)。
扩展关键字
extends是用于继承类属性的关键字。 以下是extends关键字的语法。
Syntax
class Super {
.....
.....
}
class Sub extends Super {
.....
.....
}
示例代码 (Sample Code)
以下是演示Java继承的示例。 在此示例中,您可以观察两个类,即Calculation和My_Calculation。
使用extends关键字,My_Calculation继承Calculation类的方法addition()和Subtraction()。
将以下程序复制并粘贴到名为My_Calculation.java的文件中
Example
class Calculation {
int z;
public void addition(int x, int y) {
z = x + y;
System.out.println("The sum of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public void Subtraction(int x, int y) {
z = x - y;
System.out.println("The difference between the given numbers:"+z);
}
}
public class My_Calculation extends Calculation {
public void multiplication(int x, int y) {
z = x * y;
System.out.println("The product of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 20, b = 10;
My_Calculation demo = new My_Calculation();
demo.addition(a, b);
demo.Subtraction(a, b);
demo.multiplication(a, b);
}
}
编译并执行上面的代码,如下所示。
javac My_Calculation.java
java My_Calculation
执行程序后,它将产生以下结果 -
Output
The sum of the given numbers:30
The difference between the given numbers:10
The product of the given numbers:200
在给定的程序中,当创建一个My_Calculation类的对象时,会在其中创建超类的内容的副本。 这就是为什么,使用子类的对象,您可以访问超类的成员。
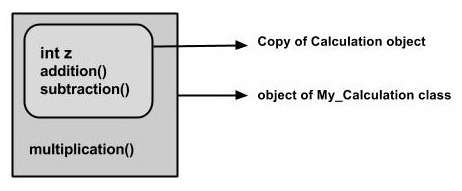
Superclass引用变量可以包含子类对象,但是使用该变量只能访问超类的成员,因此要访问两个类的成员,建议始终为子类创建引用变量。
如果考虑上述程序,可以实例化下面给出的类。 但是使用超类引用变量(在本例中为cal ),您无法调用方法multiplication() ,它属于子类My_Calculation。
Calculation demo = new My_Calculation();
demo.addition(a, b);
demo.Subtraction(a, b);
Note - 子类从其超类继承所有成员(字段,方法和嵌套类)。 构造函数不是成员,因此它们不是由子类继承的,但是可以从子类调用超类的构造函数。
超级关键字
super关键字与this关键字类似。 以下是使用super关键字的方案。
如果它们具有相同的名称,它用于differentiate the members超类的成员和子类的成员。
它用于从子类invoke the superclass构造函数。
区分会员
如果一个类继承了另一个类的属性。 如果超类的成员具有与子类相同的名称,为了区分这些变量,我们使用super关键字,如下所示。
super.variable
super.method();
示例代码 (Sample Code)
本节为您提供演示super关键字用法的程序。
在给定的程序中,您有两个类,即Sub_class和Super_class ,它们都有一个名为display()的方法,具有不同的实现,以及一个名为num的变量,具有不同的值。 我们调用两个类的display()方法并打印两个类的变量num的值。 在这里,您可以观察到我们使用了super关键字来区分超类和子类的成员。
将程序复制并粘贴到名为Sub_class.java的文件中。
Example
class Super_class {
int num = 20;
// display method of superclass
public void display() {
System.out.println("This is the display method of superclass");
}
}
public class Sub_class extends Super_class {
int num = 10;
// display method of sub class
public void display() {
System.out.println("This is the display method of subclass");
}
public void my_method() {
// Instantiating subclass
Sub_class sub = new Sub_class();
// Invoking the display() method of sub class
sub.display();
// Invoking the display() method of superclass
super.display();
// printing the value of variable num of subclass
System.out.println("value of the variable named num in sub class:"+ sub.num);
// printing the value of variable num of superclass
System.out.println("value of the variable named num in super class:"+ super.num);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Sub_class obj = new Sub_class();
obj.my_method();
}
}
使用以下语法编译并执行上述代码。
javac Super_Demo
java Super
执行程序时,您将获得以下结果 -
Output
This is the display method of subclass
This is the display method of superclass
value of the variable named num in sub class:10
value of the variable named num in super class:20
调用超类构造函数
如果类继承了另一个类的属性,则子类会自动获取超类的默认构造函数。 但是如果要调用超类的参数化构造函数,则需要使用super关键字,如下所示。
super(values);
示例代码 (Sample Code)
本节中给出的程序演示了如何使用super关键字来调用超类的参数化构造函数。 该程序包含一个超类和一个子类,其中超类包含一个接受整数值的参数化构造函数,我们使用super关键字来调用超类的参数化构造函数。
将以下程序复制并粘贴到名为Subclass.java的文件中
Example
class Superclass {
int age;
Superclass(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void getAge() {
System.out.println("The value of the variable named age in super class is: " +age);
}
}
public class Subclass extends Superclass {
Subclass(int age) {
super(age);
}
public static void main(String argd[]) {
Subclass s = new Subclass(24);
s.getAge();
}
}
使用以下语法编译并执行上述代码。
javac Subclass
java Subclass
执行程序时,您将获得以下结果 -
Output
The value of the variable named age in super class is: 24
IS-A Relationship
IS-A是一种说法:该对象是该对象的一种。 让我们看看如何使用extends关键字来实现继承。
public class Animal {
}
public class Mammal extends Animal {
}
public class Reptile extends Animal {
}
public class Dog extends Mammal {
}
现在,基于上面的例子,在面向对象的术语中,以下是真实的 -
- 动物是哺乳动物类的超类。
- Animal是Reptile类的超类。
- 哺乳动物和爬行动物是动物类的亚类。
- 狗是哺乳动物和动物类的子类。
现在,如果我们考虑IS-A关系,我们可以说 -
- Mammal IS-A Animal
- Reptile IS-A Animal
- Dog IS-A Mammal
- 因此:狗IS-A动物也是如此
通过使用extends关键字,子类将能够继承超类的所有属性,除了超类的私有属性。
我们可以通过使用实例运算符来确保Mammal实际上是一个Animal。
Example
class Animal {
}
class Mammal extends Animal {
}
class Reptile extends Animal {
}
public class Dog extends Mammal {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Animal a = new Animal();
Mammal m = new Mammal();
Dog d = new Dog();
System.out.println(m instanceof Animal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Mammal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Animal);
}
}
这将产生以下结果 -
Output
true
true
true
由于我们对extends关键字有很好的理解,因此我们来看看implements关键字如何用于获取IS-A关系。
通常, implements关键字与类一起使用以继承接口的属性。 接口永远不能由类扩展。
Example
public interface Animal {
}
public class Mammal implements Animal {
}
public class Dog extends Mammal {
}
关键字的实例
让我们使用instanceof运算符来检查确定Mammal是否实际上是Animal,而dog实际上是Animal。
Example
interface Animal{}
class Mammal implements Animal{}
public class Dog extends Mammal {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Mammal m = new Mammal();
Dog d = new Dog();
System.out.println(m instanceof Animal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Mammal);
System.out.println(d instanceof Animal);
}
}
这将产生以下结果 -
Output
true
true
true
HAS-A relationship
这些关系主要基于用法。 这决定了某某类HAS-A是否有某种东西。 这种关系有助于减少代码重复和错误。
让我们看一个例子 -
Example
public class Vehicle{}
public class Speed{}
public class Van extends Vehicle {
private Speed sp;
}
这表明class有HAS-A速度。 通过为Speed提供一个单独的类,我们不必将属于speed的整个代码放在Van类中,这样就可以在多个应用程序中重用Speed类。
在面向对象的功能中,用户无需担心哪个对象正在进行实际工作。 为了实现这一点,Van类隐藏了Van类用户的实现细节。 因此,基本上会发生的事情是用户会要求Van类执行某个操作,而Van类要么自己完成工作要么要求另一个类执行操作。
继承的类型
如下所示,存在各种类型的继承。
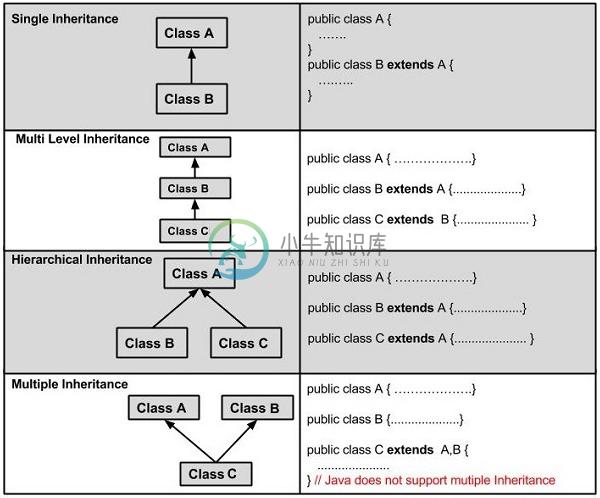
需要记住的一个非常重要的事实是Java不支持多重继承。 这意味着一个类不能扩展多个类。 因此以下是非法的 -
Example
public class extends Animal, Mammal{}
但是,一个类可以实现一个或多个接口,这有助于Java摆脱多重继承的不可能性。

