Database Handling
Spring Boot为创建数据库的DataSource提供了非常好的支持。 我们不需要编写任何额外的代码来在Spring Boot中创建DataSource。 只需添加依赖项并执行配置详细信息就足以创建DataSource并连接数据库。
在本章中,我们将使用Spring Boot JDBC驱动程序连接来连接数据库。
首先,我们需要在构建配置文件中添加Spring Boot Starter JDBC依赖项。
Maven用户可以在pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
Gradle用户可以在build.gradle文件中添加以下依赖项。
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc')
连接到H2数据库
要连接H2数据库,我们需要在构建配置文件中添加H2数据库依赖项。
对于Maven用户,请在pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
对于Gradle用户,请在build.gradle文件中添加以下依赖项。
compile('com.h2database:h2')
我们需要在classpath src/main/resources目录下创建schema.sql文件和data.sql文件来连接H2数据库。
schema.sql文件如下所示。
CREATE TABLE PRODUCT (ID INT PRIMARY KEY, PRODUCT_NAME VARCHAR(25));
data.sql文件如下所示。
INSERT INTO PRODUCT (ID,PRODUCT_NAME) VALUES (1,'Honey');
INSERT INTO PRODUCT (ID,PRODUCT_NAME) VALUES (2,'Almond');
连接MySQL
要连接MySQL数据库,我们需要将MySQL依赖项添加到我们的构建配置文件中。
对于Maven用户,请在pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项。
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
对于Gradle用户,请在build.gradle文件中添加以下依赖项。
compile('mysql:mysql-connector-java')
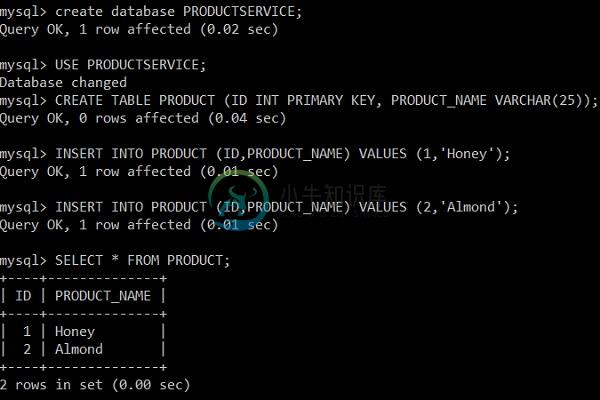
现在,在MySQL中创建数据库和表,如图所示 -
对于属性文件用户,请在application.properties文件中添加以下属性。
spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/PRODUCTSERVICE?autoreconnect = true
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
spring.datasource.testOnBorrow = true
spring.datasource.testWhileIdle = true
spring.datasource.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 60000
spring.datasource.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 30000
spring.datasource.validationQuery = SELECT 1
spring.datasource.max-active = 15
spring.datasource.max-idle = 10
spring.datasource.max-wait = 8000
对于YAML用户,请在application.yml文件中添加以下属性。
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/PRODUCTSERVICE?autoreconnect=true"
username: "root"
password: "root"
testOnBorrow: true
testWhileIdle: true
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 30000
validationQuery: SELECT 1
max-active: 15
max-idle: 10
max-wait: 8000
连接Redis
Redis是一个用于存储内存数据结构的开源数据库。 要在Spring Boot应用程序中连接Redis数据库,我们需要在构建配置文件中添加Redis依赖项。
Maven用户应在pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
Gradle用户应在build.gradle文件中添加以下依赖项。
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis')
对于Redis连接,我们需要使用RedisTemplate。 对于RedisTemplate,我们需要提供JedisConnectionFactory的详细信息。
@Bean
JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory() {
JedisConnectionFactory jedisConFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
jedisConFactory.setHostName("localhost");
jedisConFactory.setPort(6000);
jedisConFactory.setUsePool(true);
return jedisConFactory;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory());
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
现在自动连接RedisTemplate类并从Redis数据库访问数据。
@Autowired
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redis;
Map<Object,Object> datalist = redis.opsForHash().entries(“Redis_code_index_key”);
JDBCTemplate
要在Spring Boot应用程序中使用JdbcTemplate访问关系数据库,我们需要在构建配置文件中添加Spring Boot Starter JDBC依赖项。
然后,如果您@Autowired JdbcTemplate类,Spring Boot会自动连接数据库并为JdbcTemplate对象设置数据源。
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
Collection<Map<String, Object>> rows = jdbc.queryForList("SELECT QUERY");
应将@Repository注释添加到类文件中。 @Repository注释用于为Spring Boot应用程序创建数据库存储库。
@Repository
public class ProductServiceDAO {
}
多个数据源
我们可以在一个Spring Boot应用程序中保留'n'个数据源。 此处给出的示例显示了如何在Spring Boot应用程序中创建多个数据源。 现在,在应用程序属性文件中添加两个数据源配置详细信息。
对于属性文件用户,请将以下属性添加到application.properties文件中。
spring.dbProductService.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.dbProductService.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/PRODUCTSERVICE?autoreconnect = true
spring.dbProductService.username = root
spring.dbProductService.password = root
spring.dbProductService.testOnBorrow = true
spring.dbProductService.testWhileIdle = true
spring.dbProductService.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 60000
spring.dbProductService.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 30000
spring.dbProductService.validationQuery = SELECT 1
spring.dbProductService.max-active = 15
spring.dbProductService.max-idle = 10
spring.dbProductService.max-wait = 8000
spring.dbUserService.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.dbUserService.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/USERSERVICE?autoreconnect = true
spring.dbUserService.username = root
spring.dbUserService.password = root
spring.dbUserService.testOnBorrow = true
spring.dbUserService.testWhileIdle = true
spring.dbUserService.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 60000
spring.dbUserService.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 30000
spring.dbUserService.validationQuery = SELECT 1
spring.dbUserService.max-active = 15
spring.dbUserService.max-idle = 10
spring.dbUserService.max-wait = 8000
Yaml用户应在application.yml文件中添加以下属性。
spring:
dbProductService:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/PRODUCTSERVICE?autoreconnect=true"
password: "root"
username: "root"
testOnBorrow: true
testWhileIdle: true
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 30000
validationQuery: SELECT 1
max-active: 15
max-idle: 10
max-wait: 8000
dbUserService:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/USERSERVICE?autoreconnect=true"
password: "root"
username: "root"
testOnBorrow: true
testWhileIdle: true
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 30000
validationQuery: SELECT 1
max-active: 15
max-idle: 10
max-wait: 8000
现在,创建一个Configuration类,为多个数据源创建DataSource和JdbcTemplate。
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
@Configuration
public class DatabaseConfig {
@Bean(name = "dbProductService")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.dbProductService")
@Primary
public DataSource createProductServiceDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "dbUserService")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.dbUserService")
public DataSource createUserServiceDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcProductService")
@Autowired
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate_ProductService(@Qualifier("dbProductService") DataSource productServiceDS) {
return new JdbcTemplate(productServiceDS);
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcUserService")
@Autowired
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate_UserService(@Qualifier("dbUserService") DataSource userServiceDS) {
return new JdbcTemplate(userServiceDS);
}
}
然后,使用@Qualifier注释自动连接JDBCTemplate对象。
@Qualifier("jdbcProductService")
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Qualifier("jdbcUserService")
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;

