用CNN做深度学习

卷积神经网络(CNN)
卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)是将二维离散卷积运算和人工神经网络相结合的一种深度神经网络。它的特点是可以自动提取特征。有关卷积神经网络的数学原理和训练过程请见我的另一篇文章《机器学习教程 十五-细解卷积神经网络》。
手写数字识别
为了试验,我们直接采用http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/中的手写数据集,下载到的手写数据集数据文件是用二进制以像素为单位保存的几万张图片文件,通过我的github项目https://github.com/lcdevelop/ChatBotCourse中的read_images.c把图片打印出来是像下面这样的输出:

具体文件格式和打印方式请见我的另一篇基于简单的softmax模型的机器学习算法文章《机器学习教程 十四-利用tensorflow做手写数字识别》中的讲解
多层卷积网络设计
为了对mnist手写数据集做训练,我们设计这样的多层卷积网络:
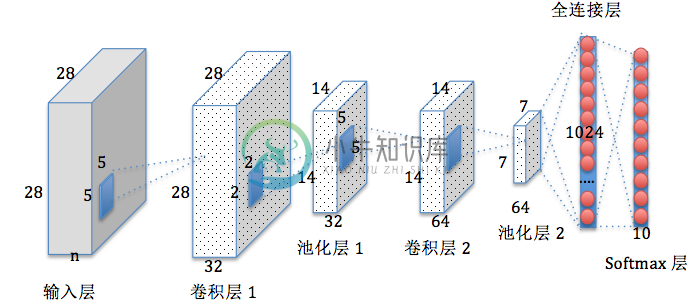
第一层由一个卷积和一个max pooling完成,其中卷积运算的“视野”是5×5的像素范围,卷积使用1步长、0边距的模板(保证输入输出是同一个大小),1个输入通道(因为图片是灰度的,单色),32个输出通道(也就是设计32个特征)。由于我们通过上面read_images.c的打印可以看到每张图片都是28×28像素,那么第一次卷积输出也是28×28大小。max pooling采用2×2大小的模板,那么池化后输出的尺寸就是14×14,因为一共有32个通道,所以一张图片的输出一共是14×14×32=6272像素
第二层同样由一个卷积和一个max pooling完成,和第一层不同的是输入通道有32个(对应第一层的32个特征),输出通道我们设计64个(即输出64个特征),因为这一层的输入是每张大小14×14,所以这一个卷积层输出也是14×14,再经过这一层max pooling,输出大小就是7×7,那么一共输出像素就是7×7×64=3136
第三层是一个密集连接层,我们设计一个有1024个神经元的全连接层,这样就相当于第二层输出的7×7×64个值都作为这1024个神经元的输入
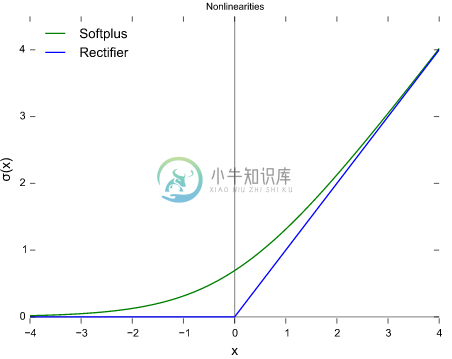
为了让算法更“智能”,我们把这些神经元的激活函数设计为ReLu函数,即如下图像中的蓝色(其中绿色是它的平滑版g(x)=log(1+e^x)):
最终的输出层,我们以第三层的1024个输出为输入,设计一个softmax层,输出10个概率值
tensorflow代码实现
# coding:utf-8
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding( "utf-8" )
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
flags = tf.app.flags
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', './', 'Directory for storing data')
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.data_dir, one_hot=True)
# 初始化生成随机的权重(变量),避免神经元输出恒为0
def weight_variable(shape):
# 以正态分布生成随机值
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 初始化生成随机的偏置项(常量),避免神经元输出恒为0
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 卷积采用1步长,0边距,保证输入输出大小相同
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 池化采用2×2模板
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 28*28=784
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
# 输出类别共10个:0-9
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None,10])
# 第一层卷积权重,视野是5*5,输入通道1个,输出通道32个
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
# 第一层卷积偏置项有32个
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
# 把x变成4d向量,第二维和第三维是图像尺寸,第四维是颜色通道数1
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
# 第二层卷积权重,视野是5*5,输入通道32个,输出通道64个
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
# 第二层卷积偏置项有64个
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# 第二层池化后尺寸编程7*7,第三层是全连接,输入是64个通道,输出是1024个神经元
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
# 第三层全连接偏置项有1024个
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 按float做dropout,以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# 最后的softmax层生成10种分类
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
# Adam优化器来做梯度最速下降
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
for i in range(20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x:batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print "step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_accuracy)
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
print "test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0})输出结果
[root@centos $] python digital_recognition_cnn.py
Extracting ./train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting ./train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting ./t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting ./t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
step 0, training accuracy 0.14
step 100, training accuracy 0.86
step 200, training accuracy 0.9
step 300, training accuracy 0.86
step 400, training accuracy 1
step 500, training accuracy 0.92
step 600, training accuracy 1
step 700, training accuracy 0.96
step 800, training accuracy 0.88
step 900, training accuracy 1
step 1000, training accuracy 0.96
step 1100, training accuracy 0.98
step 1200, training accuracy 0.94
step 1300, training accuracy 0.92
step 1400, training accuracy 0.98
……最终准确率大概能达到99.2%

