第23章:分页实现
我们可以非常容易地使用 CBV 来实现分页功能。但首先我想手工分页,这样就更有助于我们理解背后的机制,这样它就不那么神秘了。
实际上对 boards 列表视图分页并没有意义,因为我们不期望有很多 boards。但无疑对于主题列表和帖子列表来说是需要一些分页的。
从现在起,我们将在 board_topics 这个视图中来操作。
首先,我们添加一些帖子。我们可以直接使用应用程序的用户界面来添加几个帖子,或者打开 python shell 编写一个小脚本来为我们完成:
python manage.py shell
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from boards.models import Board, Topic, Post
user = User.objects.first()
board = Board.objects.get(name='Django')
for i in range(100):
subject = 'Topic test #{}'.format(i)
topic = Topic.objects.create(subject=subject, board=board, starter=user)
Post.objects.create(message='Lorem ipsum...', topic=topic, created_by=user)
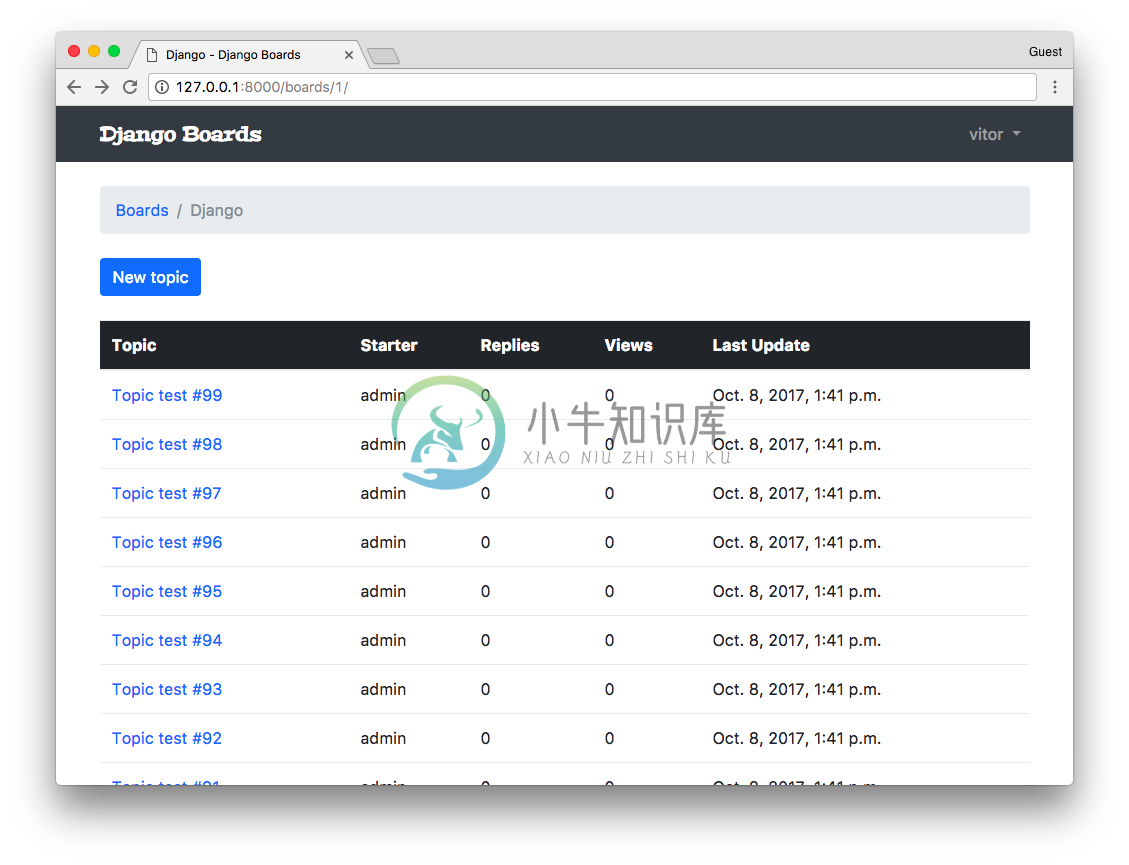
很好,现在我们有一些数据可以玩了。
在我们返回去写代码之前,让我们用 python shell 来做一些更多的实验:
python manage.py shell
from boards.models import Topic
# All the topics in the app
Topic.objects.count()
107
# Just the topics in the Django board
Topic.objects.filter(board__name='Django').count()
104
# Let's save this queryset into a variable to paginate it
queryset = Topic.objects.filter(board__name='Django').order_by('-last_updated')
定义一个你要分页的查询集(QuerySet)的排序是很重要的。否则,会返回给你错误的结果。
现在让我们导入 Paginator 工具:
from django.core.paginator import Paginator paginator = Paginator(queryset, 20)
这里我们告诉Django将查询集按照每页20个元素分页。现在让我们来研究一些 paginator 的属性:
# count the number of elements in the paginator paginator.count 104 # total number of pages # 104 elements, paginating 20 per page gives you 6 pages # where the last page will have only 4 elements paginator.num_pages 6 # range of pages that can be used to iterate and create the # links to the pages in the template paginator.page_range range(1, 7) # returns a Page instance paginator.page(2) <Page 2 of 6> page = paginator.page(2) type(page) django.core.paginator.Page type(paginator) django.core.paginator.Paginator
这里我们必须注意,因为如果我们试图找到一个不存在的页面,分页器会抛出一个异常:
paginator.page(7) EmptyPage: That page contains no results
或者如果我们随意传递进去一个不是页码数字的参数,也会报错:
paginator.page('abc')
PageNotAnInteger: That page number is not an integer
我们必须在设计用户界面时牢记这些细节。
我们来简单看一下 Page 类提供的属性和方法:
page = paginator.page(1) # Check if there is another page after this one page.has_next() True # If there is no previous page, that means this one is the first page page.has_previous() False page.has_other_pages() True page.next_page_number() 2 # Take care here, since there is no previous page, # if we call the method `previous_page_number() we will get an exception: page.previous_page_number() EmptyPage: That page number is less than 1
FBV 分页
这里是我们如何使用 FBV 来实现分页:
boards/views.py 查看完整文件
from django.db.models import Count
from django.core.paginator import Paginator, EmptyPage, PageNotAnInteger
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404, render
from django.views.generic import ListView
from .models import Board
def board_topics(request, pk):
board = get_object_or_404(Board, pk=pk)
queryset = board.topics.order_by('-last_updated').annotate(replies=Count('posts') - 1)
page = request.GET.get('page', 1)
paginator = Paginator(queryset, 20)
try:
topics = paginator.page(page)
except PageNotAnInteger:
# fallback to the first page
topics = paginator.page(1)
except EmptyPage:
# probably the user tried to add a page number
# in the url, so we fallback to the last page
topics = paginator.page(paginator.num_pages)
return render(request, 'topics.html', {'board': board, 'topics': topics})
这部分的实现是使用了 Bootstrap 的四个分页组件来正确的渲染页面。你需要花时间阅读代码,看看它是否适合你。我们在这里使用的是我们之前用过的方法。在这种情况下,topics 不再是一个查询集(QuerySet),而是一个 paginator.page 的实例。
在 topics HTML列表的基础上,我们可以渲染分页组件:
templates/topics.html 查看完整文件
{% if topics.has_other_pages %}
<nav aria-label="Topics pagination" class="mb-4">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if topics.has_previous %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ topics.previous_page_number }}">Previous</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Previous</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% for page_num in topics.paginator.page_range %}
{% if topics.number == page_num %}
<li class="page-item active">
<span class="page-link">
{{ page_num }}
<span class="sr-only">(current)</span>
</span>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_num }}">{{ page_num }}</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% if topics.has_next %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ topics.next_page_number }}">Next</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Next</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
{% endif %}
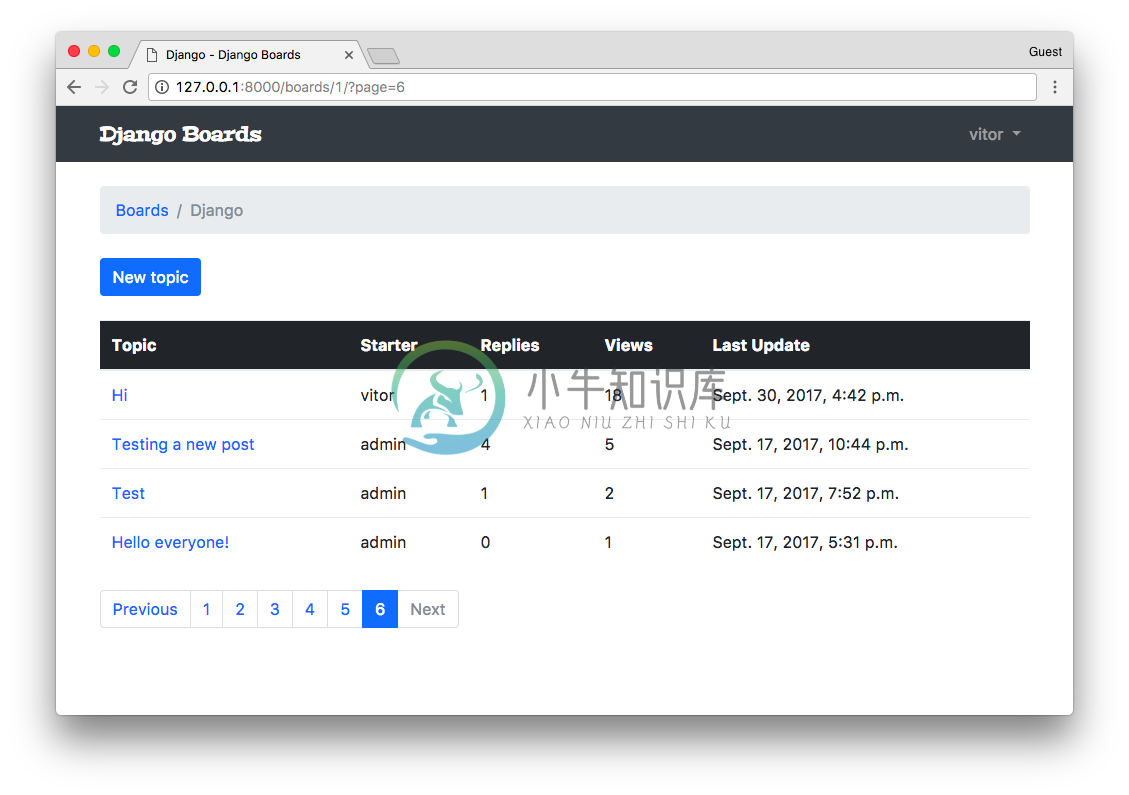
GCBV 分页
下面,相同的实现,但这次使用ListView。
boards/views.py 查看完整文件
class TopicListView(ListView):
model = Topic
context_object_name = 'topics'
template_name = 'topics.html'
paginate_by = 20
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
kwargs['board'] = self.board
return super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
def get_queryset(self):
self.board = get_object_or_404(Board, pk=self.kwargs.get('pk'))
queryset = self.board.topics.order_by('-last_updated').annotate(replies=Count('posts') - 1)
return queryset
在使用基于类的视图分页时,我们与模板中paginator进行交互的方式有点不同。它会在模板中提供以下变量:paginator,page_obj,is_paginated,object_list,还有一个我们在 context_object_name 中定义名字的变量。在我们的例子中,这个额外的变量将被命名为 topics ,并且它将等同于 object_list。
关于这个 get_context_data ,其实,它就是我们在扩展 GCBV 时向请求上下文添加内容的方式。
但这里的主要是 paginate_by 属性。一般情况下,只需添加它就足够了。
要记得更新 urls.py 哦:
myproject/urls.py 查看完整文件
from django.conf.urls import url
from boards import views
urlpatterns = [
# ...
url(r'^boards/(?P<pk>\d+)/$', views.TopicListView.as_view(), name='board_topics'),
]
现在我们来修改一下模板:
templates/topics.html 查看完整文件
{% block content %}
<div class="mb-4">
<a href="{% url 'new_topic' board.pk %}" class="btn btn-primary">New topic</a>
</div>
<table class="table mb-4">
<!-- table content suppressed -->
</table>
{% if is_paginated %}
<nav aria-label="Topics pagination" class="mb-4">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if page_obj.has_previous %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.previous_page_number }}">Previous</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Previous</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% for page_num in paginator.page_range %}
{% if page_obj.number == page_num %}
<li class="page-item active">
<span class="page-link">
{{ page_num }}
<span class="sr-only">(current)</span>
</span>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_num }}">{{ page_num }}</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% if page_obj.has_next %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.next_page_number }}">Next</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Next</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
{% endif %}
{% endblock %}
现在花点时间运行一下测试代码,如果有需要调整的地方就修一下。
boards/tests/test_view_board_topics.py
from django.test import TestCase
from django.urls import resolve
from ..views import TopicListView
class BoardTopicsTests(TestCase):
# ...
def test_board_topics_url_resolves_board_topics_view(self):
view = resolve('/boards/1/')
self.assertEquals(view.func.view_class, TopicListView)
可复用的分页模板
就像我们在 form.html 中封装模板时做的一样,我们也可以为分页的HTML代码片创建类似的东西。
我们来对主题帖子页面进行分页,进而找到一种复用分页组件的方法。
boards/views.py 查看完整文件
class PostListView(ListView):
model = Post
context_object_name = 'posts'
template_name = 'topic_posts.html'
paginate_by = 2
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
self.topic.views += 1
self.topic.save()
kwargs['topic'] = self.topic
return super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
def get_queryset(self):
self.topic = get_object_or_404(Topic, board__pk=self.kwargs.get('pk'), pk=self.kwargs.get('topic_pk'))
queryset = self.topic.posts.order_by('created_at')
return queryset
更新一下 url.py [查看完整文件]
from django.conf.urls import url
from boards import views
urlpatterns = [
# ...
url(r'^boards/(?P<pk>\d+)/topics/(?P<topic_pk>\d+)/$', views.PostListView.as_view(), name='topic_posts'),
]
现在,我们从topics.html模板中获取分页部分的html代码片,并在 templates/includes 文件夹下面创建一个名为 pagination.html 的新文件,和 forms.html 同级目录:
myproject/ |-- myproject/ | |-- accounts/ | |-- boards/ | |-- myproject/ | |-- static/ | |-- templates/ | | |-- includes/ | | | |-- form.html | | | +-- pagination.html <-- here! | | +-- ... | |-- db.sqlite3 | +-- manage.py +-- venv/
templates/includes/pagination.html
{% if is_paginated %}
<nav aria-label="Topics pagination" class="mb-4">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if page_obj.has_previous %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.previous_page_number }}">Previous</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Previous</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% for page_num in paginator.page_range %}
{% if page_obj.number == page_num %}
<li class="page-item active">
<span class="page-link">
{{ page_num }}
<span class="sr-only">(current)</span>
</span>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_num }}">{{ page_num }}</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% if page_obj.has_next %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.next_page_number }}">Next</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="page-item disabled">
<span class="page-link">Next</span>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
{% endif %}
现在,我们在 topic_posts.html 文件中来使用它:
templates/topic_posts.html 查看完整文件
{% block content %}
<div class="mb-4">
<a href="{% url 'reply_topic' topic.board.pk topic.pk %}" class="btn btn-primary" role="button">Reply</a>
</div>
{% for post in posts %}
<div class="card {% if forloop.last %}mb-4{% else %}mb-2{% endif %} {% if forloop.first %}border-dark{% endif %}">
{% if forloop.first %}
<div class="card-header text-white bg-dark py-2 px-3">{{ topic.subject }}</div>
{% endif %}
<div class="card-body p-3">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-2">
<img src="{% static 'img/avatar.svg' %}" alt="{{ post.created_by.username }}" class="w-100">
<small>Posts: {{ post.created_by.posts.count }}</small>
</div>
<div class="col-10">
<div class="row mb-3">
<div class="col-6">
<strong class="text-muted">{{ post.created_by.username }}</strong>
</div>
<div class="col-6 text-right">
<small class="text-muted">{{ post.created_at }}</small>
</div>
</div>
{{ post.message }}
{% if post.created_by == user %}
<div class="mt-3">
<a href="{% url 'edit_post' post.topic.board.pk post.topic.pk post.pk %}"
class="btn btn-primary btn-sm"
role="button">Edit</a>
</div>
{% endif %}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% include 'includes/pagination.html' %}
{% endblock %}
别忘了修改主循环为 {% for post in posts %}。
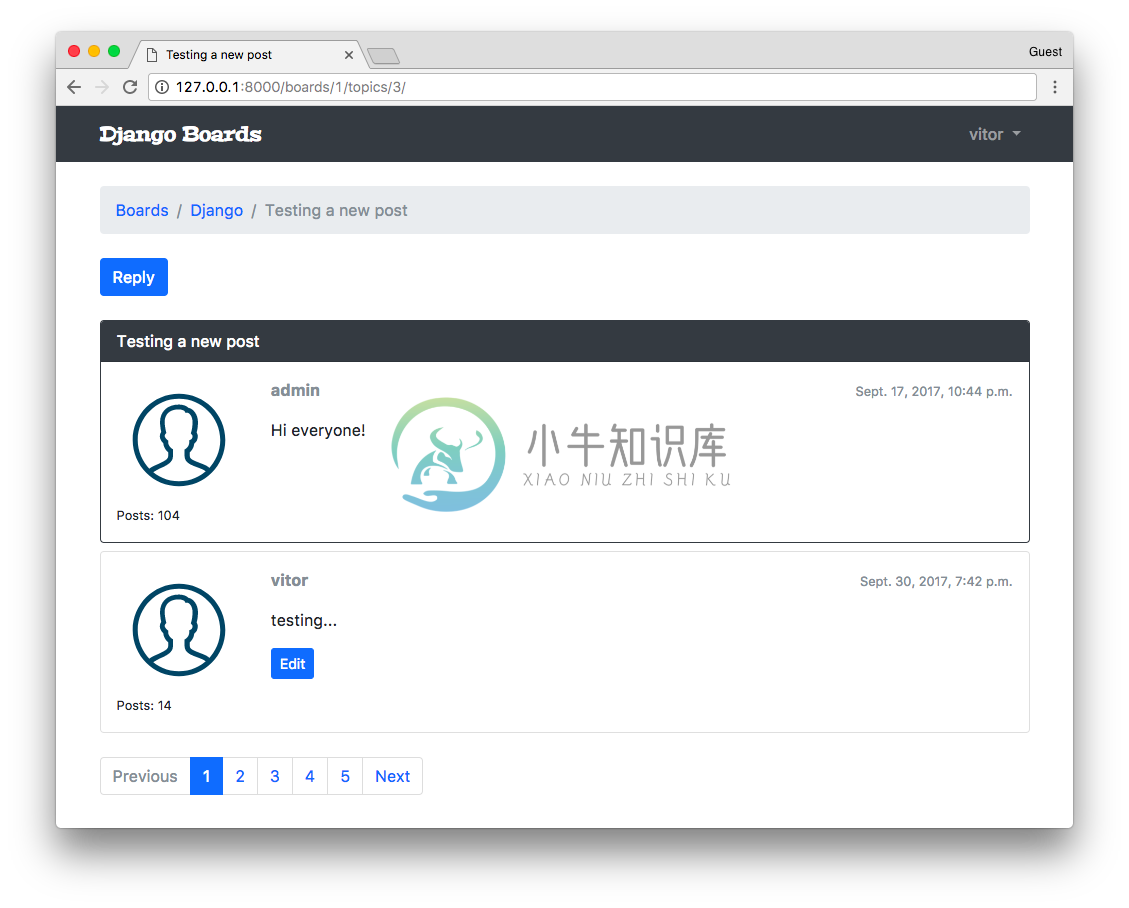
我们同样也可以更新一下先前的模板,topics.html 模板同样也可以这个封装的分页模板。
templates/topics.html 查看完整文件
{% block content %}
<div class="mb-4">
<a href="{% url 'new_topic' board.pk %}" class="btn btn-primary">New topic</a>
</div>
<table class="table mb-4">
<!-- table code suppressed -->
</table>
{% include 'includes/pagination.html' %}
{% endblock %}
为了测试目的,你需要添加一些帖子(或者通过 python shell 去创建),然后修改代码中的 paginate_by 到一个较小的数字,比如 2 ,然后看看页面会发生什么变化。
更新一下测试用例:
boards/tests/test_view_topic_posts.py
from django.test import TestCase
from django.urls import resolve
from ..views import PostListView
class TopicPostsTests(TestCase):
# ...
def test_view_function(self):
view = resolve('/boards/1/topics/1/')
self.assertEquals(view.func.view_class, PostListView)

