模板(Templating)
帕格是Express的模板引擎。 模板引擎用于通过HTML消除我们的服务器代码的混乱,将字符串与现有的HTML模板串联起来。 帕格是一个非常强大的模板引擎,具有各种功能,包括filters, includes, inheritance, interpolation等。有很多地面可以覆盖。
要使用Pug with Express,我们需要安装它,
npm install --save pug
现在安装了Pug,将其设置为应用程序的模板引擎。 你不需要“要求”它。 将以下代码添加到index.js文件中。
app.set('view engine', 'pug');
app.set('views','./views');
现在创建一个名为views的新目录。 在里面创建一个名为first_view.pug的文件,并在其中输入以下数据。
doctype html
html
head
title = "Hello Pug"
body
p.greetings#people Hello World!
要运行此页面,请将以下路由添加到您的应用程序 -
app.get('/first_template', function(req, res){
res.render('first_view');
});
您将获得输出 - Hello World! 帕格将这个非常简单的标记转换为HTML。 我们不需要跟踪关闭我们的标签,也不需要使用class和id关键字,而是使用'。' 和'#'来定义它们。 上面的代码首先被转换为 -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello Pug</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class = "greetings" id = "people">Hello World!</p>
</body>
</html>
Pug能够做的不仅仅是简化HTML标记。
帕格的重要特征
现在让我们探讨一下帕格的一些重要特征。
简单标签
标签根据其缩进嵌套。 就像在上面的例子中一样, 《title》在《head》标签中缩进,因此它位于其中。 但是《body》标签是在同一个缩进上,所以它是《head》标签的兄弟。
我们不需要关闭标签,只要Pug遇到相同或外部缩进级别的下一个标签,它就会为我们关闭标签。
要将文本放在标记内,我们有3种方法 -
Space seperated
h1 Welcome to Pug
Piped text
div
| To insert multiline text,
| You can use the pipe operator.
Block of text
div.
But that gets tedious if you have a lot of text.
You can use "." at the end of tag to denote block of text.
To put tags inside this block, simply enter tag in a new line and
indent it accordingly.
注释 (Comments)
Pug使用与JavaScript(//)相同的语法来创建注释。 这些注释转换为html注释(“! - comment--”)。 例如,
//This is a Pug comment
此评论将转换为以下内容。
<!--This is a Pug comment-->
属性 (Attributes)
为了定义属性,我们在括号中使用逗号分隔的属性列表。 类和ID属性具有特殊表示。 以下代码行包括定义给定html标记的属性,类和ID。
div.container.column.main#division(width = "100", height = "100")
这行代码转换为以下内容。 -
<div class = "container column main" id = "division" width = "100" height = "100"></div>将值传递给模板
当我们渲染Pug模板时,我们实际上可以从路由处理程序中传递一个值,然后我们可以在模板中使用它。 使用以下内容创建新的路由处理程序。
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/dynamic_view', function(req, res){
res.render('dynamic', {
name: "xnip",
url:"https://www.xnip.cn"
});
});
app.listen(3000);
并在views目录中创建一个名为dynamic.pug的新视图文件,其代码如下 -
html
head
title=name
body
h1=name
a(href = url) URL
在浏览器中打开localhost:3000/dynamic_view; 你应该得到以下输出 -
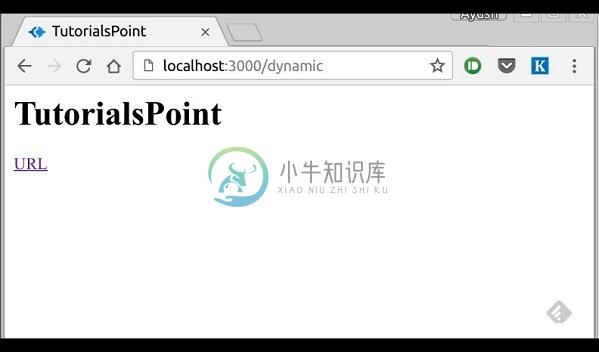
我们也可以在文本中使用这些传递的变量。 要在标记文本之间插入传递的变量,我们使用#{variableName}语法。 例如,在上面的例子中,如果我们想从xnip中提出问候语,那么我们就可以完成以下操作。
html
head
title = name
body
h1 Greetings from #{name}
a(href = url) URL
这种使用值的方法称为interpolation 。 上面的代码将显示以下输出。 -

条件(Conditionals)
我们也可以使用条件语句和循环结构。
考虑以下 -
如果用户已登录,则页面应显示"Hi, User" ,如果没有,则显示"Login/Sign Up"链接。 为此,我们可以定义一个简单的模板,如 -
html
head
title Simple template
body
if(user)
h1 Hi, #{user.name}
else
a(href = "/sign_up") Sign Up
当我们使用我们的路线渲染时,我们可以传递一个对象,如下面的程序 -
res.render('/dynamic',{
user: {name: "Ayush", age: "20"}
});
你会收到一条消息 - Hi, Ayush 。 但是如果我们没有传递任何对象或传递没有用户密钥的对象,那么我们将获得一个注册链接。
包含和组件
Pug提供了一种非常直观的方式来为网页创建组件。 例如,如果您看到新闻网站,则标识和类别的标题始终是固定的。 我们可以使用include功能,而不是将其复制到我们创建的每个视图。 以下示例显示了我们如何使用此功能 -
使用以下代码创建3个视图 -
HEADER.PUG
div.header.
I'm the header for this website.
CONTENT.PUG
html
head
title Simple template
body
include ./header.pug
h3 I'm the main content
include ./footer.pug
FOOTER.PUG
div.footer.
I'm the footer for this website.
为此创建一个路由如下 -
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/components', function(req, res){
res.render('content');
});
app.listen(3000);转到localhost:3000/components,您将收到以下输出 -
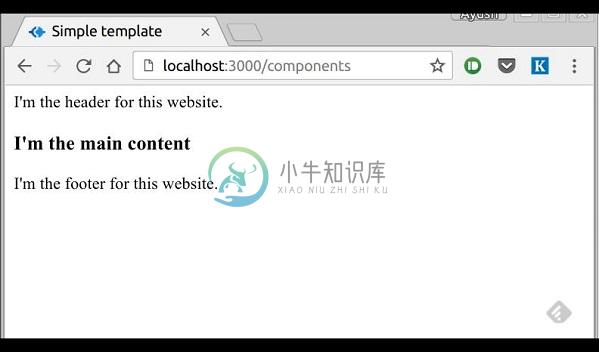
include也可以用于包括明文,CSS和JavaScript。

