使用Python
通过使用Python操控Codey Rocky,您可以:
- 和实物结合,更有趣地学习Python
- 比拖放语句块更方便地编写有一定规模的代码,比如实现算法
- 使用积木式编程很难做到的事情,比如使用字典等数据结构
为Codey写的Python程序,一定要上传到Codey之后才能生效。
开始使用Python
通过将和脚本区上方的编程方式从“语句块”切换成“Python”即可开始编写Python。

注意:请确保标签选中的是“设备”,角色选择的是”程小奔“。
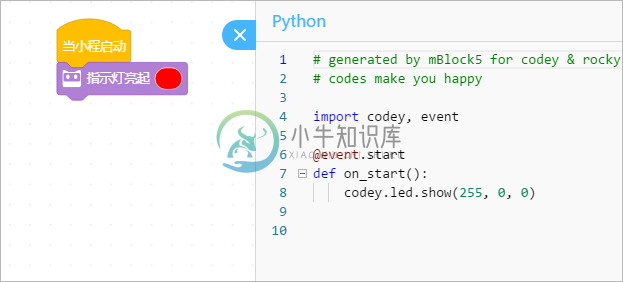
下面是一段简单的示例代码:
import codey
import rocky
import time
import event
@event.start
def on_start():
codey.led.show(255,0,0)
rocky.forward(50,1)
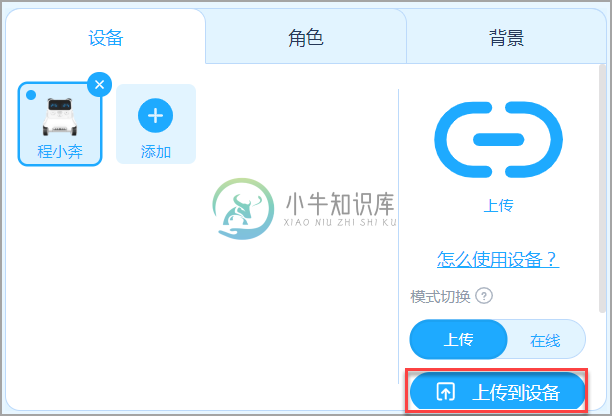
代码编写完成之后,点击“上传到设备”,编写的Python代码就会执行。
将积木块转换为Python
在脚本区,点击  将积木块转换为Python。如下示例:
将积木块转换为Python。如下示例:
在表情面板(点阵)上显示内容
display.show(文字内容,wait)
将文字内容显示在Codey的表情面板上。
codey.display.show("hello world", wait=False)
codey.display.show(3.14, wait=False)
codey.display.show("14:02", wait=False)
display.show_image(点阵像素内容, 时间)
将一个点阵图案显示在Codey的表情面板上。 如果时间不为0, 则显示相应时间后点阵熄灭.
codey.display.show_image("00003c7e7e3c000000003c7e7e3c0000", time_s=1)
display.show_image(点阵像素内容, x, y)
在指定的x, y坐标处显示点阵内容。
codey.display.show_image("000c18181c0c000000000c1c18180c00", 0, 0)
# 在屏幕的左上角显示一个笑脸
codey.display.set_pixel(x, y, status) / codey.display.toggle_pixel(x, y)
- set_pixel: 点亮或熄灭点阵上某个位置(x, y)的像素;“True”为点亮,“False”为熄灭;
- toggle_pixel: 反转某个位置(x, y)的像素:如果是灭的则点亮,如果是亮的则点灭。
codey.display.set_pixel(5, 5, True) # 点亮坐标为(5, 5)处的像素
codey.display.set_pixel(5, 5, False) # 熄灭坐标为(5, 5)处的像素
codey.display.toggle_pixel(5, 5) # 将(5, 5)处的像素反转。现在是灭的,所以结果会是亮的
display.get_pixel(x, y)
检查Codey的指定像素处是否点亮:如果点亮则返回True, 反之False。
print(codey.display.get_pixel(5, 5)) # 如果已经点亮,输出True
display.clear()
清空表情面板上所有的显示内容。
codey.display.clear() # 熄灭表情面板
使用Codey的指示灯
led.show(r, g, b, 时间)
将Codey指示灯设置为指定颜色。
如果“时间”参数不为0,则在指定秒数后熄灭。
codey.led.show(255, 255, 0, 1) # 设置颜色,在1秒后熄灭
codey.led.show(255, 0, 0) # 设置指示灯为红色,不熄灭
led_off()
熄灭Codey的指示灯。
codey.led_off() # 熄灭指示灯
led.set_red(值) / led.set_green(值) / led.set_blue(值)
独立设置Codey指示灯的红绿蓝数值,取值范围为 0-255。
codey.led.set_red(255)
codey.led.set_green(255)
codey.led.set_blue(255)
让Codey发出声音
speaker.play_melody(声音名)
播放Codey内存储的指定声音文件。
codey.speaker.play_melody("meow")
codey.speaker.play_melody("meow.wav") # 是否带.wav,效果是一样的
可选声音文件:
hello.wav: 哈喽hi.wav: 嗨bye.wav: 拜yeah.wav: 耶wow.wav: 哇哦laugh.wav: 笑声hum.wav: 哼唱sad.wav: 难过sigh.wav: 叹气annoyed.wav: 哼!angry.wav: 生气surprised.wav: 惊吓yummy.wav: 撒娇curious.wav: 好奇embarrassed.wav: 尴尬ready.wav: 准备sprint.wav: 冲刺sleepy.wav: 打呼meow.wav: 喵start.wav: 启动switch.wav: 开关beeps.wav: 哔哔buzzing.wav: 蜂鸣exhaust.wav: 排气explosion.wav: 爆炸gotcha.wav: 获取hurt.wav: 痛苦jump.wav: 跳动laser.wav: 激光level up.wav: 升级low energy.wav: 低能量metal clash.wav: 金属音prompt tone.wav: 提示right.wav: 正确wrong.wav: 错误ring.wav: 铃声score.wav: 得分shot.wav: 发射step_1.wav: 脚步声1step_2.wav: 脚步声2wake.wav: 激活warning.wav: 警告
speaker.play_note(音符, 拍数)
让Codey播放一个音符,并持续指定拍数。
音符编号指音符的Midi编号,也可以使用"c3"(第三级do), "d4"(第四级re)这样的音符名称。不正确的音符名称会报错。
codey.speaker.play_note(36, 1)
codey.speaker.play_note('c3', 0.25)
speaker.play_tone(频率, 拍数)
让Codey播放指定频率的音调,并持续一定拍数。
codey.speaker.play_tone(700, 1)
speaker.rest(拍数)
让Codey暂停播放指定拍数,相当于音乐中的休止符。
codey.speaker.rest(0.25)
speaker.stop_sounds()
让Codey停止播放一切声音
codey.speaker.stop_sounds()
speaker.volume
设置Codey的音量大小,也可读取当前音量值。
codey.speaker.volume = (70) # 将Codey的音量设置为70%
print(codey.speaker.volume) # 输出当前音量大小
使用Codey的内置传感器
button_a.is_pressed()/button_b.is_pressed()/button_c.is_pressed()
如果指定按钮被按下,返回True; 否则返回False
print(codey.button_a.is_pressed()) # 当按钮A被按下时输出True
potentiometer.get_value()
获得齿轮电位器的位置,范围是0-100。
print(codey.potentiometer.get_value()) # 输出现在电位器的0-100的位置
sound_sensor.get_loudness()
获得声音传感器感受到环境音量的大小,范围是0-100。
print(codey.sound_sensor.get_loudness()) # 输出现在环境音量的大小
light_sensor.get_value()
获得Codey光线传感器的数值,范围是0-100。数字越大环境光越亮
print(codey.light_sensor.get_value()) # 输出现在环境光线强度
motion_sensor.is_shaked()
获得Codey当前是否被摇晃,结果是True或者False。
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_shaked()) # 如果Codey正在被摇晃,输出True
motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()/motion_sensor.is_tilted_right()/
motion_sensor.is_ears_up()/motion_sensor.is_ears_down()
获得Codey当前是否向某个方向(左、右)倾斜,或是否正面朝上、下。结果是True或者False。
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()) # 如果Codey正在向左倾斜,输出True
print(codey.motion_sensor.is_ears_up()) # 如果Codey正面朝上,输出True
陀螺仪:gyroscope
可以获得陀螺仪的偏转角,翻滚角和俯仰角:
- motion_sensor.get_roll()
- motion_sensor.get_pitch()
- motion_sensor.get_yaw()
可以使用gyro.rotation获得陀螺仪绕某一坐标轴旋转的角度:
- motion_sensor.get_rotation(axis): 绕x、y、z轴旋转的角度;
- motion_sensor.reset_rotation(axis="all"):重置陀螺仪旋转角度
可以使用motion_sensor.get_shake_strength()获得陀螺仪被摇晃的强度(范围0-100)。
print("俯仰和偏转角:", codey.motion_sensor.get_yaw(), codey.motion_sensor.get_pitch()) # 输出陀螺仪的俯仰和偏转角
print("陀螺仪绕3轴旋转角:", codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(x), codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(y), codey.motion_sensor.get_rotation(z))
codey.motion_sensor.reset_rotation(axis="all") # 重置旋转角
print("摇晃力度:", motion_sensor.get_shake_strength())
get_timer()
获得计数器的值(距启动或上次归零经过的秒数)。
print(codey.get_timer()) # 输出距启动或上次归零经过的秒数
reset_timer()
将计数器归零。
codey.reset_timer() # 先归零计数器
print(codey.get_timer()) # 应该输出0
Codey的事件和执行控制
Codey支持事件(比如当按钮被按下)触发代码,也支持多线程。这是Codey和市面上其他机器人的主控的一个显著不同。
如要使用事件,需要先定义一个事件处理函数,然后将它分配到相应的事件上。
TODO: 一个程序最多同时执行N个事件
比如:
def on_button_a_pressed(): # 先定义一个函数,作为按钮A被按下的事件
print("A按钮被按下!")
codey.on_button_a_pressed() # 然后将该函数分配到“按钮A被按下”的事件中
按钮被按下:on_button_a_pressed()/on_button_b_pressed()/on_button_c_pressed()
当按钮被按下时,调用处理函数。
def on_button_b_pressed():
print("B按钮被按下!")
codey.on_button_b_pressed()
当摇晃小程:on_shaked
当小程摇晃时,调用处理函数。
def on_shaked():
print("我被摇晃了!")
codey.on_shaked()
当左倾斜小程:on_tilted_left()
当小程向左倾斜时,调用处理函数。
def on_tilted_left():
print("我被左倾!")
codey.on_tilted_left()
当声音大于:on_greater_than(响度, 'sound_sensor')
当声音传感器的音量大于特定数值时,触发处理函数。
def on_greater_than():
print("音量大于50,太吵了!")
codey.on_greater_than(50, 'sound_sensor')
当光线小于:on_less_than(光线, 'light_sensor')
当光线传感器的光线强度小于特定数值时,触发处理函数。
def on_less_than():
print("光线小于30,太暗了!")
codey.on_less_than(30, 'light_sensor')
当收到消息:on_received(消息名)
当收到Scratch消息为指定名称的广播时,触发处理函数。
def on_received():
print("游戏开始!")
codey.on_received('game_start')
广播消息:broadcast(消息名)
向舞台和硬件角色广播某种消息。
codey.broadcast('game_start')
stop_all_scripts()/stop_this_script()/stop_other_scripts()
停止全部脚本,该脚本,或其他脚本。
codey.stop_all_scripts() # 停止全部脚本
让Rocky动起来
forward(速度, 时间)
让Rocky以指定速度向前运动指定时间。如果不设置时间则一直运动下去。速度的范围是0-100。
rocky.forward(50, 1) # 以50的速度向前运动1秒
rocky.forward(100) # 以最高速度100一直前进下去,直到停止
backward(速度, 时间)
让Rocky以指定速度向后运动指定时间。如果不设置时间则一直运动下去。速度的范围是0-100.
rocky.backward(50, 1) # 以50的速度向后运动1秒
rocky.backward(100) # 以最高速度100一直后退下去,直到停止
turn_right(速度, 时间)
让Rocky以指定速度右转指定时间。如果不设置时间则一直运动下去
速度的范围是0-100。
rocky.turn_right(50, 1) # 以50的速度右转,持续1秒
rocky.turn_right(100) # 以最高速度100一直向右旋转
turn_left(速度, 时间)
让Rocky以指定速度左转指定时间。如果不设置时间则一直运动下去
速度的范围是0-100
rocky.turn_left(50, 1) # 以50的速度左转,持续1秒
rocky.turn_left(100) # 以最高速度100一直向左旋转
turn_right_by_degree(角度)
让Rocky右转指定角度,直到运动结束。
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(90) # 右转90度,直到完成
turn_left_by_degree(角度)
让Rocky左转指定角度,直到运动结束。
rocky.turn_right_by_degree(90) # 左转90度,直到完成
drive(左轮动力, 右轮动力)
同时设置Rocky左轮和右轮的动力参数。
rocky.drive(50, 50) # 将两个轮子的速度同时设为50
stop()
停止Rocky轮子的运动。
rocky.stop() # 让Rocky的运动停止
使用Rokey底盘上的传感器和指示灯
color_ir_sensor.set_led_color(颜色)
设置底部传感器LED灯的颜色。颜色只能在"red", "green", "blue", "yellow", "purple", "cyan", "white", "black"之中选。选择“black”关闭LED灯。
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led("red")
rocky.color_ir_sensor.set_led("black")
color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead()
得知前方是否有障碍物,结果是True或者False(Rokey底盘传感器必须朝前)。
print(rocky.color_ir_sensor.is_obstacle_ahead())
底盘传感器:color_ir_sensor
使用color_ir_sensor可以获得底盘传感器的一系列信息:
- color_ir_sensor.get_light_strength(): 获得环境光强度,范围是0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_light(): 获得反射光强度,范围是0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_infrared(): 获得红外线反射光强度,范围是0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_greyness(): 获得反射灰度值,范围是0-100
- color_ir_sensor.get_red(): 获得检测到的红色值,范围是0-255
- color_ir_sensor.get_green(): 获得检测到的绿色值,范围是0-255
- color_ir_sensor.get_blue(): 获得检测到的蓝色值,范围是0-255
- color_ir_sensor.is_color(color_str): 获取颜色传感器读到的颜色是否为指定颜色,返回True或False。其中颜色名需要是"red", "green", "blue", "yellow", "purple", "cyan", "white", "black"其中之一
print("环境和反射光: ",color_ir_sensor.get_light_strength(), color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_light())
print("红外反射光: ", color_ir_sensor.get_reflected_infrared())
print("灰度值: ", color_ir_sensor.get_greyness())
print("红绿蓝: ", color_ir_sensor.get_red(), color_ir_sensor.get_green(), color_ir_sensor.get_blue())
print("是否为红色? ", color_ir_sensor.is_color("red"))
使用红外通信
小程可以接收和发送红外信号
ir_send(字符串信息)
使用红外发射器发射一段字符串信息。另一台小程可以使用ir_receive接收这样的信息。
codey.ir_send("A")
ir_receive()
使用红外接收器接收一条红外线信息。会返回接收到的字符串数据
codey.show(codey.ir_receive())

