Java 线程通信
精华
小牛编辑
117浏览
2023-03-14
1 什么是Java线程通信
线程间通信或协作就是允许同步线程彼此通信。
线程间通信是一种机制,其中一个线程在其关键部分中暂停运行,并允许另一个线程进入(或锁定)在同一关键部分中执行,这是通过以下Object类的方法实现的:
- wait()
- notify()
- notifyAll()
1.1 wait()方法
使当前线程释放锁定,并等待直到另一个线程为此对象调用notify()方法或notifyAll()方法,或者经过了指定的时间。
当前线程必须拥有此对象的监视器,因此只能从同步方法中调用它,否则它将引发异常。
| 构造方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public final void wait()throws InterruptedException | 等待直到对象被通知。 |
| public final void wait(long timeout)throws InterruptedException | 等待指定的时间。 |
1.2 notify()方法
唤醒正在此对象的监视器上等待的单个线程。如果有任何线程在该对象上等待,则选择其中一个唤醒。该选择是任意的,并且可以根据实现情况进行选择。语法为:
public final void notify()
1.3 notifyAll()方法
唤醒正在此对象的监视器上等待的所有线程。语法为:
public final void notifyAll()
2 线程间通信的过程分析
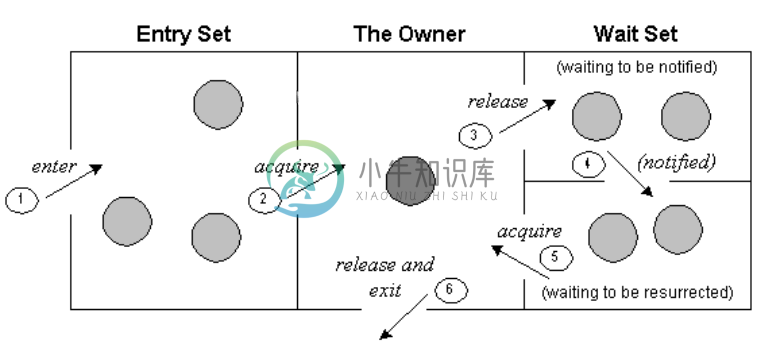
对上图的每个点的解释如下:
- 线程进入以获取锁。
- 锁是通过线程获取的。
- 如果您在对象上调用wait(()法,线程将进入等待状态。否则,它将释放锁定并退出。
- 如果调用notify() 或notifyAll()方法,线程将转到已通知状态(可运行状态)。
- 现在可以使用线程来获取锁。
- 任务完成后,线程释放锁定并退出对象的监视状态。
3 线程间通信的疑问
问题:为什么在是在Object类上调用类wait(),notify()和notifyAll()方法,而不是Thread类上调用?
答案:这是因为这些方法与锁相关,并且对象具有锁。
4 wait()和sleep()的区别
| wait()方法 | sleep()方法 |
|---|---|
| wait()方法会释放锁 | sleep()方法不会释放锁。 |
| Object类的方法 | Thread类的方法 |
| 是非static静态方法 | 是static静态方法 |
| 通过notify()或notifyAll()方法唤醒 | 在指定的时间后,睡眠完成。 |
5 Java线程通信的例子
让我们看一下线程间通信的简单示例。
package cn.xnip;
/**
* 小牛知识库网: https://www.xnip.cn
*/
/**
* Java线程通信的例子
*/
class Customer{
int amount=10000;
synchronized void withdraw(int amount){
System.out.println("going to withdraw...");
if(this.amount<amount){
System.out.println("Less balance; waiting for deposit...");
try{wait();}catch(Exception e){}
}
this.amount-=amount;
System.out.println("withdraw completed...");
}
synchronized void deposit(int amount){
System.out.println("going to deposit...");
this.amount+=amount;
System.out.println("deposit completed... ");
notify();
}
}
class Demo{
public static void main(String args[]){
final Customer c=new Customer();
new Thread(){
public void run(){c.withdraw(15000);}
}.start();
new Thread(){
public void run(){c.deposit(10000);}
}.start();
}
}
输出结果为:
going to withdraw...
Less balance; waiting for deposit...
going to deposit...
deposit completed...
withdraw completed...
