从矩阵的一点移动到零的位置

这是我的代码,它不起作用:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class A2Rcs {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\nEnter board size: ");
int size = input.nextInt();
int[][]board = new int[size][size];
for (int i = 0; i<size; i++) {
System.out.println("\nEnter the row: ");
for (int j = 0; j<size; j++) {
board[i][j] = input.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("\nData you entered: ");
for(int x = 0; x< size; x++){
for(int y = 0 ; y< size; y++){
System.out.print(board[x][y]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\nEnter starting position: ");
int p1 = input.nextInt();
int p2 = input.nextInt();
if (magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size))
System.out.println("Solvable");
}
public static Boolean magicBoard(int p1, int p2, int[][] board, int size) {
boolean result = false;
int temp;
while(!result) {
if(board[p1][p2] == 0) {
System.out.println("Reached 0.");
result = true;
break;
}
//can only down
if((p1+board[p1][p2]) < size && (p1-board[p1][p2]) < 0 && ((p2+board[p1][p2]) > size && (p2-board[p1][p2]) < 0)) {
temp = board[p1+board[p1][p2]][p2];
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
result = false;
break;
}
// If don't go back and forth, then we continue
else {
p1 = p1+board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move south " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
//can only up
else if((p1+board[p1][p2]) > size && (p1-board[p1][p2]) > 0 && ((p2+board[p1][p2]) > size && (p2-board[p1][p2]) < 0)){
temp = board[p1-board[p1][p2]][p2];
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
result = false;
break;
}
else {
p1 = p1-board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move north " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
//can only up right
else if((p2+board[p1][p2])<size && (p2-board[p1][p2])<0 && ((p1+board[p1][p2])>size && (p1-board[p1][p2])<0)) {
temp = board[p1][p2+board[p1][p2]];
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
result = false;
break;
}
else {
p2 = p2+board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move east " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
//can only left
else if((p2+board[p1][p2]) > size && (p2-board[p1][p2])> 0 && ((p1+board[p1][p2])>size && (p1-board[p1][p2])<0)) {
temp = board[p1][p2-board[p1][p2]];
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
result = false;
break;
}
else {
p2 = p2-board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move west " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
// can any direction
else {
// try moving south
SOUTH:
if(p1-board[p1][p2] < 0 && p1-board[p1][p2] > -size) {
temp = board[p1+board[p1][p2]][p2];
// Verify if we go back and forth if we go south, if we do, then we the result will be
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
break SOUTH;
}
else {
p1 = p1+board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move south " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
NORTH:
if(p1-board[p1][p2] > 0 && p1-board[p1][p2] < size) {
temp = board[p1-board[p1][p2]][p2];
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
break NORTH;
}
else {
p1 = p1-board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move north " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
// try moving east
EAST:
if(p2-board[p1][p2] < 0 ) {
temp = board[p1][p2+board[p1][p2]];
// If will go back and forth at that position, then we exit the EAST label and we go to the next label
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
break EAST;
}
else {
p2 = p2+board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move east " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
// Try moving west
WEST:
if(p2-board[p1][p2] > 0) {
temp = board[p1][p2-board[p1][p2]];
// If we go back and forth in that position, then we exit the EAST label
if(board[p1][p2] == temp) {
System.out.print("The MagicBoard is unsolvable");
result = false;
break WEST;
}
else {
p2 = p2-board[p1][p2];
System.out.print("Move west " + board[p1][p2] + ", ");
magicBoard(p1, p2, board, size);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
我已经做了一个星期了,还是搞不清楚。我不确定在这里发布是否合适,但欢迎任何形式的帮助。

共有2个答案
该搜索是一种经典的宽度优先搜索(BFS),可以通过递归BFS求解
下面是MagicBoard的BFS解决方案的mre(1):
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class A2Rcs {
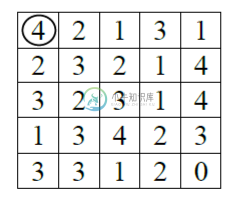
private static int[][] board1 = {//test case 1
{4, 2, 1, 3, 1},
{2, 3, 2, 1, 4},
{3, 2, 3, 1, 4},
{1, 3, 4, 2, 3},
{3, 3, 1, 2, 0}
};
private static int[][] board2 = {//test case 2
{1, 4, 1, 3, 1},
{4, 3, 2, 1, 4},
{3, 2, 3, 1, 4},
{1, 3, 4, 2, 3},
{3, 4, 1, 2, 0}
};
private static boolean[][] visited; //mark visited nodes
//bfs uses queue. In this case each entry (List) in the queue represents an entire path.
//such path is represented by a list of row, column pairs
private static Queue<List<int[]>> queue;
public static void main(String[] args) {
magicBoard(0, 0, board1);
magicBoard(0, 0, board2);
}
public static Boolean magicBoard(int row, int col, int[][] board) {
List<int[]> path = new ArrayList<>(); //construct an empty path
path.add(new int[]{row,col}); //add starting point to the path
queue = new LinkedList<>(); //initialize queue
queue.add(path);//add path to queue
visited = new boolean[board.length][board[0].length]; //initialize visited
for (int i=0; i<visited.length ; i++){
for (int j=0; j<visited[0].length ; j++){
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
visited[row][col] = true;//mark origin as visited
boolean result = magicBoardBFS(board); //run search
if (! result) {
System.out.println("\nPath not found.");
}
return result;
}
public static Boolean magicBoardBFS(int[][] board) {
List<int[]>path = queue.poll(); //pull head (first entered) entry from queue
if(path == null) return false; //no more entries to process and target not found so return false
if(targetFound(board, path)) return true; //check if target reached
int[] rowColumnPair = path.get(path.size()-1); //last row, col pair in path
//get next reachable positions
List<int[]>neighbors = getNeighbors(board, rowColumnPair[0], rowColumnPair[1]);
//add neighbors to queue
for(int[] rowColPair : neighbors){
List<int[]>newPath = new ArrayList<>(path); //copy path
//and neighbor (next reachable position) to the path
newPath.add(rowColPair);
queue.add(newPath); //add new path to queue
}
return magicBoardBFS(board);
}
//check if last pair in path is the target
private static boolean targetFound(int[][] board,List<int[]>path ) {
int[] rowColPair = path.get(path.size()-1); //last row, col pair in path
int row = rowColPair[0], col = rowColPair[1];
if(board[row][col] == 0 ){//target found
System.out.println("Path found: ");
printPath(path);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static List<int[]> getNeighbors(int[][] board, int row, int col) {
List<int[]>neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
int move = board[row][col];
//todo : assert that move is > 0
int[][] newRowColPairs = {{row + move, col},{row - move, col}, {row , col + move},{row , col - move} };
for(int[] rowColPair: newRowColPairs){
int newRow = rowColPair[0], newCol =rowColPair[1];
if(newRow < board.length && newRow >= 0
&& newCol < board[0].length && newCol >=0) { //valid row col
if(!visited[newRow][newCol]) { //unvisited
neighbors.add(new int[]{newRow, newCol});
visited[newRow][newCol] = true;
}
}
}
return neighbors;
}
private static void printPath(List<int[]> path) {
if(path == null) return;
for(int[] rowColPair : path){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(rowColPair) +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
我们可以编写更少的代码,这将使我们更容易思考和考虑其逻辑。首先,很明显,我们不需要访问一个牢房不止一次。我们可以使用回溯例程,标记和取消标记访问的单元格。我不精通Java,所以我希望这个JavaScript代码易于翻译:
js prettyprint-override">function backtrack(M, i, j, visited){
// Reached the goal!
if (M[i][j] == 0)
return true;
const d = M.length;
const move = M[i][j];
// Try visiting all directions
if (i + move < d && !visited[i + move][j]){
visited[i + move][j] = true;
if (backtrack(M, i + move, j, visited))
return true;
visited[i + move][j] = false;
}
if (i - move >= 0 && !visited[i - move][j]){
visited[i - move][j] = true;
if (backtrack(M, i - move, j, visited))
return true;
visited[i - move][j] = false;
}
if (j + move < d && !visited[i][j + move]){
visited[i][j + move] = true;
if (backtrack(M, i, j + move, visited))
return true;
visited[i][j + move] = false;
}
if (j - move >= 0 && !visited[i][j - move]){
visited[i][j - move] = true;
if (backtrack(M, i, j - move, visited))
return true;
visited[i][j - move] = false;
}
return false;
}
function f(M, start_i, start_j){
const d = M.length;
const visited = new Array(d);
for (let i=0; i<d; i++)
visited[i] = new Array(d).fill(false);
visited[start_i][start_j] = true;
return backtrack(M, start_i, start_j, visited);
}
var board_1 = [
[4, 2, 1, 3, 1],
[2, 3, 2, 1, 4],
[3, 2, 3, 1, 4],
[1, 3, 4, 2, 3],
[3, 3, 1, 2, 0]
];
var board_2 = [
[1, 4, 1, 3, 1],
[4, 3, 2, 1, 4],
[3, 2, 3, 1, 4],
[1, 3, 4, 2, 3],
[3, 4, 1, 2, 0]
];
console.log(f(board_1, 0, 0));
console.log(f(board_2, 0, 0));-
在matlab中,我有一个非负数项的矩阵a。见以下一条: 我想找到所有零元素的邻居,除了零元素。这意味着我想在向量v中存储a(1,1),a(2,5),a(3,1),a(3,6),a(4,5)和a(5,1)的邻居,如果这些邻居中的一个是零,那么我就不存储它。 所谓元素(i,j)的邻居,是指离(i,j)远一个元素的元素,即A(i,j+1)、A(i,j-1)、A(i-1,j)、A(i-1,j-1)、A(
-
我有两个带枢轴的矩形, 我需要根据红色矩形的旋转来附加绿色矩形的位置 结果应该如图所示: 我尝试了不同的公式,但没有成功 红色矩形: 绿色矩形: 我尝试了这样的方法: 非常感谢所有帮助过我的人!
-
A=矩阵(c(1,2,3,0,2,2,0,2,3),nrow=3,ncol=3) B=矩阵(c(1,2,3,1,4,2,2,1),nrow=3,ncol=3) C=A B/(总和差为零) C=矩阵(c(1,2,3, 1, 3, 2, 2,2 ,2),nrow=3,nco=3) 我需要对N个矩阵的列表执行此操作(mat_vect[[I]]): 求和矩阵并得到平均值 这里是所有数字的除法,包括零。我不
-
假设我使用大小为8的字符数组来表示图像的碰撞掩码。字符的每一位代表一个像素。实际上,对于64x64矩阵,我将使用长[64]阵列。 因此,框将显示为: 45度的示例输出应该是这样的,尽管旋转可以是任何角度。这个形状对于45度旋转可能不准确,因为我是用手做的。 另一个例子是向右旋转10度?这些值可能是错误的,因为从数学上讲,我不知道它将如何精确旋转,但我认为可以安全地假设,如果每个位的覆盖率超过旧形状
-
在用CV::SolvePnPransac估计摄像机姿态时,输入是objectPoints和ImagePoints。输出是旋转和平移矩阵,加上内点数 利用遗传算法生成一个新的旋转平移矩阵。我喜欢用我的新的旋转和平移来计算内点的数目。 谢谢你的支持
-
基本上,我想做的过程描述在这里(特别是看到图像接近尾声),但从一个已知的相机模型和姿态开始。 是否有一个直接的函数调用来获取相机的内部和外部参数,并计算透视矩阵以用于? 在对图像调用之后,我将调用。 原则上,在指定约束之后,我可以通过求解opencv摄像机校准文档顶部定义的方程组来导出解决方案,但我认为必须有一个罐装例程来允许我正射校正我的测试图像。 在我的搜索中,我发现很难通过所有的立体声校准结

