3.6 Map 字典
Map字典
在Go中,Map又称字典类型,它就是一个hash表。计算机科学里面最有用的数据结构之一就是hash表。不同的hash表实现提供了很多独特的特性。但是基本上都包括元素查询,添加和删除。Go提供了一个内置的类型map,这个类型实现了hash表的基本功能。
所以在Go语言里面如果你需要使用hash表,那么就用map吧。因为Go是强类型语言,所以你必须为map的键和对应的值指定具体的类型。这些键或值的类型可以是字符串,整型,指向结构体的指针等。
map的创建
map的创建有四种方式:
make ( map [KeyType] ValueType, initialCapacity )
make ( map [KeyType] ValueType )
map [KeyType ] ValueType {}
map [KeyType ] ValueType { key1 : value1, key2: value2, ... , keyN : valueN}
其中第一种和第二种的区别在于,有没有指定初始容量,不过使用的时候则无需在意这些,因为map的本质决定了,一旦容量不够,它会自动扩容。 pro03_6_1.go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
map1 := make(map[string]int, 7)
map2 := make(map[string]int)
map3 := map[string]int{}
map4 := map[string]int{"Mon": 0, "Tue": 1, "Wed": 2, "Thu": 3, "Fri": 4, "Sat": 5, "Sun": 6}
fmt.Println(map1, map2, map3, map4)
}
输出结果:
map[] map[] map[] map[Mon:0 Tue:1 Wed:2 Thu:3 Fri:4 Sat:5 Sun:6]
map的每个单位就是一对key:value,key 可以是任意可以用 == 或者 != 操作符比较的类型,比如 string、int、float。所以数组、切片和结构体不能作为 key,但是指针和接口类型可以。Go语言中大部分类型都能做key,某些类型是不能的,这些不能作为Key的类型的共同特点是:不能使用==来比较,包括: slice, map, function.
value 可以是任意类型的;通过使用空接口类型,我们可以存储任意值,但是使用这种类型作为值时需要先做一次类型断言。
为了说明value 可以是任意类型的,我举一个例子: pro03_6_2.go
func main() {
sunnyMap := map[int]func() string{
0: func() string { return "aaaa" }, //使用匿名函数做map的value
1: func() string { return "bbbb" },
2: func() string { return "cccc" },
}
fmt.Println(sunnyMap)
}
输出结果:
map[0:0x401200 3:0x401220 9:0x401240]
value都被映射到了匿名函数地址。
map的填充和遍历
map的遍历使用for range pro03_6_3.go
func main() {
sunnyMap := make(map[int]string)
sunnyMap[0] = "Mon"
sunnyMap[1] = "Tue"
sunnyMap[2] = "Wed"
sunnyMap[3] = "Thu"
sunnyMap[4] = "Fri"
sunnyMap[5] = "Sat"
sunnyMap[6] = "Sun"
for key, value := range sunnyMap {
fmt.Printf("%d->%s\r\n", key, value)
}
}
遍历的输出结果,我们正常的会以为,输出结果是这样的
0->Mon
1->Tue
2->Wed
3->Thu
4->Fri
5->Sat
6->Sun
可是更可能,我们见到的输出结果是这样的
2->Wed
3->Thu
4->Fri
5->Sat
6->Sun
0->Mon
1->Tue
而且每次运行的输出结果顺序都是随机的。Go语言的设计者们注意到人们过于依赖这种通常情况下key的存储顺序和key的添加顺序一致的特性,所以他们把key的遍历顺序随机化了。GO的map 类似c++里的unordered_map,是无序的,开发者不希望map有内置的有序特性。因此,如果你希望key的输出顺序和添加顺序一致的话,你需要自己做一下排序。 pro03_6_4.go
func main() {
sunnyMap := make(map[int]string)
sunnyMap[0] = "Mon"
sunnyMap[1] = "Tue"
sunnyMap[2] = "Wed"
sunnyMap[3] = "Thu"
sunnyMap[4] = "Fri"
sunnyMap[5] = "Sat"
sunnyMap[6] = "Sun"
var keys []int
for key, _ := range sunnyMap {
keys = append(keys, key)
}
sort.Ints(keys)
for _, i := range keys {
fmt.Printf("%d->%s\r\n", i, sunnyMap[i])
}
}
长度、查询、查找、修改和删除
map的长度计算用len,但是注意一点:map不支持cap计算容量。
查找
value, isExist := sunnyMap["Mon"]
map指定key取对应的value时,可以指定两个返回值,第一个是对应的value,第二个是一个bool值,表示是否有值。true表示有值,false表示没值。
func main() {
sunnyMap := map[string]string{"Mon": "一", "Tue": "二", "Wed": "三", "Thu": "四", "Fri": "五", "Sat": "六", "Sun": "日"}
val1, isExist1 := sunnyMap["Sat"]
val2, isExist2 := sunnyMap["sat"]
fmt.Println("Sat is exist?", isExist1, "value:", val1)
fmt.Println("sat is exist?", isExist2, "value:", val2)
}
输出结果: Sat is exist? true value: 六 sat is exist? false value: 有一点要注意,如果value是数值型的,isExist返回值为false的时候,value的值是0。还有,从key是Sta有值,而sat无值可以看出Go是区分大小写的。
修改 sunnyMap["key"]=value
删除 则是使用go的内置函数delete
func main() {
sunnyMap := map[string]string{"Mon": "一", "Tue": "二", "Wed": "三", "Thu": "四", "Fri": "五", "Sat": "六", "Sun": "日"}
delete(sunnyMap, "Mon")
fmt.Println(sunnyMap)
}
显示结果:map[Sun:日 Tue:二 Wed:三 Thu:四 Fri:五 Sat:六]
map的value使用slice
使用过PHP的程序员都很喜欢PHP里面array,这个使用起来非常的随意方便,GO中的map就相当于PHP里面的array,尤其是配合上切片slice一起使用:pro03_6_7.go
func main() {
sunnyMap := map[string][]string{"a": {"一", "a", "b"}, "b": {"二", "hello"}, "c": {"三"}}
sunnyMap["c"] = append(sunnyMap["c"], "hhh")
fmt.Println(sunnyMap)
}
显示结果:map[b:[二 hello] c:[三 hhh] a:[一 a b]]
内部结构 hashmap结构
golang的map是hash结构的,同传统的hashmap一样,由一个个bucket组成: 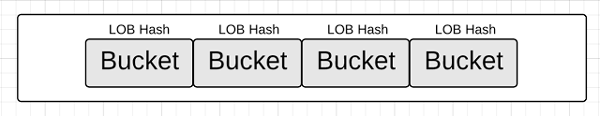
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the Hmap is encoded in ../../cmd/internal/gc/reflect.go and
// ../reflect/type.go. Don't change this structure without also changing that code!
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
// If both key and value do not contain pointers and are inline, then we mark bucket
// type as containing no pointers. This avoids scanning such maps.
// However, bmap.overflow is a pointer. In order to keep overflow buckets
// alive, we store pointers to all overflow buckets in hmap.overflow.
// Overflow is used only if key and value do not contain pointers.
// overflow[0] contains overflow buckets for hmap.buckets.
// overflow[1] contains overflow buckets for hmap.oldbuckets.
// The first indirection allows us to reduce static size of hmap.
// The second indirection allows to store a pointer to the slice in hiter.
overflow *[2]*[]*bmap
}
bucket内部
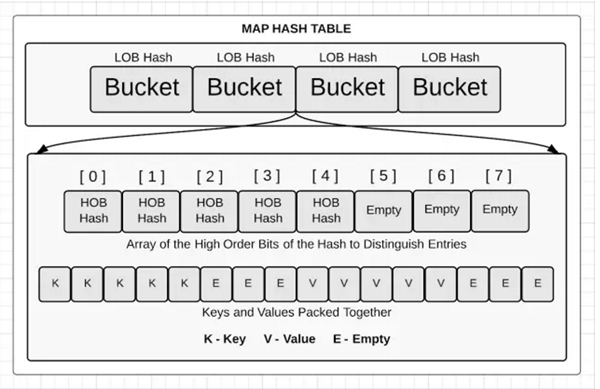
// A bucket for a Go map.
type bmap struct {
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8 // Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt values.
// NOTE: packing all the keys together and then all the values together makes the
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/value/key/value/... but it allows
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
}
根据一个key得到value
func mapaccess1(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer
maptype为map的类型信息,是编译器在编译期静态生成的,里面包含了map的一些元信息,比如 key和value的类型信息等等
- *hmap为map的header,即map的引用
- key是一个通用的指针,代表了key的引用
- 返回值为一个指针,指向对应的value引用
hash计算找到bucket
那我们怎么访问到对应的bucket呢,我们需要得到对应key的hash值
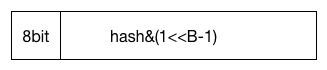
alg := t.key.alghash := alg.
hash(key, uintptr(h.hash0))
m := uintptr(1)<<h.B - 1
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
根据 tophash 和 key 定位到具体的 bucket
tophash 可以快速试错,如果 tophash 不相等直接跳过 tophash 相等的话,根据 key 的比较来判断是否相等,如果相等则找到 如果当前 bucket 都试玩还没有找到,则调到下一个 bucket
扩容
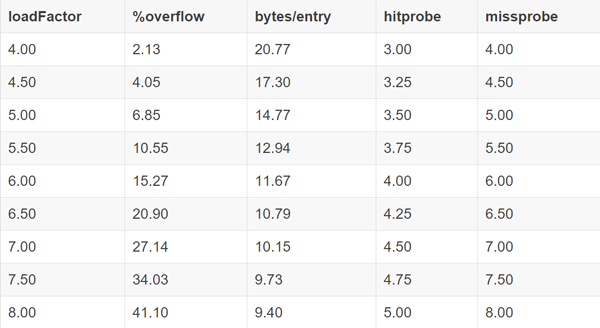
各个参数的意思:
- %overflow 溢出率,平均一个 bucket 有多少个 kv 的时候会溢出
- bytes/entry 平均存一个 kv 需要额外存储多少字节的数据
- hitprobe 找到一个存在的 key 平均需要找几下
- missprobe 找到一个不存在的 key 平均需要找几下
目前采用的是这一行:


