React 组件生命周期
精华
小牛编辑
112浏览
2023-03-14
在本章节中我们将讨论 React 组件的生命周期。
组件的生命周期可分成三个状态:
- Mounting(挂载):已插入真实 DOM
- Updating(更新):正在被重新渲染
- Unmounting(卸载):已移出真实 DOM
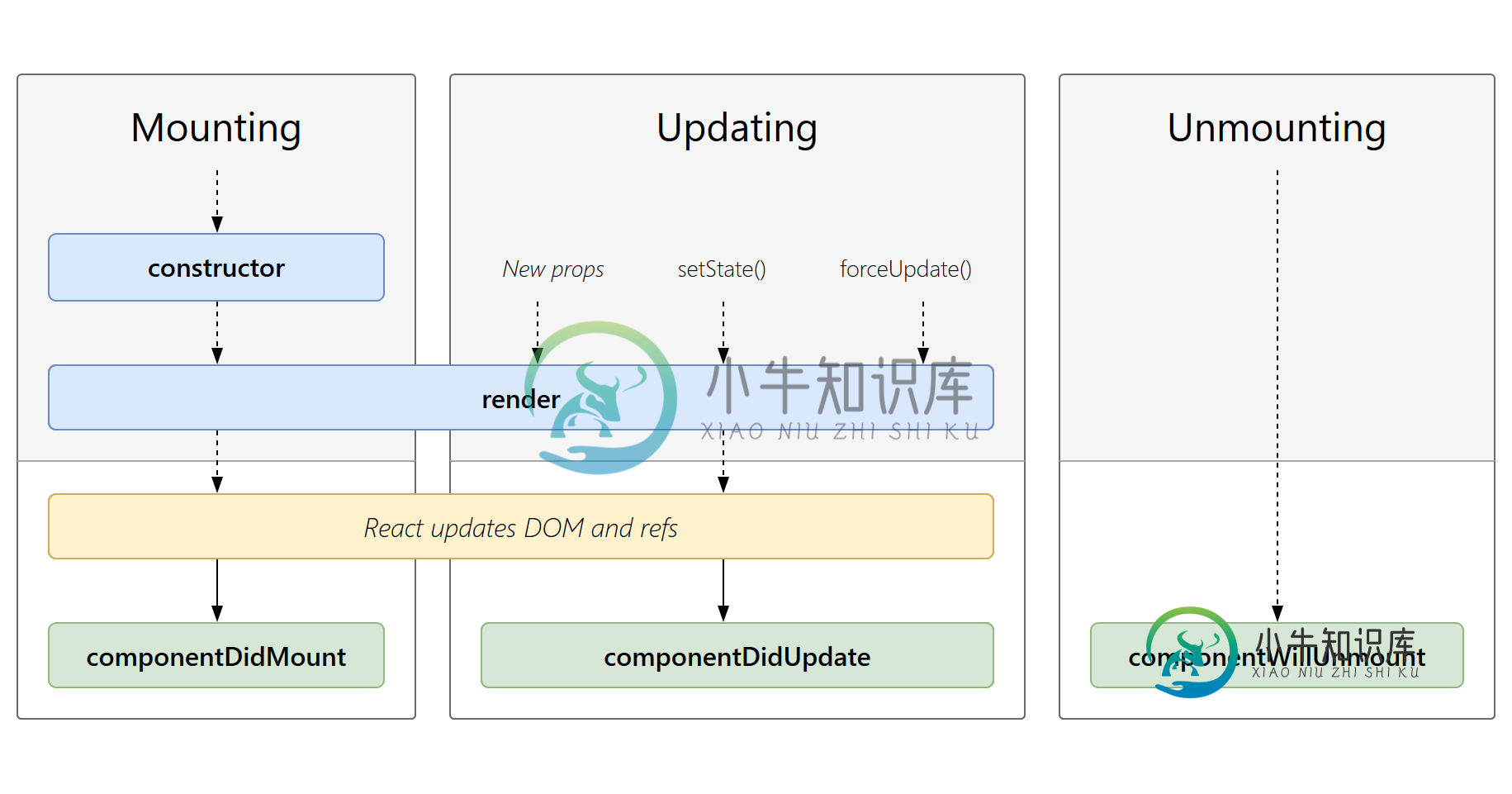
挂载
当组件实例被创建并插入 DOM 中时,其生命周期调用顺序如下:
constructor(): 在 React 组件挂载之前,会调用它的构造函数。getDerivedStateFromProps(): 在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。render(): render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法。componentDidMount(): 在组件挂载后(插入 DOM 树中)立即调用。
render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法,其他方法可以根据自己的需要来实现。
这些方法的详细说明,可以参考官方文档。
更新
每当组件的 state 或 props 发生变化时,组件就会更新。
当组件的 props 或 state 发生变化时会触发更新。组件更新的生命周期调用顺序如下:
getDerivedStateFromProps(): 在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。根据 shouldComponentUpdate() 的返回值,判断 React 组件的输出是否受当前 state 或 props 更改的影响。shouldComponentUpdate():当 props 或 state 发生变化时,shouldComponentUpdate() 会在渲染执行之前被调用。render(): render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法。getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(): 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。componentDidUpdate(): 在更新后会被立即调用。
render() 方法是 class 组件中唯一必须实现的方法,其他方法可以根据自己的需要来实现。
这些方法的详细说明,可以参考官方文档。
卸载
当组件从 DOM 中移除时会调用如下方法:
componentWillUnmount(): 在组件卸载及销毁之前直接调用。
这些方法的详细说明,可以参考官方文档。
实例
以下是一个当前时间的实例,每秒更新:
实例
class Clock extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: new Date()};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.timerID = setInterval(
() => this.tick(),
1000
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timerID);
}
tick() {
this.setState({
date: new Date()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, Xnip!</h1>
<h2>现在时间是:{this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Clock />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
以下实例在 Hello 组件加载以后,通过 componentDidMount 方法设置一个定时器,每隔100毫秒重新设置组件的透明度,并重新渲染:
React 实例
class Hello extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {opacity: 1.0};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.timer = setInterval(function () {
var opacity = this.state.opacity;
opacity -= .05;
if (opacity < 0.1) {
opacity = 1.0;
}
this.setState({
opacity: opacity
});
}.bind(this), 100);
}
render () {
return (
<div style={{opacity: this.state.opacity}}>
Hello {this.props.name}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Hello name="world"/>,
document.body
);
以下实例初始化 state , setNewnumber 用于更新 state。所有生命周期在 Content 组件中。
React 实例
class Button extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {data: 0};
this.setNewNumber = this.setNewNumber.bind(this);
}
setNewNumber() {
this.setState({data: this.state.data + 1})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick = {this.setNewNumber}>INCREMENT</button>
<Content myNumber = {this.state.data}></Content>
</div>
);
}
}
class Content extends React.Component {
componentWillMount() {
console.log('Component WILL MOUNT!')
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('Component DID MOUNT!')
}
componentWillReceiveProps(newProps) {
console.log('Component WILL RECEIVE PROPS!')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) {
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('Component WILL UPDATE!');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('Component DID UPDATE!')
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('Component WILL UNMOUNT!')
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.props.myNumber}</h3>
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<Button />
</div>,
document.getElementById('example')
);
