Android入门之AlertDialog用法实例分析
本文实例讲述的是AlertDialog,这种对话框会经常遇到。AlertDialog跟WIN32开发中的Dialog不一样,AlertDialog是非阻塞的,而阻塞的对话框用的是PopupWindow。
先贴出该程序运行的截图:
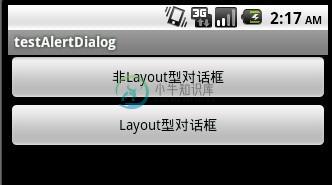
main.xml的源码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <Button android:id="@+id/Button01" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="非Layout型对话框" android:layout_width="fill_parent"></Button> <Button android:id="@+id/Button02" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Layout型对话框" android:layout_width="fill_parent"></Button><View android:id="@+id/View01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></View> </LinearLayout>
下图是非Layout型对话框,直接使用AlertDialog
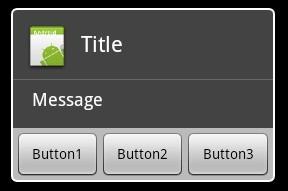
下图是使用了Layout的对话框,可以自定义控件,实现更复杂的对话框
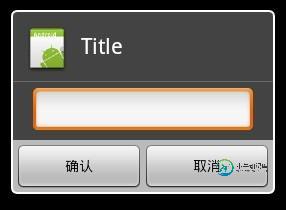
dialoglayout.xml的源码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_marginLeft="20dip" android:layout_marginRight="20dip" android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" android:id="@+id/edtInput"/> </LinearLayout>
程序源码:
package com.testAlertDialog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Gravity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.PopupWindow;
public class testAlertDialog extends Activity {
Button btnShowDialog;
Button btnShowDialog_Layout;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//定义按钮
btnShowDialog=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button01);
btnShowDialog.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnShowDialog_Layout=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button02);
btnShowDialog_Layout.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
}
//统一处理按键事件
class ClickEvent implements OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v==btnShowDialog)
showDialog(testAlertDialog.this);
else if(v==btnShowDialog_Layout)
showDialog_Layout(testAlertDialog.this);
}
}
//显示基本的AlertDialog
private void showDialog(Context context) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
builder.setTitle("Title");
builder.setMessage("Message");
builder.setPositiveButton("Button1",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button1");
}
});
builder.setNeutralButton("Button2",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button2");
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("Button3",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button3");
}
});
builder.show();
}
//显示基于Layout的AlertDialog
private void showDialog_Layout(Context context) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
final View textEntryView = inflater.inflate(
R.layout.dialoglayout, null);
final EditText edtInput=(EditText)textEntryView.findViewById(R.id.edtInput);
final AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setCancelable(false);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
builder.setTitle("Title");
builder.setView(textEntryView);
builder.setPositiveButton("确认",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle(edtInput.getText());
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("");
}
});
builder.show();
}
}
-
本文向大家介绍Android开发入门之Appwidget用法分析,包括了Android开发入门之Appwidget用法分析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android Appwidget用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: App Widgets 是一个小型应用程序的View 他可以嵌入到其他应用程序中(如 桌面程序) 并且可以得到周期性刷新。 在创建App Widg
-
本文向大家介绍Android开发入门之Notification用法分析,包括了Android开发入门之Notification用法分析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android中Notification用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: Notification可以理解为通知的意思一般用来显示广播信息 用Notification就必须要用到NotificationM
-
本文向大家介绍Pytorch入门之mnist分类实例,包括了Pytorch入门之mnist分类实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了Pytorch入门之mnist分类的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持呐喊教程。
-
本文向大家介绍Android入门之TabHost与TabWidget实例解析,包括了Android入门之TabHost与TabWidget实例解析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例介绍的是Android的Tab控件,Tab控件可以达到分页的效果,让一个屏幕的内容尽量丰富,当然也会增加开发的复杂程度,在有必要的时候再使用。Android的Tab控件使用起来有点奇怪,必须包含和按照以下
-
本文向大家介绍Android开发之BroadcastReceiver用法实例分析,包括了Android开发之BroadcastReceiver用法实例分析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android开发中BroadcastReceiver用法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下: 在Android系统中,广播(Broadcast)是在组件之间传播数据(Intent)的一种
-
本文向大家介绍Android控件之TabHost用法实例分析,包括了Android控件之TabHost用法实例分析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android控件之TabHost用法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下: 以下通过TabHost实现android选项卡。 main.xml布局文件: TabHostActivity类: 运行结果: 希望本文所述对大家的Andro

