拖动绘制的形状
图形界面允许您使用不同的类创建图形。
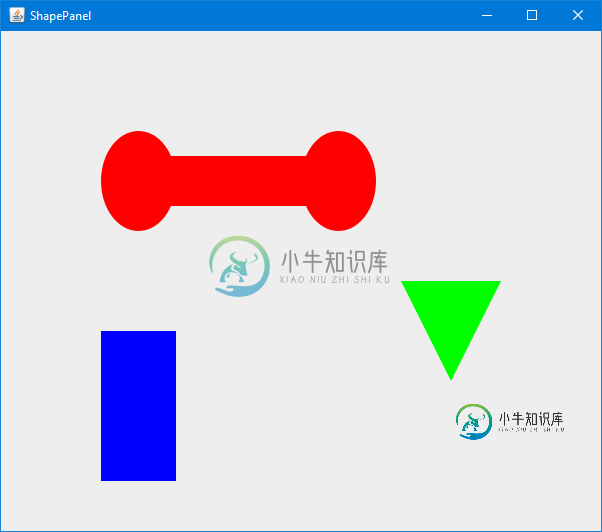
在下面的代码中,我使用3个不同的类创建形状:
GeneralPath barBell = new GeneralPath();
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(100, 100, 75, 100), true);
barBell.append(new Rectangle2D.Double(150, 125, 175, 50), true);
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(300, 100, 75, 100), true);
shapePanel.addShape(barBell, Color.RED);
shapePanel.addShape(new Rectangle2D.Double(100, 300, 75, 150), Color.BLUE);
Polygon triangle = new Polygon();
triangle.addPoint(0, 0);
triangle.addPoint(100, 0);
triangle.addPoint(50, 100);
triangle.translate(400, 250);
shapePanel.addShape(triangle, Color.GREEN);
产生屏幕图像:
不幸的是,Shape接口不提供任何用于转换Shape的功能。
例如,要将形状移动到新位置,我使用以下方法:
if (dragShape instanceof Path2D)
((Path2D)dragShape).transform(AffineTransform.getTranslateInstance(deltaX, deltaY));
else if (dragShape instanceof Polygon)
((Polygon)dragShape).translate(deltaX, deltaY);
else if (dragShape instanceof RectangularShape)
{
RectangularShape rs = (RectangularShape)dragShape;
Rectangle r = rs.getBounds();
r.x += deltaX;
r.y += deltaY;
rs.setFrame( r );
}
我不喜欢逻辑的实例。
是否有一种更通用的方法可以在不使用instanceof逻辑的面板周围拖动任何形状?
完整示例:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ShapePanel2 extends JPanel
{
private ArrayList<ColoredShape> coloredShapes = new ArrayList<ColoredShape>();
public ShapePanel2()
{
DragListener dl = new DragListener();
addMouseListener(dl);
addMouseMotionListener(dl);
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
super.paintComponent(g);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
for (ColoredShape cs : coloredShapes)
{
g2.setColor( cs.getForeground() );
g2.fill( cs.getShape() );
}
}
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(600, 500);
}
public void addShape(Shape shape, Color color)
{
ColoredShape cs = new ColoredShape(color, shape);
coloredShapes.add( cs );
repaint();
}
class ColoredShape
{
private Color foreground;
private Shape shape;
public ColoredShape(Color foreground, Shape shape)
{
this.foreground = foreground;
this.shape = shape;
}
public Color getForeground()
{
return foreground;
}
public void setForeground(Color foreground)
{
this.foreground = foreground;
}
public Shape getShape()
{
return shape;
}
}
class DragListener extends MouseAdapter
{
private Shape dragShape;
private Point pressed;
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e)
{
if (SwingUtilities.isLeftMouseButton(e))
{
pressed = e.getPoint();
for (int i = coloredShapes.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ColoredShape cs = coloredShapes.get(i);
if (cs.getShape().contains( pressed ))
{
coloredShapes.remove(i);
coloredShapes.add(cs);
repaint();
dragShape = cs.getShape();
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e)
{
if (dragShape != null)
{
int deltaX = e.getX() - pressed.x;
int deltaY = e.getY() - pressed.y;
if (dragShape instanceof Path2D)
((Path2D)dragShape).transform(AffineTransform.getTranslateInstance(deltaX, deltaY));
else if (dragShape instanceof Polygon)
((Polygon)dragShape).translate(deltaX, deltaY);
else if (dragShape instanceof RectangularShape)
{
RectangularShape rs = (RectangularShape)dragShape;
Rectangle r = rs.getBounds();
r.x += deltaX;
r.y += deltaY;
rs.setFrame( r );
}
pressed = e.getPoint();
repaint();
}
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)
{
dragShape = null;
}
}
private static void createAndShowGUI()
{
ShapePanel2 shapePanel = new ShapePanel2();
GeneralPath barBell = new GeneralPath();
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(100, 100, 75, 100), true);
barBell.append(new Rectangle2D.Double(150, 125, 175, 50), true);
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(300, 100, 75, 100), true);
shapePanel.addShape(barBell, Color.RED);
shapePanel.addShape(new Rectangle2D.Double(100, 300, 75, 150), Color.BLUE);
Polygon triangle = new Polygon();
triangle.addPoint(0, 0);
triangle.addPoint(100, 0);
triangle.addPoint(50, 100);
triangle.translate(400, 250);
shapePanel.addShape(triangle, Color.GREEN);
JFrame frame = new JFrame("ShapePanel2");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.add(shapePanel);
frame.pack();
frame.setLocationByPlatform(true);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
java.awt.EventQueue.invokeLater( () -> createAndShowGUI() );
}
}
共有1个答案
一种方法可能是在将形状添加到面板时,将每个形状转换为通用路径。
现在拖动逻辑只需要支持实现Shape接口的单个类:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ShapePanel extends JPanel
{
private ArrayList<ColoredShape> coloredShapes = new ArrayList<ColoredShape>();
public ShapePanel()
{
DragListener dl = new DragListener();
addMouseListener(dl);
addMouseMotionListener(dl);
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
super.paintComponent(g);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
for (ColoredShape cs : coloredShapes)
{
g2.setColor( cs.getForeground() );
g2.fill( cs.getShape() );
}
}
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(600, 500);
}
public void addShape(Shape shape, Color color)
{
// Convert the Shape to a GeneralPath so the Shape can be translated
// to a new location when dragged
ColoredShape cs = new ColoredShape(color, new GeneralPath(shape));
coloredShapes.add( cs );
repaint();
}
class ColoredShape
{
private Color foreground;
private GeneralPath shape;
public ColoredShape(Color foreground, GeneralPath shape)
{
this.foreground = foreground;
this.shape = shape;
}
public Color getForeground()
{
return foreground;
}
public void setForeground(Color foreground)
{
this.foreground = foreground;
}
public GeneralPath getShape()
{
return shape;
}
}
class DragListener extends MouseAdapter
{
private GeneralPath dragShape;
private Point pressed;
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e)
{
// the clicked Shape will be moved to the end of the List
// so it is painted on top of all other shapes.
if (SwingUtilities.isLeftMouseButton(e))
{
pressed = e.getPoint();
for (int i = coloredShapes.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ColoredShape cs = coloredShapes.get(i);
if (cs.getShape().contains( pressed ))
{
coloredShapes.remove(i);
coloredShapes.add(cs);
repaint();
dragShape = cs.getShape();
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e)
{
if (dragShape != null)
{
int deltaX = e.getX() - pressed.x;
int deltaY = e.getY() - pressed.y;
dragShape.transform(AffineTransform.getTranslateInstance(deltaX, deltaY));
pressed = e.getPoint();
repaint();
}
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)
{
dragShape = null;
}
}
private static void createAndShowGUI()
{
ShapePanel shapePanel = new ShapePanel();
GeneralPath barBell = new GeneralPath();
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(100, 100, 75, 100), true);
barBell.append(new Rectangle2D.Double(150, 125, 175, 50), true);
barBell.append(new Ellipse2D.Double(300, 100, 75, 100), true);
shapePanel.addShape(barBell, Color.RED);
shapePanel.addShape(new Rectangle2D.Double(100, 300, 75, 150), Color.BLUE);
Polygon triangle = new Polygon();
triangle.addPoint(0, 0);
triangle.addPoint(100, 0);
triangle.addPoint(50, 100);
triangle.translate(400, 250);
shapePanel.addShape(triangle, Color.GREEN);
JFrame frame = new JFrame("ShapePanel");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.add(shapePanel);
frame.pack();
frame.setLocationByPlatform(true);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
java.awt.EventQueue.invokeLater( () -> createAndShowGUI() );
}
}
-
通过 Entity 添加形状 先来看一个添加立方体的例子 var viewer = new Cesium.Viewer('cesiumContainer'); var redBox = viewer.entities.add({ name : 'Red box with black outline', position: Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(-107
-
使用closePath()闭合图形 首先我们用上节课的方法绘制一个矩形。 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UT
-
我已经使用MP Android chart创建了一个折线图,并希望创建一条可拖动的线来设置限制。因此,如果该值超过行值,则用户会收到警报。我的用例类似于Android系统数据使用限制。 我遇到了LimitLines-https://github.com/PhilJay/MPAndroidChart/wiki/The-Axis,还使用触摸事件回调拖动https://github.com/PhilJa
-
问题内容: 我正在使用Java。我想根据mousedrag事件绘制矩形。如果用户拖动鼠标,则小程序上的矩形应根据当前鼠标坐标增加或减少。我有以下代码。 在下面的代码中,我使用[b] SelectionArea [/ b]类扩展了在其上执行绘制操作的画布。我在此类中使用[b] image [/ b]变量进行双缓冲,以减少闪烁并保存小程序的先前状态(即,绘制小程序的内容) 但如果我画第一个矩形,代码工
-
可以使用包的相应方法在图像上绘制各种形状,如圆形,矩形,线条,椭圆,多段线,凸起,多段线,多段线。 可以使用类的方法在图像上绘制一个圆形。 以下是这种方法的语法 - 该方法接受以下参数 - mat - Mat对象,表示要在其上绘制圆的图像。 point - 代表圆中心的对象。 radius - 表示圆的半径的整型变量。 scalar - 表示圆的颜色的标量对象(BGR)。 thickness -
-
绘制矩形 点击菜单栏中的“绘制矩形”按钮可以绘制矩形,绘制矩形在数据下载的时候经常要用到,绘制矩形操作及信息与绘制面相同。 修改矩形 添加后可以使用“选中对象”后双击更改面的样式,也可右键“属性”修改线的属性信息。点击属性信息框下方的整体移动(单点修改)键对面进行位置的更改。在“空间信息”栏修改矩形的节点坐标后,需要注意的是修改完可能就不是标准矩形了,要调整。 删除矩形

