在OpenCL内核中实现FIFO的最佳方法
目标:在OpenCL中实现下面所示的图表。OpenCl内核需要做的主要工作是将系数数组和临时数组相乘,然后在最后将所有这些值累加为一。(这可能是时间最密集的操作,并行性在这里非常有用)。
我正在为执行乘法和加法的内核使用一个辅助函数(我希望这个函数也是并行的)。
图片描述:
每次一个值被传递到与系数数组大小相同的数组(临时数组)中。现在,每次一个值被传递到这个数组中,临时数组都会并行地与系数数组相乘,然后每个索引的值被级联到一个元素中。这将持续到输入数组到达它的最终元素。
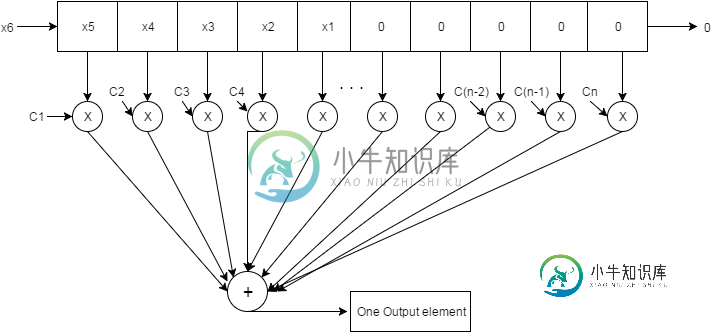
我的代码怎么了?
对于来自输入的60个元素,它需要8000毫秒!!我总共有120万输入需要传递。我知道有一个更好的解决方案来做我正在尝试的事情。下面是我的代码。
以下是我知道的一些代码错误的地方。当我试图将系数值与临时数组相乘时,它崩溃了。这是因为全局id。我想要这条线做的只是将两个数组并行相乘。
我试图弄清楚为什么做FIFO函数要花这么长时间,所以我开始注释行。我首先注释除了FIFO函数的第一个for循环之外的所有内容。结果这花了50毫秒。然后当我取消注释下一个循环时,它跳到了8000毫秒。所以延迟与数据传输有关。
我可以在OpenCl中使用寄存器移位吗?也许对整数数组使用一些逻辑移位方法?(我知道有一个
float constant temp[58];
float constant tempArrayForShift[58];
float constant multipliedResult[58];
float fifo(float inputValue, float *coefficients, int sizeOfCoeff) {
//take array of 58 elements (or same size as number of coefficients)
//shift all elements to the right one
//bring next element into index 0 from input
//multiply the coefficient array with the array thats the same size of coefficients and accumilate
//store into one output value of the output array
//repeat till input array has reached the end
int globalId = get_global_id(0);
float output = 0.0f;
//Shift everything down from 1 to 57
//takes about 50ms here
for(int i=1; i<58; i++){
tempArrayForShift[i] = temp[i];
}
//Input the new value passed from main kernel. Rest of values were shifted over so element is written at index 0.
tempArrayForShift[0] = inputValue;
//Takes about 8000ms with this loop included
//Write values back into temp array
for(int i=0; i<58; i++){
temp[i] = tempArrayForShift[i];
}
//all 58 elements of the coefficient array and temp array are multiplied at the same time and stored in a new array
//I am 100% sure this line is crashing the program.
//multipliedResult[globalId] = coefficients[globalId] * temp[globalId];
//Sum the temp array with each other. Temp array consists of coefficients*fifo buffer
for (int i = 0; i < 58; i ++) {
// output = multipliedResult[i] + output;
}
//Returned summed value of temp array
return output;
}
__kernel void lowpass(__global float *Array, __global float *coefficients, __global float *Output) {
//Initialize the temporary array values to 0
for (int i = 0; i < 58; i ++) {
temp[i] = 0;
tempArrayForShift[i] = 0;
multipliedResult[i] = 0;
}
//fifo adds one element in and calls the fifo function. ALL I NEED TO DO IS SEND ONE VALUE AT A TIME HERE.
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i ++) {
Output[i] = fifo(Array[i], coefficients, 58);
}
}
我对OpenCl有这个问题已经很久了,我不确定如何一起实现并行和顺序指令。
我在想的另一个选择
在主cpp文件中,我考虑在那里实现fifo缓冲区,并让内核执行乘法和加法。但这意味着我必须在一个循环中调用内核1000次。这是更好的解决方案吗?还是完全没有效率。
共有2个答案
这是另一个你可以尝试的内核。有很多同步点(障碍),但这应该表现得相当好。65个项目的工作组不是很理想。
步骤如下:
- 初始化本地值为0
- 将系数复制到局部变量
在要计算的输出元素上循环:
代码:
__kernel void lowpass(__global float *Array, __constant float *coefficients, __global float *Output, __local float *localArray, __local float *localSums){
int globalId = get_global_id(0);
int localId = get_local_id(0);
int localSize = get_local_size(0);
//1 init local values to 0
localArray[localId] = 0.0f
//2 copy coefficients to local
//don't bother with this id __constant is working for you
//requires another local to be passed in: localCoeff
//localCoeff[localId] = coefficients[localId];
//barrier for both steps 1 and 2
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
float tmp;
for(int i = 0; i< outputSize; i++)
{
//3 shift elements (+barrier)
if(localId > 0){
tmp = localArray[localId -1]
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
localArray[localId] = tmp
//4 copy new element (work item 0 only, + barrier)
if(localId == 0){
localArray[0] = Array[i];
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
//5 compute dot product
//5a multiply + barrier
localSums[localId] = localArray[localId] * coefficients[localId];
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
//5b reduction loop + barrier
for(int j = 1; j < localSize; j <<= 1) {
int mask = (j << 1) - 1;
if ((localId & mask) == 0) {
localSums[local_index] += localSums[localId +j]
}
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
}
//6 copy dot product (WI 0 only)
if(localId == 0){
Output[i] = localSums[0];
}
//7 barrier
//only needed if there is more code after the loop.
//the barrier in #3 covers this in the case where the loop continues
//barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
}
}
更多的工作组呢?
这是稍微简化的,允许一个1x65工作组计算机整个1.2M输出。为了允许多个工作组,您可以使用/get_num_groups(0)来计算每个组应该做的工作量(workAmount),并调整i for循环:
for (i = workAmount * get_group_id(0); i< (workAmount * (get_group_id(0)+1) -1); i++)
步骤#1也必须更改,以便初始化到localArray的正确启动状态,而不是全部0。
//1 init local values
if(groupId == 0){
localArray[localId] = 0.0f
}else{
localArray[localSize - localId] = Array[workAmount - localId];
}
这两个变化应该允许你使用更多的工作组;我建议将设备上的计算单元数增加几倍。不过,尽量让每个小组的工作量保持在数千。考虑到这一点,有时在高级上看起来是最优的东西在内核运行时会对内核有害。
优点
在这个内核的几乎每一点上,工作项都有一些事情要做。只有在步骤5b中的还原循环期间,少于100%的项目工作。阅读更多关于为什么这是一件好事的信息。
缺点
障碍会减慢内核的速度,这仅仅是障碍的性质:暂停一个工作项目,直到其他项目到达那个点。也许有一种方法可以用更少的障碍来实现这一点,但是我仍然觉得这是最佳的,因为你正在试图解决这个问题。
每个组没有空间容纳更多的工作项目,65不是一个非常理想的大小。理想情况下,你应该尝试使用2的幂,或者64的倍数。不过这不是一个大问题,因为内核中有很多障碍,这使得它们都相当有规律地等待。
为了获得GPU的良好性能,需要将工作并行化到多个线程。在您的代码中,您只使用一个线程,而GPU每个线程的速度非常慢,但如果多个线程同时运行,则速度可能非常快。在这种情况下,每个输出值都可以使用一个线程。实际上,您不需要通过数组移动值:对于每个输出值,都会考虑一个包含58个值的窗口,您可以从内存中获取这些值,将它们与系数相乘,然后写回结果。
一个简单的实现将是(启动与输出值一样多的线程):
__kernel void lowpass(__global float *Array, __global float *coefficients, __global float *Output)
{
int globalId = get_global_id(0);
float sum=0.0f;
for (int i=0; i< 58; i++)
{
float tmp=0;
if (globalId+i > 56)
{
tmp=Array[i+globalId-57]*coefficient[57-i];
}
sum += tmp;
}
output[globalId]=sum;
}
这并不完美,因为它生成的内存访问模式对图形处理器来说并不是最佳的。缓存可能会有所帮助,但显然有很大的优化空间,因为这些值会被重复使用几次。您试图执行的操作称为卷积(1D)。英伟达在其图形处理器计算软件开发工具包中有一个名为oclConvoltionFilable的2D示例,该示例显示了一个优化版本。您可以使用他们的卷积行内核进行1D卷积。
-
问题内容: 图形处理单元(GPGPU)上的通用计算是一个非常吸引人的概念,可以利用GPU的能力进行任何类型的计算。 我很想使用GPGPU进行图像处理,粒子和快速几何运算。 现在,似乎这个领域的两个竞争者是CUDA和OpenCL。我想知道: Windows / Mac上的Java是否可以使用OpenCL? 与OpenCL / CUDA接口的库方法是什么? 直接使用JNA是一种选择吗? 我忘记了什么吗
-
问题内容: 我打算通过此库在android中实现Socket.io,用于基于聊天的应用程序。据我了解,该图书馆似乎还不错。我想知道如何始终保持整个应用程序中的 单个 套接字连接吗?在这里,我列出了实现的方法,其中我需要最好和稳定的方法。 三种方式 MainApplication 类扩展 应用程序 这样,我们就可以在 主线程 (或应用程序的生命周期)中维护套接字连接,并且只要活动需要套接字实例,我们
-
问题内容: 假设我们有一个活动,该活动有很多视图要注册。 最常见的实现方法是让Activity-Subclass实现OnClickListener,如下所示: 我喜欢实现它的方式是在Activity-Subclass内部创建一个私有类,并让该内部类实现OnClickListener: 这样,代码看起来更加井井有条,易于维护。 此外,在谈论“ Is-a”,“ Has-a”关系时,后者似乎是一个好习惯
-
问题内容: 我正在尝试编写工厂模式以在程序中创建MainMode或TestMode。我以前用来创建这些对象的代码是: 我的游戏(游戏)将根据布尔值(isMode)创建MainMode对象或TestMode对象。如您所见,我正在向我的TestMode对象(randNo())添加一个额外的值。在TestMode中使用此值,以允许用户输入自己的“随机数”,而在MainMode构造函数中,则是随机生成的。
-
问题内容: 考虑以下代码: writer.c reader.c 我的问题是: 由于事先不知道foo和bar将有多少个字节,我如何知道要从reader.c读取多少个字节? 因为例如,如果我在reader中读取10个字节,而foo和bar小于10个字节,那么我会将它们都放在同一个变量中,而这是我不希望的。 理想情况下,我将对每个变量都具有一个读取功能,但是我又一次事先不知道数据将具有多少字节。 我考虑
-
问题内容: 我们如何确定用于集合的方法的最佳实现(假设equals方法已被正确覆盖)? 问题答案: 最好的实现?这是一个难题,因为它取决于使用模式。 在几乎所有情况下,Josh Bloch的 有效Java项目8(第二版)中都提出了合理的良好实现。最好的办法是在那里查找,因为作者在那里解释了为什么这种方法很好。 简短版 1. 创建一个并分配一个非零值。 对于在方法中测试的每个字段 f,通过以下equ

