Matplotlib渲染所有内部体素(带有Alpha)
我想在matplotlib中渲染一个卷。该体积是一个简单的7x7x7多维数据集,并且我希望能够看到所有内部体素(即使我知道它看起来像一团糟)。
 我已经能够渲染透明的体素,但是似乎从未绘制过表面上没有的任何体素。
我已经能够渲染透明的体素,但是似乎从未绘制过表面上没有的任何体素。
该卷的每个7x7切片应如下所示:

我汇集了MWE
以下代码使用5x5的红色,绿色,蓝色,黄色和青色层创建5x5x5的体积。每层的Alpha设置为.5,因此整个过程应该是透明的。
然后,我将所有非表面体素的颜色更改为带有alpha 1的黑色,因此如果显示出来,我们应该能够在中心看到一个黑框。
单独渲染它会产生左侧的图形,但是如果我们从青色层中删除填充,我们可以看到黑框确实存在,只是没有显示它,因为即使那些遮盖了体素的遮盖物也被100%遮盖了alpha小于1。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # NOQA
spatial_axes = [5, 5, 5]
filled = np.ones(spatial_axes, dtype=np.bool)
colors = np.empty(spatial_axes + [4], dtype=np.float32)
alpha = .5
colors[0] = [1, 0, 0, alpha]
colors[1] = [0, 1, 0, alpha]
colors[2] = [0, 0, 1, alpha]
colors[3] = [1, 1, 0, alpha]
colors[4] = [0, 1, 1, alpha]
# set all internal colors to black with alpha=1
colors[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1, 0:3] = 0
colors[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1, 3] = 1
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot('111', projection='3d')
ax.voxels(filled, facecolors=colors, edgecolors='k')
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot('111', projection='3d')
filled[-1] = False
ax.voxels(filled, facecolors=colors, edgecolors='k')
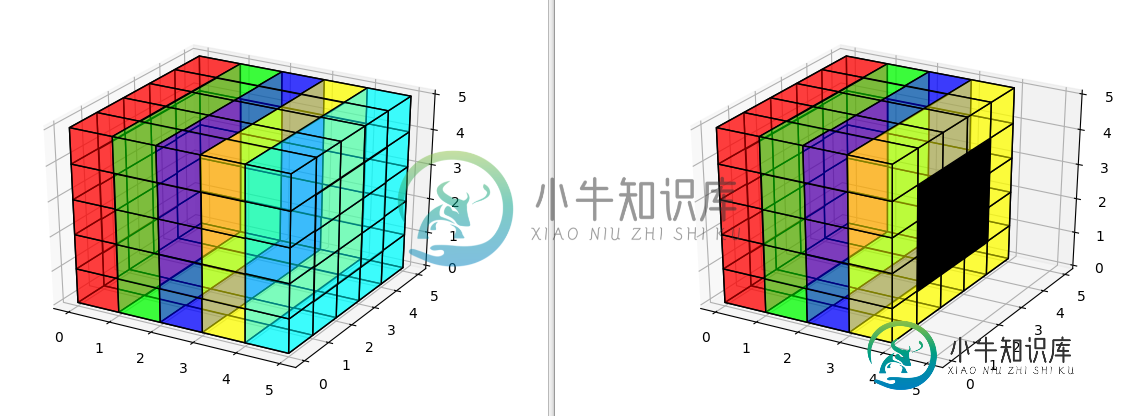
有什么办法渲染所有被遮挡的体素?
问题答案:
要将以上我的评论变成答案:
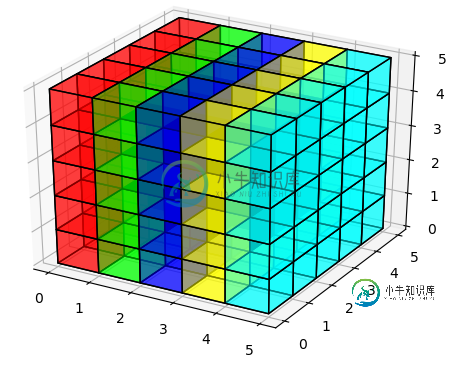
- 您可能总是像这样绘制所有体素
- 用matplotlib表示体素
- matplotlib中的3D离散热图
- 该负责人举例通过offsettingt体素的一个位面解决了这个问题,这样他们都绘制。
- 这个matplotlib问题讨论了内部多维数据集上缺少的面。有一个拉取请求仍然存在一些问题,因此尚未合并。
尽管存在一些小问题,但您仍可以在代码中插入pull请求的当前状态:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D, art3d # NOQA
from matplotlib.cbook import _backports
from collections import defaultdict
import types
def voxels(self, *args, **kwargs):
if len(args) >= 3:
# underscores indicate position only
def voxels(__x, __y, __z, filled, **kwargs):
return (__x, __y, __z), filled, kwargs
else:
def voxels(filled, **kwargs):
return None, filled, kwargs
xyz, filled, kwargs = voxels(*args, **kwargs)
# check dimensions
if filled.ndim != 3:
raise ValueError("Argument filled must be 3-dimensional")
size = np.array(filled.shape, dtype=np.intp)
# check xyz coordinates, which are one larger than the filled shape
coord_shape = tuple(size + 1)
if xyz is None:
x, y, z = np.indices(coord_shape)
else:
x, y, z = (_backports.broadcast_to(c, coord_shape) for c in xyz)
def _broadcast_color_arg(color, name):
if np.ndim(color) in (0, 1):
# single color, like "red" or [1, 0, 0]
return _backports.broadcast_to(
color, filled.shape + np.shape(color))
elif np.ndim(color) in (3, 4):
# 3D array of strings, or 4D array with last axis rgb
if np.shape(color)[:3] != filled.shape:
raise ValueError(
"When multidimensional, {} must match the shape of "
"filled".format(name))
return color
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid {} argument".format(name))
# intercept the facecolors, handling defaults and broacasting
facecolors = kwargs.pop('facecolors', None)
if facecolors is None:
facecolors = self._get_patches_for_fill.get_next_color()
facecolors = _broadcast_color_arg(facecolors, 'facecolors')
# broadcast but no default on edgecolors
edgecolors = kwargs.pop('edgecolors', None)
edgecolors = _broadcast_color_arg(edgecolors, 'edgecolors')
# include possibly occluded internal faces or not
internal_faces = kwargs.pop('internal_faces', False)
# always scale to the full array, even if the data is only in the center
self.auto_scale_xyz(x, y, z)
# points lying on corners of a square
square = np.array([
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]
], dtype=np.intp)
voxel_faces = defaultdict(list)
def permutation_matrices(n):
""" Generator of cyclic permutation matices """
mat = np.eye(n, dtype=np.intp)
for i in range(n):
yield mat
mat = np.roll(mat, 1, axis=0)
for permute in permutation_matrices(3):
pc, qc, rc = permute.T.dot(size)
pinds = np.arange(pc)
qinds = np.arange(qc)
rinds = np.arange(rc)
square_rot = square.dot(permute.T)
for p in pinds:
for q in qinds:
p0 = permute.dot([p, q, 0])
i0 = tuple(p0)
if filled[i0]:
voxel_faces[i0].append(p0 + square_rot)
# draw middle faces
for r1, r2 in zip(rinds[:-1], rinds[1:]):
p1 = permute.dot([p, q, r1])
p2 = permute.dot([p, q, r2])
i1 = tuple(p1)
i2 = tuple(p2)
if filled[i1] and (internal_faces or not filled[i2]):
voxel_faces[i1].append(p2 + square_rot)
elif (internal_faces or not filled[i1]) and filled[i2]:
voxel_faces[i2].append(p2 + square_rot)
# draw upper faces
pk = permute.dot([p, q, rc-1])
pk2 = permute.dot([p, q, rc])
ik = tuple(pk)
if filled[ik]:
voxel_faces[ik].append(pk2 + square_rot)
# iterate over the faces, and generate a Poly3DCollection for each voxel
polygons = {}
for coord, faces_inds in voxel_faces.items():
# convert indices into 3D positions
if xyz is None:
faces = faces_inds
else:
faces = []
for face_inds in faces_inds:
ind = face_inds[:, 0], face_inds[:, 1], face_inds[:, 2]
face = np.empty(face_inds.shape)
face[:, 0] = x[ind]
face[:, 1] = y[ind]
face[:, 2] = z[ind]
faces.append(face)
poly = art3d.Poly3DCollection(faces,
facecolors=facecolors[coord],
edgecolors=edgecolors[coord],
**kwargs
)
self.add_collection3d(poly)
polygons[coord] = poly
return polygons
spatial_axes = [5, 5, 5]
filled = np.ones(spatial_axes, dtype=np.bool)
colors = np.empty(spatial_axes + [4], dtype=np.float32)
alpha = .5
colors[0] = [1, 0, 0, alpha]
colors[1] = [0, 1, 0, alpha]
colors[2] = [0, 0, 1, alpha]
colors[3] = [1, 1, 0, alpha]
colors[4] = [0, 1, 1, alpha]
# set all internal colors to black with alpha=1
colors[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1, 0:3] = 0
colors[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1, 3] = 1
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot('111', projection='3d')
ax.voxels = types.MethodType(voxels, ax)
ax.voxels(filled, facecolors=colors, edgecolors='k',internal_faces=True)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot('111', projection='3d')
ax.voxels = types.MethodType(voxels, ax)
filled[-1] = False
ax.voxels(filled, facecolors=colors, edgecolors='k',internal_faces=True)
plt.show()
-
我使用的是React Router v4的最新版本,我试图在div中呈现我的页面组件Home/About,但我遇到的问题是,如果我将路由添加到我的头中,它将切换路由,但它们将显示Home/About组件作为头的一部分,而不是我希望它们出现的位置。 如果我将路由放入中,则路由器不工作,但不会在控制台上抛出任何错误。 如何在div中显示和切换组件? 网页链接 app.js Header.js home
-
问题内容: 我需要能够在文本区域(即,,,)中呈现一些HTML标记,但是textareas仅将其内容解释为文本。有没有一种简单的方法,而无需依赖外部库/插件(我正在使用jQuery)?如果没有,您知道我可以使用任何jQuery插件吗? 问题答案: 这与不可能。您正在寻找的是一个内容可编辑的 div,这很容易做到:
-
我想知道我是否可以使用MathJax渲染LaTeX符号,而不封装LaTeX符号周围的\(......\)。例如,对于\frac{2}{3}而不是\(\frac{2}{3}\),如果是,我如何设置它? 非常感谢!
-
问题内容: 我需要能够在文本区域(即)中呈现一些HTML标记,但是textareas仅将其内容解释为文本。有没有一种简单的方法,而无需依赖外部库/插件(我正在使用jQuery)?如果没有,您知道我可以使用任何jQuery插件吗? 问题答案: 这与不可能。您正在寻找的是一个内容可编辑的 div,这很容易做到: jsFiddle
-
本文向大家介绍说说页面中字体渲染规则是怎样的?会有哪些因素影响字体的渲染?相关面试题,主要包含被问及说说页面中字体渲染规则是怎样的?会有哪些因素影响字体的渲染?时的应答技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 字体渲染: 1.解码,根据web服务器返回的(或者本地网页本身的)content-type charset等信息确定编码,将网页解码成Unicode字符流; 2.分段,把文本分为由不同语言(中文、
-
问题内容: 我一直在尝试增强我用Java编写的GUI系统,以使用亚 像素抗锯齿功能,并且除两个剩余的 异常现象之外,都已经取得了成功。这是我的一个后续从几个星期的其他问题 之前。 第一个问题是将渲染提示KEY_ANTIALIASING设置为 VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON会导致将KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING设置 为LCD(子像素)AA值时被忽略。谁能对此有所启发?目前,我 被迫

