云的实施(Implementation of Cloud)
优质
小牛编辑
136浏览
2023-12-01
Cloud computing可以定义为通过Internet提供给用户的托管服务的集合。 它使组织能够使用甚至计算资源,包括虚拟机(VM),存储或应用程序作为实用程序。
在Python编程语言中构建应用程序的最重要优势之一是它包括在任何平台上虚拟部署应用程序的能力,包括cloud 。 这意味着Python可以在云服务器上执行,也可以在台式机,平板电脑或智能手机等便捷设备上启动。
其中一个有趣的观点是通过生成Rainbow tables创建云基础。 它有助于集成应用程序的单个和多个处理版本,这需要一些考虑因素。
Pi Cloud
Pi Cloud是云计算平台,它将Python编程语言与Amazon Web Services的计算能力集成在一起。
我们来看一个用rainbow tables实现Pi云的例子。
彩虹表
rainbow table被定义为特定于给定散列算法的加密密码的所有可能的纯文本排列的列表。
彩虹表遵循标准模式,创建一个散列密码列表。
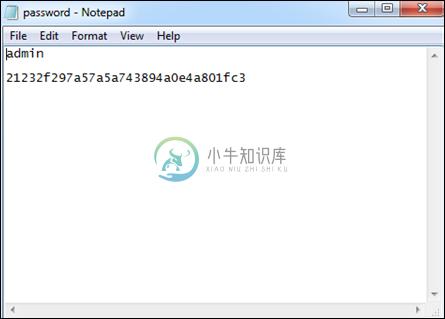
文本文件用于生成密码,其中包括要加密的密码的字符或纯文本。
该文件由Pi cloud使用,它调用要存储的主函数。
散列密码的输出也存储在文本文件中。
此算法也可用于在数据库中保存密码,并在云系统中具有备份存储。
以下内置程序在文本文件中创建加密密码列表。
例子 (Example)
import os
import random
import hashlib
import string
import enchant #Rainbow tables with enchant
import cloud #importing pi-cloud
def randomword(length):
return ''.join(random.choice(string.lowercase) for i in range(length))
print('Author- Radhika Subramanian')
def mainroutine():
engdict = enchant.Dict("en_US")
fileb = open("password.txt","a+")
# Capture the values from the text file named password
while True:
randomword0 = randomword(6)
if engdict.check(randomword0) == True:
randomkey0 = randomword0+str(random.randint(0,99))
elif engdict.check(randomword0) == False:
englist = engdict.suggest(randomword0)
if len(englist) > 0:
randomkey0 = englist[0]+str(random.randint(0,99))
else:
randomkey0 = randomword0+str(random.randint(0,99))
randomword3 = randomword(5)
if engdict.check(randomword3) == True:
randomkey3 = randomword3+str(random.randint(0,99))
elif engdict.check(randomword3) == False:
englist = engdict.suggest(randomword3)
if len(englist) > 0:
randomkey3 = englist[0]+str(random.randint(0,99))
else:
randomkey3 = randomword3+str(random.randint(0,99))
if 'randomkey0' and 'randomkey3' and 'randomkey1' in locals():
whasher0 = hashlib.new("md5")
whasher0.update(randomkey0)
whasher3 = hashlib.new("md5")
whasher3.update(randomkey3)
whasher1 = hashlib.new("md5")
whasher1.update(randomkey1)
print(randomkey0+" + "+str(whasher0.hexdigest())+"\n")
print(randomkey3+" + "+str(whasher3.hexdigest())+"\n")
print(randomkey1+" + "+str(whasher1.hexdigest())+"\n")
fileb.write(randomkey0+" + "+str(whasher0.hexdigest())+"\n")
fileb.write(randomkey3+" + "+str(whasher3.hexdigest())+"\n")
fileb.write(randomkey1+" + "+str(whasher1.hexdigest())+"\n")
jid = cloud.call(randomword) #square(3) evaluated on PiCloud
cloud.result(jid)
print('Value added to cloud')
print('Password added')
mainroutine()
输出 (Output)
此代码将生成以下输出 -
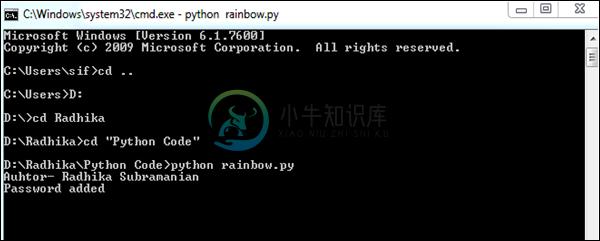
密码存储在文本文件中,这些文件是可见的,如以下屏幕截图所示。