Mandelbrot Set
Visualizing the Mandelbrot set doesn't have anything to do with machine learning, but it makes for a fun example of how one can use TensorFlow for general mathematics. This is actually a pretty naive implementation of the visualization, but it makes the point. (We may end up providing a more elaborate implementation down the line to produce more truly beautiful images.)
Note: This tutorial was originally prepared as an IPython notebook.
Basic Setup
We'll need a few imports to get started.
# Import libraries for simulation
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# Imports for visualization
import PIL.Image
from cStringIO import StringIO
from IPython.display import clear_output, Image, display
import scipy.ndimage as ndNow we'll define a function to actually display the image once we have iteration counts.
def DisplayFractal(a, fmt='jpeg'):
"""Display an array of iteration counts as a
colorful picture of a fractal."""
a_cyclic = (6.28*a/20.0).reshape(list(a.shape)+[1])
img = np.concatenate([10+20*np.cos(a_cyclic),
30+50*np.sin(a_cyclic),
155-80*np.cos(a_cyclic)], 2)
img[a==a.max()] = 0
a = img
a = np.uint8(np.clip(a, 0, 255))
f = StringIO()
PIL.Image.fromarray(a).save(f, fmt)
display(Image(data=f.getvalue()))Session and Variable Initialization
For playing around like this, we often use an interactive session, but a regular session would work as well.
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()It's handy that we can freely mix NumPy and TensorFlow.
# Use NumPy to create a 2D array of complex numbers on [-2,2]x[-2,2]
Y, X = np.mgrid[-1.3:1.3:0.005, -2:1:0.005]
Z = X+1j*YNow we define and initialize TensorFlow tensors.
xs = tf.constant(Z.astype("complex64"))
zs = tf.Variable(xs)
ns = tf.Variable(tf.zeros_like(xs, "float32"))TensorFlow requires that you explicitly initialize variables before using them.
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()Defining and Running the Computation
Now we specify more of the computation...
# Compute the new values of z: z^2 + x
zs_ = zs*zs + xs
# Have we diverged with this new value?
not_diverged = tf.complex_abs(zs_) < 4
# Operation to update the zs and the iteration count.
#
# Note: We keep computing zs after they diverge! This
# is very wasteful! There are better, if a little
# less simple, ways to do this.
#
step = tf.group(
zs.assign(zs_),
ns.assign_add(tf.cast(not_diverged, "float32"))
)... and run it for a couple hundred steps
for i in range(200): step.run()Let's see what we've got.
DisplayFractal(ns.eval())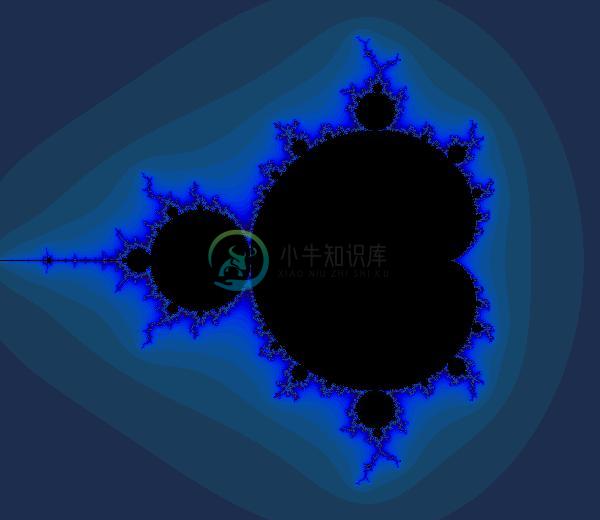
Not bad!

