1.3.2 使用示例
使用——一个场景示例
我们打算用Pact测试在消费者Zoo App和提供者Animal Service之间写一个集成测试。在消费者项目中,我们打算使用一个模型(Alligator类)来表示从Animal Service返回的数据,以及一个客户端(AnimalServiceClient)来负责向Animal Service发起HTTP调用。
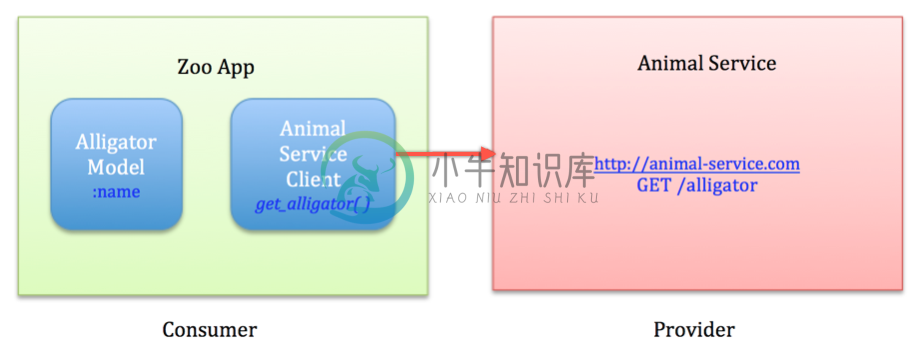
在Zoo App(消费者)项目中
1. 从模型类开始
设想有一个类似这样的模型类。Alligator的属性依赖于远程服务,需要通过向Animal Service发HTTP调用才能够取到。
class Alligator
attr_reader :name
def initialize name
@name = name
end
def == other
other.is_a?(Alligator) && other.name == name
end
end
2. 创建Animal Service客户端类的骨架
设想有一个类似这样的Animal Service客户端类。
require 'httparty'
class AnimalServiceClient
include HTTParty
base_uri 'http://animal-service.com'
def get_alligator
# Yet to be implemented because we're doing Test First Development...
end
end
3. 配置模拟的Animal Service
以下代码将在localhost:1234端口上创建一个模拟的服务,用于对应用的HTTP查询请求作出响应,就像是真实的“Animal Service”一样。这里还创建了一个模拟的提供者对象,用于设置期望值。用于访问模拟的服务提供者的名字可以是你在服务参数中所给出的任何名字——在本例中为“animal_service”。
# In /spec/service_providers/pact_helper.rb
require 'pact/consumer/rspec'
# or require 'pact/consumer/minitest' if you are using Minitest
Pact.service_consumer "Zoo App" do
has_pact_with "Animal Service" do
mock_service :animal_service do
port 1234
end
end
end
4. 给Animal Service客户端写一个失败的测试用例
# In /spec/service_providers/animal_service_client_spec.rb
# When using RSpec, use the metadata `:pact => true` to include all the pact functionality in your spec.
# When using Minitest, include Pact::Consumer::Minitest in your spec.
describe AnimalServiceClient, :pact => true do
before do
# Configure your client to point to the stub service on localhost using the port you have specified
AnimalServiceClient.base_uri 'localhost:1234'
end
subject { AnimalServiceClient.new }
describe "get_alligator" do
before do
animal_service.given("an alligator exists").
upon_receiving("a request for an alligator").
with(method: :get, path: '/alligator', query: '').
will_respond_with(
status: 200,
headers: {'Content-Type' => 'application/json'},
body: {name: 'Betty'} )
end
it "returns a alligator" do
expect(subject.get_alligator).to eq(Alligator.new('Betty'))
end
end
end
5. 执行测试用例
执行AnimalServiceClient用例,将会在一个可配置的pact文件夹(默认为spec/pacts)下生成一个pact文件。
日志将输出在一个可配置的日志文件夹(默认为log)下,可用于诊断问题。
当然,以上这个用例将会失败,因为Animal Service的客户端方法还没有实现,那么下一步,来实现你的提供者客户端方法吧。
6. 实现Animal Service的消费者客户端方法
class AnimalServiceClient
include HTTParty
base_uri 'http://animal-service.com'
def get_alligator
name = JSON.parse(self.class.get("/alligator").body)['name']
Alligator.new(name)
end
end
7. 再次运行该用例
通过!现在你就会得到一个pact文件,可用于在Animal Service提供者端的项目中验证期望。
现在,对于其他可能的返回状态码重复上述步骤。例如,考虑以下场景中你的客户端需要如何响应:
- 404(返回null,还是抛出错误?)
- 500(具体说明响应体中所包含的错误信息,并确保客户端日志记录下了这些错误信息,这样当出现问题时会省很多事)
- 校验授权时是否需要返回401/403。
在Animal Service(提供者)项目中
1. 创建API类的骨架
使用你所选择的框架创建API类(Pact的作者更喜欢使用Webmachine和Roar)——先不用实现方法,我们要做测试优先开发,还记得吧?
2. 告诉提供者需要遵守之前的pact文件中的规约
在Rakefile中引入“pact/tasks”。
# In Rakefile
require 'pact/tasks'
在服务提供者项目中创建名为pact_helper.rb的文件。推荐放在spec/service_consumers/pact_helper.rb下。
更多信息,查看配置文档中的验证契约和提供者章节。
# In specs/service_consumers/pact_helper.rb
require 'pact/provider/rspec'
Pact.service_provider "Animal Service" do
honours_pact_with 'Zoo App' do
# This example points to a local file, however, on a real project with a continuous
# integration box, you would use a [Pact Broker](https://github.com/bethesque/pact_broker) or publish your pacts as artifacts,
# and point the pact_uri to the pact published by the last successful build.
pact_uri '../zoo-app/specs/pacts/zoo_app-animal_service.json'
end
end
3. 运行失败的测试
$ rake pact:verify
恭喜你!现在你有一个失败的测试需要通过了。
在这一阶段,你可能会想要在每实现一个特性之后能够只运行众多用例中的某一个。在pact:verify的失败输出结果的底部,你可以看到用于重新独立运行每条失败的请求的命令。只运行一条请求的命令类似这样:
$ rake pact:verify PACT_DESCRIPTION="a request for an alligator" PACT_PROVIDER_STATE="an alligator exists"
4. 实现代码让你的第一个测试用例通过
然后重复上述步骤。
5. 如此继续直到所有测试通过
耶!你的Animal Service现在已经可以遵守与你的Zoo App消费者之间的契约了。现在你就有把握让你的消费者和提供者一起很好地工作了。

