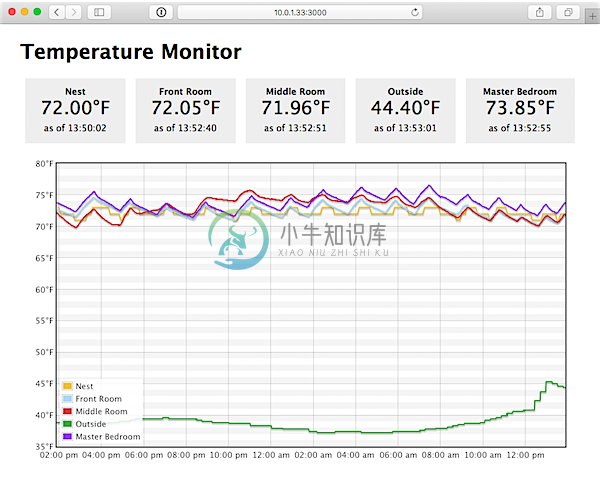
Simple Temperature Monitoring App
I've created this project to power a network of temperature and environmental monitors in my home.
The architecture uses one 'master' Pi to aggregate and display log data, and many 'remotes' place around a house to send log data back to the 'master'.
I recommend a Pi model 2 B for the master (since it's running a heavier-weight Node.js-based application, but you can use any Pi for the remotes. I use the A+ or Zero for remotes since they're cheap and use minimal power when running headless.
Each Pi should already have:
- Raspbian running on the microSD card, with
raspi-configsetup already completed. - Networking configured (either wired LAN or WiFi via USB).
This is a living project, so a lot of things will change while I experiment with making my monitoring more robust, more fully-featured, and eventually, more integrated with my smart thermostat and other environmental controls.
Vagrant quickstart for hacking
Set up the virtual machine:
- Install Vagrant, VirtualBox and Ansible.
cdintoplaybooksand runansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yml.cdback into this directory and runvagrant up.
Overall Setup
Before anything else, you need to install Ansible, then do the following:
- Copy
example.config.ymltoconfig.yml, andinventory-exampletoinventory, and update the values inside to match your desired environment and Pi IP addresses. - Run
ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.ymlinside theplaybooksdirectory to install the required Ansible roles.
Raspberry Pi Master Setup (Data Logger & Dashboard App)
An Ansible playbook builds the master logger and dashboard Pi, installing all the requirements for the Node.js-based data logger and dashboard app for viewing temperature data.
Run the Ansible playbook to configure the master Pi and start the dashboard app: ansible-playbook -i config/inventory playbooks/master/main.yml
Raspberry Pi Remote(s) Setup (Temperature Monitors)
An Ansible playbook builds the remote temperature monitoring Pi(s), installing all the requirements for the Python-based temperature data collection scripts. It also starts the script and begins sending temperature data to the Master Pi.
Before running the Ansible playbook to configure the remote(s), add a file named after the hostname or IP address of each remote Raspberry Pi inside config/host_vars (e.g. if the Pi's IP is 10.0.1.34, then add a host_vars file named 10.0.1.34 and put overrides inside, like the local_sensor_id for that Pi).
Run the Ansible playbook to configure the remote Pi(s): ansible-playbook -i config/inventory playbooks/remote-monitor/main.yml
scripts - Python Scripts for Logging Data
The scripts directory contains a variety of temperature logging scripts, written in Python, to assist with logging temperatures from DS18B20 1-Wire temperature sensors (connected via Raspberry Pi GPIO ports), external weather APIs, and even the Nest learning thermostat.
Connecting the Raspberry Pi to the DS18B20
Connect the DS18B20 to your Pi
You can use a breadboard, a shield, a GPIO ribbon cable, or whatever, but you basically need to connect the following (this is using the waterproof sensor—follow diagrams found elsewhere for the small transistor-sized chip):
- 3V3 - Red wire
- Ground - Black wire
- GPIO 4 - Yellow wire (with 4.7K pull-up resistor between this and 3V3).
The 3V3 and Ground wire can be connected to any 3.3V or Ground pin, respectively (follow this great Raspberry Pi pinout diagram for your model of Pi), but by default, the 1-Wire library uses GPIO pin 4, which is the 7th physical pin on a B+/A+/B rev 2.
Edit /boot/config.txt and add the configuration line dtoverlay=w1-gpio, then reboot the Raspberry Pi (note that this configuration is done for you when you run the remote-monitor playbook).
To test whether the DS18B20 is working, you can cd into /sys/bus/w1/devices. ls the contents, and you should see a directory like 28-xxxxxxx, one directory per connected sensor. cd into that directory, then cat w1_slave, and you should see some output, with a value like t=23750 at the end. This is the temperature value. Divide by 1,000 and you have the value in °C.
Outdoor temperature logging via Weather APIs
There are multiple scripts for reading current local temperatures via online weather APIs:
- Open Weather Map API, using
scripts/outdoor-temps-owm.py. (No signup required, rate limit not specified, but temperature data is only updated about every 15-30 minutes). - Weather Underground API, using
scripts/outdoor-temps-wu.py. This API requires a 'paid' account, but the free plan allows for 500 calls per day, up to 10/min. This would allow you to call the API via cron every 3 minutes, maximum. The data is more real-time, but you have to sign up for access and can't poll the service as often as OWM. You must set two environment variables,WU_API_KEYandWU_LOCATION(e.g.MO/Saint_Louis, to use this script.
The Ansible playbook for the master Pi will automatically configure a cron job to get data from the Weather Underground API every minute if you have an API key configured in config/config.yml.
Notes:
- Prior to logging outdoor temperatures, you should add a sensor within the Dashboard app and set the id inside
config/config.yml. Seedashboard's API documentation for more info. - If you need to diagnose cron issues, install
postfixusingsudo apt-get install -y postfix, and remove the> /dev/null 2>&1from the end of the line in the cron job.
Nest temperature logging via Nest API
There is another script, nest-temps.py, which requires you to have a Nest Developer account for API access. More information inside that script for now, but basically, once you're configured, get an access token then find your Nest thermostat ID.
The Ansible playbook for the master Pi will automatically configure a cron job to get data from the Nest Developer API every 5 minutes if you have an API key configured in config/config.yml.
Notes:
- Nest's API documentation suggests "To avoid errors, we recommend you limit requests to one call per minute, maximum.", and since every call requires the Nest to wake up to return data to Nest's API servers, the default setting calls the API only once every 5 minutes.
- If you need to diagnose cron issues, install
postfixusingsudo apt-get install -y postfix, and remove the> /dev/null 2>&1from the end of the line in the cron job.
dashboard - Express App/API for Displaying and Adding Data
Once the master Pi is set up, you can view the dashboard app at http://[raspberry-pi-ip]:3000/ (where [raspberry-pi-ip] is the IP address or domain name of your Raspberry Pi).
dashboard API
The dashboard app has a simple REST API that allows you to add sensors to your dashboard, send temperature data directly to the dashboard from other devices, and retrieve sensor and temperature information.
More documentation may be added, but here's a list of the relevant API endpoints and example usage:
/sensorsGET: Returns a listing of all sensor data.POST: Send a POST request with alocation(maximum 255 characters) andgroup(maximum 32 characters) parameter, and it will respond with a new sensor ID.DELETE: Not yet implemented.
/tempsPOST: Send a POST request with asensor,temp, andtimeparameter, and it will respond with a new temperature record ID.GET/temps/:id: Get temperature data for a given sensor ID from the past 24h (by default). Add parameterstartTimeto set a starting time.GET/temps/all: Get temperature data from all sensors the past 24h (by default). Add parameterstartTimeto set a starting time.
The API returns the following HTTP Status Codes:
200on success400if you are missing some data or have an otherwise-invalid request501if the method you're using is not yet implemented
An error message will also be returned in the body of the response.
License
MIT
Author
This project was created in 2015 by Jeff Geerling.
-
[200830] temperature monitoring CPU Use ‘lm_sensors’ to monitor CPU: Linux 查看CPU温度 # check rpm -q lm_sensors # install sudo apt-get install lm-sensors -y # configure sensors yes | sudo sensors-detect
-
# smartctl -i /dev/sda smartctl version 5.38 [x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu] Copyright (C) 2002-8 Bruce Allen Home page is http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net/ === START OF INFORMATION SECTION === Model F
-
一、CPU负载计算的实用程序 平均负载表示了对CPU 资源的需求,通过汇总正在运行的线程数(使用率)和正在排队等待运行的线程数(饱和度)计算得出。计算平均负载的一个新方法是把使用率加上线程调度器延时得出,而不是去取样队列长度,从而提高精度。 这个值的意义为,平均负载大于CPU 数量表示CPU 不足以服务线程,有些线程在等待。如果平均负载小于CPU 数量,这(很可能)代表还有一些余量,线程可以在它们
-
Monitor算法温控的常见算法之一,在main函数中调用了thermal_monitor函数.Monitor算法是一种静态算法,当超过每一个设置的温度值就会调频,当小于clr的温度就会停止调频算法。 1. thermal_monitor函数 thermal_monitor函数先是从dev_list中获取了各个device_info放入device_info_arr中,然后过滤setting放入t
-
现在天气越来越热了,使用笔记本的人,一定都有烤'猪蹄'的感觉了。特别是使用UBUNTU系统的人。我推荐一个目前我在使用的测试温度的软件。 Computer Temperature Monitor,在Ubuntu的软件中心里面有,也可以到官方网站上下载一个。 安装完后在gnome面板上右键添加到面板,会找到Computer Temperature Monitor,添加就可以用了。 更多屏幕截图请看:
-
DEPRECATION NOTICE This package is deprecated. Please use homebridge-mqtthing instead. It is more mature, better tested, and offers additional-features. homebridge-mqtt-temperature Get Temperature Sen
-
Bluetooth temperature sensors Read Bluetooth Advertising Packets from BLE temperature sensors and publish data to MQTT. This C language program runs on Linux. I have successfully used it on Raspberry
-
homebridge-temperature-file This is a plugin for homebridge which makes it possible to create a temperature sensorin HomeKit via file. Why via file? When you have a DHT-sensor, you need sudo to read f
-
homebridge-raspberrypi-temperature a homebridge plugin that get RaspberryPi CPU temperature. Configuration simple configuration "accessories": [{ "accessory": "RaspberryPiTemperature", "name": "
-
homebridge-http-temperature-sensor Plugin This Homebridge plugin can be used integrate your temperature sensor which has ahttp api into HomeKit. Installation First of all you need to have Homebridge i