python实现马丁策略的实例详解
马丁策略本来是一种赌博方法,但在投资界应用也很广泛,不过对于投资者来说马丁策略过于简单,所以本文将其改进并使得其在震荡市中获利,以下说明如何实现马丁策略。
策略
逢跌加仓,间隔由自己决定,每次加仓是当前仓位的一倍。
连续跌两次卖出,且卖出一半仓位。
如果爆仓则全仓卖出止损。
初始持仓设置为10%~25%,则可进行2到3次补仓。
初始化马丁策略类属性
def __init__(self,startcash, start, end): self.cash = startcash #初始化现金 self.hold = 0 #初始化持仓金额 self.holdper = self.hold /startcash #初始化仓位 self.log = [] #初始化日志 self.cost = 0 #成本价 self.stock_num = 0 #股票数量 self.starttime = start #起始时间 self.endtime = end #终止时间 self.quantlog = [] #交易量记录 self.earn = [] #总资产记录 self.num_log = [] self.droplog = [0]
为了记录每次买卖仓位的变化初始化了各种列表。
交易函数
首先导入需要的模块
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import tushare as ts import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def buy(self, currentprice, count):
self.cash -= currentprice*count
self.log.append('buy')
self.hold += currentprice*count
self.holdper = self.hold / (self.cash+ self.hold)
self.stock_num += count
self.cost = self.hold / self.stock_num
self.quantlog.append(count//100)
print('买入价:%.2f,手数:%d,现在成本价:%.2f,现在持仓:%.2f,现在筹码:%d' %(currentprice ,count//100, self.cost, self.holdper, self.stock_num//100))
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
self.droplog = [0]
def sell(self, currentprice, count):
self.cash += currentprice*count
self.stock_num -= count
self.log.append('sell')
self.hold = self.stock_num*self.cost
self.holdper = self.hold / (self.cash + self.hold)
#self.cost = self.hold / self.stock_num
print('卖出价:%.2f,手数:%d,现在成本价:%.2f,现在持仓:%.2f,现在筹码:%d' %(currentprice ,count//100, self.cost, self.holdper, self.stock_num//100))
self.quantlog.append(count//100)
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
def holdstock(self,currentprice):
self.log.append('hold')
#print('持有,现在仓位为:%.2f。现在成本:%.2f' %(self.holdper,self.cost))
self.quantlog.append(0)
self.earn.append(self.cash+ currentprice*self.stock_num)
self.num_log.append(self.stock_num)
持仓成本的计算方式是利用总持仓金额除以总手数,卖出时不改变持仓成本。持有则是不做任何操作只记录日志
数据接口
def get_stock(self, code): df=ts.get_k_data(code,autype='qfq',start= self.starttime ,end= self.endtime) df.index=pd.to_datetime(df.date) df=df[['open','high','low','close','volume']] return df
数据接口使用tushare,也可使用pro接口,到官网注册领取token。
token = '输入你的token' pro = ts.pro_api() ts.set_token(token) def get_stock_pro(self, code): code = code + '.SH' df = pro.daily(ts_code= code, start_date = self.starttime, end_date= self.endtime) return df
数据结构:
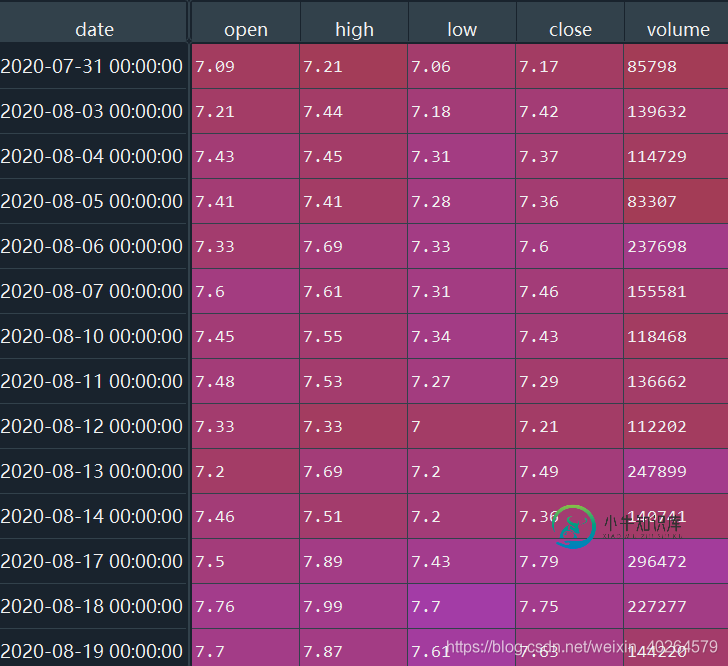
回测函数
def startback(self, data, everyChange, accDropday):
"""
回测函数
"""
for i in range(len(data)):
if i < 1:
continue
if i < accDropday:
drop = backtesting.accumulateVar(everyChange, i, i)
#print('现在累计涨跌幅度为:%.2f'%(drop))
self.martin(data[i], data[i-1], drop, everyChange,i)
elif i < len(data)-2:
drop = backtesting.accumulateVar(everyChange, i, accDropday)
#print('现在累计涨跌幅度为:%.2f'%(drop))
self.martin(data[i],data[i-1], drop, everyChange,i)
else:
if self.stock_num > 0:
self.sell(data[-1],self.stock_num)
else: self.holdstock(data[i])
因为要计算每日涨跌幅,要计算差分,所以第一天的数据不能计算在for循环中跳过,accDropday是累计跌幅的最大计算天数,用来控制入场,当累计跌幅大于某个数值且仓位为0%时可再次入场。以下是入场函数:
def enter(self, currentprice,ex_price,accuDrop):
if accuDrop < -0.01:#and ex_price > currentprice:
count = (self.cash+self.hold) *0.24 // currentprice //100 * 100
print('再次入场')
self.buy(currentprice, count)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
入场仓位选择0.24则可进行两次抄底,如果抄底间隔为7%可承受最大跌幅为14%。
策略函数
def martin(self, currentprice, ex_price, accuDrop,everyChange,i):
diff = (ex_price - currentprice)/ex_price
self.droplog.append(diff)
if sum(self.droplog) <= 0:
self.droplog = [0]
if self.stock_num//100 > 1:
if sum(self.droplog) >= 0.04:
if self.holdper*2 < 0.24:
count =(self.cash+self.hold) *(0.25-self.holdper) // currentprice //100 * 100
self.buy(currentprice, count)
elif self.holdper*2 < 1 and (self.hold/currentprice)//100 *100 > 0 and backtesting.computeCon(self.log) < 5:
self.buy(currentprice, (self.hold/currentprice)//100 *100)
else: self.sell(currentprice, self.stock_num//100 *100);print('及时止损')
elif (everyChange[i-2] < 0 and everyChange[i-1] <0 and self.cost < currentprice):# or (everyChange[i-1] < -0.04 and self.cost < currentprice):
if (self.stock_num > 0) and ((self.stock_num*(1/2)//100*100) > 0):
self.sell(currentprice, self.stock_num*(1/2)//100*100 )
#print("现在累计涨跌幅为: %.3f" %(accuDrop))
elif self.stock_num == 100: self.sell(currentprice, 100)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
else: self.holdstock(currentprice)
else: self.enter(currentprice,ex_price,accuDrop)
首先构建了droplog专门用于计算累计涨跌幅,当其大于0时重置为0,每次购买后也将其重置为0。当跌幅大于0.04则买入,一下为流程图(因为作图软件Visustin为试用版所以有水印,两个图可以结合来看):


此策略函数可以改成其他策略甚至是反马丁,因为交易函数可以通用。
作图和输出结果
buylog = pd.Series(broker.log)
close = data.copy()
buy = np.zeros(len(close))
sell = np.zeros(len(close))
for i in range(len(buylog)):
if buylog[i] == 'buy':
buy[i] = close[i]
elif buylog[i] == 'sell':
sell[i] = close[i]
buy = pd.Series(buy)
sell = pd.Series(sell)
buy.index = close.index
sell.index = close.index
quantlog = pd.Series(broker.quantlog)
quantlog.index = close.index
earn = pd.Series(broker.earn)
earn.index = close.index
buy = buy.loc[buy > 0]
sell = sell.loc[sell>0]
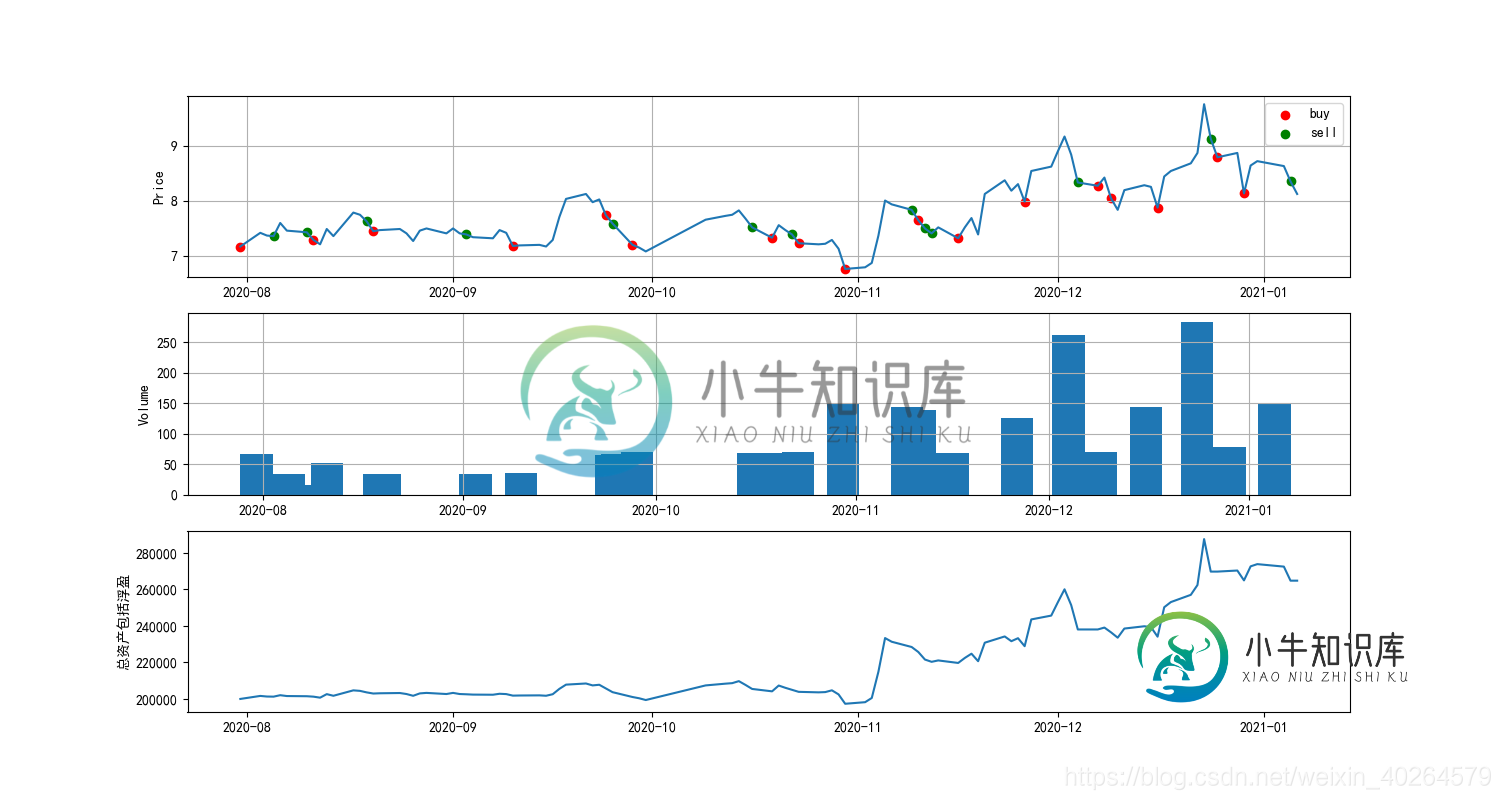
plt.plot(close)
plt.scatter(buy.index,buy,label = 'buy')
plt.scatter(sell.index,sell, label = 'sell')
plt.title('马丁策略')
plt.legend()
#画图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3,figsize=(15,8))
ax1.plot(close)
ax1.scatter(buy.index,buy,label = 'buy',color = 'red')
ax1.scatter(sell.index,sell, label = 'sell',color = 'green')
ax1.set_ylabel('Price')
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.legend()
ax1.xaxis_date()
ax2.bar(quantlog.index, quantlog, width = 5)
ax2.set_ylabel('Volume')
ax2.xaxis_date()
ax2.grid(True)
ax3.xaxis_date()
ax3.plot(earn)
ax3.set_ylabel('总资产包括浮盈')
plt.show()
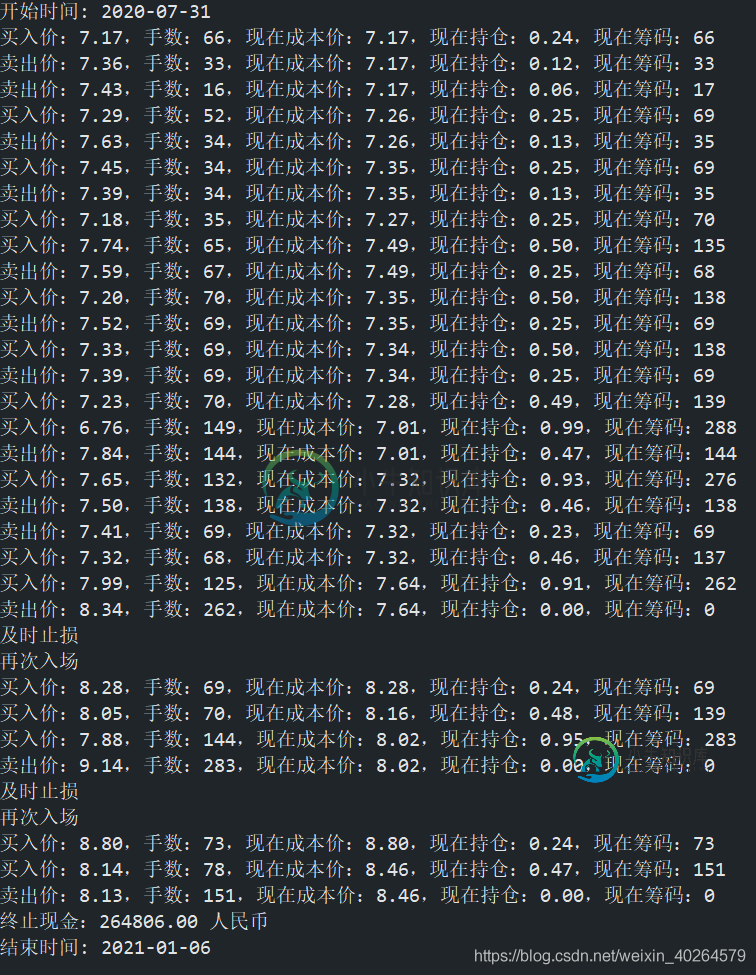
交易日志
到此这篇关于python实现马丁策略的实例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python马丁策略内容请搜索小牛知识库以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持小牛知识库!
-
本文向大家介绍Python设计模式之策略模式实例详解,包括了Python设计模式之策略模式实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Python设计模式之策略模式。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 策略模式(Strategy Pattern):它定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化,不会影响到使用算法的客户. 下面是一个商场活动的实现 运行
-
本文向大家介绍PHP实现的策略模式示例,包括了PHP实现的策略模式示例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了PHP实现的策略模式。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 个人觉得设计模式只有在实际应用中才能够慢慢的去熟悉,到最后做到心中有模式,事事有模式,哈哈 例如:一个电商首页,可以根据登陆用户的性别不同显示不同的内容,比如广告和商品类别。 传统方法:在程序内部使用多个if,else
-
本文向大家介绍Python实现DDos攻击实例详解,包括了Python实现DDos攻击实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 SYN 泛洪攻击 SYN泛洪攻击是一种比较常用的Dos方式之一。通过发送大量伪造的 TCP 连接请求,使被攻击主机资源耗尽(通常是 CPU 满负荷或内存不足)的攻击方式 我们都知道建立 TCP 连接需要三次握手。正常情况下客户端首先向服务器端发送SYN报文,随后服
-
本文向大家介绍PHP实现的策略模式简单示例,包括了PHP实现的策略模式简单示例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了PHP实现的策略模式。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 比如说购物车系统,在给商品计算总价的时候,普通会员肯定是商品单价乘以数量,但是对中级会员提供8者折扣,对高级会员提供7折折扣,这种场景就可以使用策略模式实现: 更多关于PHP相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:
-
本文向大家介绍python encrypt 实现AES加密的实例详解,包括了python encrypt 实现AES加密的实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 AES加密方式有五种 : ECB, CBC, CTR, CFB, OFB 从安全性角度推荐cbc算法 windows 下安装 : pip install pycryptodome linux 下安装 : pip install
-
问题内容: 我决定将Log4J日志记录框架用于新的Java项目。我想知道应该使用什么策略来创建/管理Logger实例,为什么? 每个类一个Logger实例,例如 } 每个线程一个Logger实例 每个应用程序一个Logger实例 水平切片:应用程序每一层(例如,视图层,控制器层和持久层)中Logger的一个实例 垂直切片:应用程序功能分区内Logger的一个实例 注意:这些文章在某种程度上已经考虑

