iOS开发中常见的项目文件与MVC结构优化思路解析
常见的项目文件介绍
一、项目文件结构示意图
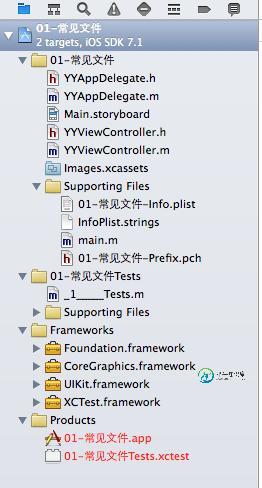
二、文件介绍
1.products文件夹:主要用于mac电脑开发的可执行文件,ios开发用不到这个文件
2.frameworks文件夹主要用来放依赖的框架
3.test文件夹是用来做单元测试的
4.常用的文件夹(项目名称文件夹)
(1)XXXinfo.plist文件(在该项目中为 01-常见文件-Info.plist)
1)简单说明
是配置文件,该文件对工程做一些运行期的配置,非常重要,不能删除。
在旧版本xcode创建的工程中,这个配置文件的名字就叫做info.plist。
注意:因此在载入自己准备的plist文件的时候,不要以info命名。
2)配置文件的属性介绍:
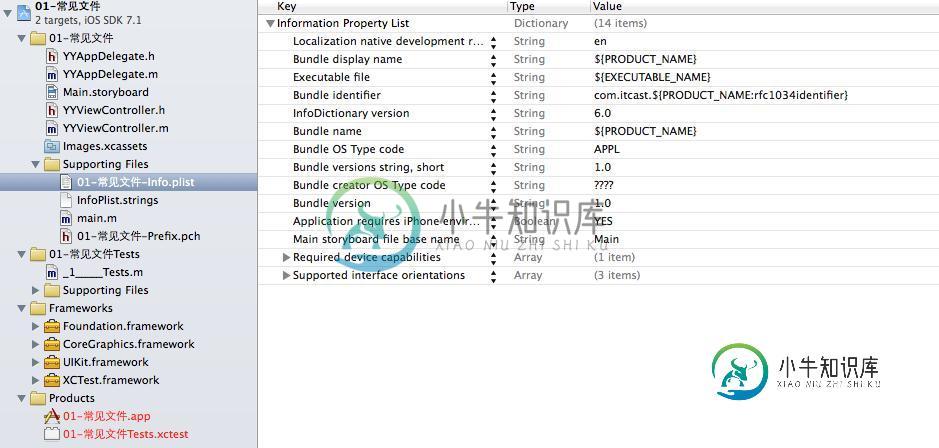
bundle display name:
应用程序显示名称。如果要修改桌面上显示的文件名称,只要修改此处就可以了。(需要先删除原始的程序,然后清空一下工程,因为程序有缓存)
bundle identifer:
唯一标识符(唯一的标识着一个应用程序,为了保证程序的唯一性,通常把域名倒过来写)
Bundle versions string, short和bundle versions
两个都用来表示应用程序的版本,前面的版本是正式的版本,后面的为内部版本,即公司内部开发的版本。要求提示:上传app的时候,后面更新的版本必须比之前的版本大。
main storyboard file base name
最主要的storyboard
有两种方式修改plist配置文件:
第一种方式即在如图所示的界面对配置信息进行修改。
第二种方式直接点击工程,可以通过可视化界面进行设置。
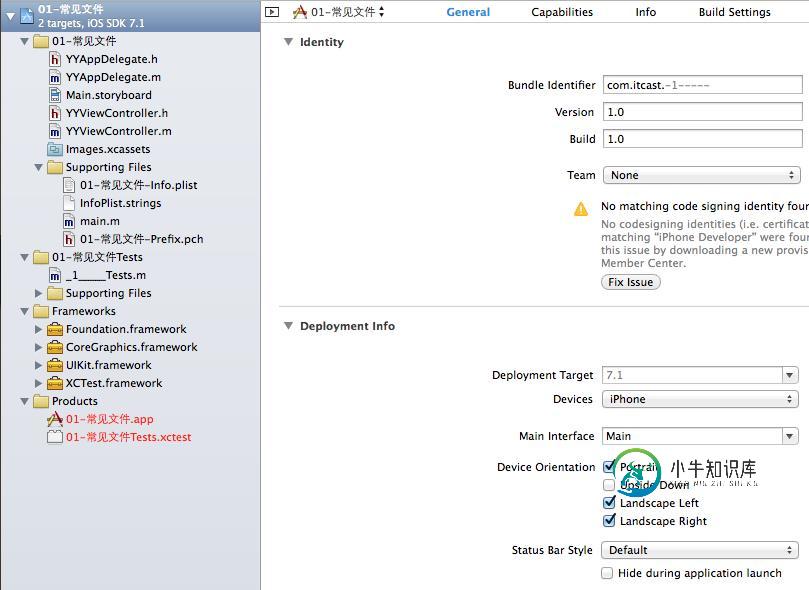
补充说明:
a.应用程序支持的旋转方向。四个方向,垂直-不支持颠倒-左-右(最多只支持三个方向)
b.plist文件打开之后是xml文件。和字典一样,是通过键值对的形式来保存数据。在xml文件中,添加了CF前缀
(2)pch文件(在该项目中为 01-常见文件-Prefix.pch)
1)简单说明
保存的内容能够被项目中的其他所有原文件共享。
通常情况下宏文件的处理,需要添加import导入头文件。以后可以把这个宏定义在这个文件中,不再需要导入头文件
2)应用场景:
1.用来定义一些全局的宏,
2.用来导入一些全局都能用到的头文件。
3.用来自定义NSlog,很消耗资源。(几乎是最消耗的),在发布的时候要把所有的打印都去掉。
(补充:在开发中,分为两个阶段。
一是开发调试阶段,需要打印log调试程序,如果程序处于调试阶段,系统会为我们定义一个名称叫做DEBUG的宏。
二是发布阶段:不需要打印log,因为log很占用资源,并且用户看不懂log,如果程序处理发布阶段,会去除这个宏。
难道在发布的时候要一个一个把NSlog都注释掉?然后在开发第二版,第三版的时候,又要把所有注释掉的NSlog都打开?
对于这个问题,在.pch文件中自定义NSlog就可以很好的解决。)
3)自定义NSlog
在做开发的时候可以先打开pch文件,看看公司中有没有自定义NSlog。
// __OBJC__这个宏,在所有的.m和.mm文件中默认就定义了这个宏 #ifdef __OBJC__ // 如果这个全局的头文件或者宏只需要在.m或者.mm文件中使用, // 请把该头文件或宏写到#ifdef __OBJC__ 中 #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>#ifdef DEBUG #define NJLog(...) NSLog(__VA_ARGS__) #else #define NJLog(...) #endif
#endif
说明:…指接收可变参数
补充:
_OBJC_这个宏,在所有的.m和.mm文件中,都默认包含了这个宏,就默认会编译下面那两句
条件编译语句,如果有这个宏,就编译下面的语句。
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
如果这个全局的头文件或者宏,只需要在.m或.mm文件中使用,请把该文件或宏写到#ifdef_ODBC_中用。
注意点:建议写在条件编译里面(注意#endif)
infoplist.strings的文件,跟info.plist文件的本地化相关
从代码的逐步优化看MVC
一、要求
要求完成下面一个小的应用程序。

二、一步步对代码进行优化
注意:在开发过程中,优化的过程是一步一步进行的。(如果一个人要吃五个包子才能吃饱,那么他是否直接吃第五个,前面四个不用吃就饱了?)
1.完成基本要求的代码(使用了字典转模型和xib连线)
(1)文件结构
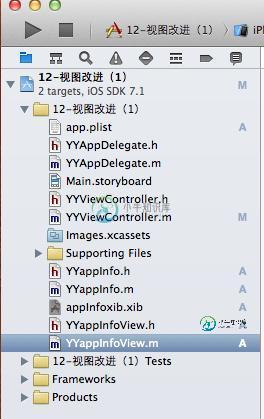
(2)主要代码
字典转模型部分:
YYappInfo.h头文件
// // YYappInfo.h // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface YYappInfo : NSObject @property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *name; @property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *icon; @property(nonatomic,strong,readonly)UIImage *img;
-(instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict; /**工厂方法*/ +(instancetype)appInfoWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict; @end
YYappInfo.m文件
// // YYappInfo.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import "YYappInfo.h" @interface YYappInfo() { UIImage *_img; } @end @implementation YYappInfo -(instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict { if (self=[super init]) { self.name=dict[@"name"]; self.icon=dict[@"icon"]; } return self; }
+(instancetype)appInfoWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict { return [[self alloc]initWithDict:dict]; }
-(UIImage *)img { _img=[UIImage imageNamed:self.icon]; return _img; } @end
xib部分(YYappInfoView.h文件):
注:(xib视图和YYappInfoView进行了关联,三个属性均进行了连线)
// // YYappInfoView.h // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface YYappInfoView : UIView @property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *appInfoViewimg;
@property (strong ,nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *appInfoViewlab; @property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *appInfoViewbtn;
@end
主要功能实现部分:
YYViewController.m文件
// // YYViewController.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import "YYViewController.h" #import "YYappInfo.h" #import "YYappInfoView.h"
@interface YYViewController () @property(nonatomic,strong)NSArray *apps; @end
//开发思路 //1.加载plist文件(字典转模型提供接口) //2.使用xib文件完成单个的view //3.计算坐标,使用for循环把view展现到界面上 //4.优化代码 @implementation YYViewController//get方法,懒加载 -(NSArray *)apps { if (!_apps) { NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"app.plist" ofType:nil]; NSArray * arrayM = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path]; NSMutableArray *appinfoarray=[NSMutableArray array]; for (NSDictionary *dict in arrayM) { [appinfoarray addObject:[YYappInfo appInfoWithDict:dict]]; } _apps = appinfoarray; } return _apps; }
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; NSLog(@"%d",self.apps.count); int totalloc = 3; CGFloat appviewW = 80; CGFloat appviewH = 90; CGFloat margin = (self.view.frame.size.width-totalloc*appviewW)/(totalloc+1); int count=self.apps.count; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { int row = i/totalloc; int loc = i%totalloc; CGFloat appviewX = margin + (margin + appviewW) * loc; CGFloat appviewY = margin + (margin + appviewH) * row; YYappInfo *appinfo=self.apps[i]; //拿出xib中的数据 NSArray *arryM=[[NSBundle mainBundle]loadNibNamed:@"appInfoxib" owner:nil options:nil]; YYappInfoView *appinfoview=[arryM firstObject]; //设置位置 appinfoview.frame=CGRectMake(appviewX, appviewY, appviewW, appviewH); //设置值 appinfoview.appInfoViewimg.image=appinfo.img; appinfoview.appInfoViewlab.text=appinfo.name; //添加到视图 appinfoview.appInfoViewbtn.tag=i; [appinfoview.appInfoViewbtn addTarget:self action:@selector(Click:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; [self.view addSubview:appinfoview]; } } -(void)Click:(UIButton *)btn { btn.enabled=NO; YYappInfo *appinfo=self.apps[btn.tag]; UILabel *lab=[[UILabel alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(60, 450, 200, 20)]; [lab setBackgroundColor:[UIColor lightGrayColor]]; [lab setTextAlignment:NSTextAlignmentCenter]; [lab setText:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@成功下载",appinfo.name]]; [self.view addSubview:lab]; lab.alpha=1.0; [UIView animateWithDuration:2.0 animations:^{ lab.alpha=0; }completion:^(BOOL finished) { [lab removeFromSuperview]; }]; } @end
2.对1进行优化(把数据呈现部分封装到视图)
说明:在1的基础上寻找还会有那些可以优化的部分
1)改进思路:
(1)1中主文件的66~67行对控件属性的设置能否拿到视图中进行?
(2)1中61~62行是从xib文件中读取信息的操作,且和主控制器没有什么太大的关联,能否把它也封装到视图中进行?
(3)当上述两个步骤完成后,主文件69行以后的按钮操作和按钮单击事件就显得很突兀,放在主控制器中已经不再合适,是否可以把它放到视图中进行处理
2)按照上述思路优化后的代码如下:
优化视图,在视图部分之对外提供一个接口,把数据的处理封装在内部
YYappInfoView.h文件代码:
// // YYappInfoView.h // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @class YYappInfo; @interface YYappInfoView : UIView
//读取 //+(instancetype)appInfoView; //只对外开放一个数据接口 +(instancetype)appInfoViewWithappInfo:(YYappInfo *)appinfo; @end
YYappInfoView.m文件代码
说明:该文件中的属性和click等均已做了连线的操作。
// // YYappInfoView.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import "YYappInfoView.h" #import "YYappInfo.h" //私有扩展,把属性拿进来 @interface YYappInfoView () @property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *appInfoViewimg; @property (strong ,nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *appInfoViewlab; @property (strong, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *appInfoViewbtn; @property(strong,nonatomic)YYappInfo *appinfo;
@end
@implementation YYappInfoView+(instancetype)appInfoView { NSArray *arryM=[[NSBundle mainBundle]loadNibNamed:@"appInfoxib" owner:nil options:nil]; YYappInfoView *appinfoview=[arryM firstObject]; return appinfoview; }
+(instancetype)appInfoViewWithappInfo:(YYappInfo *)appinfo { YYappInfoView *appInfoView=[self appInfoView]; appInfoView.appinfo=appinfo; return appInfoView; }
-(void)setAppinfo:(YYappInfo *)appinfoc { //这里一定要记录变化 _appinfo=appinfoc; self.appInfoViewimg.image=appinfoc.img; self.appInfoViewlab.text=appinfoc.name; } - (IBAction)Click { self.appInfoViewbtn.enabled=NO; //YYappInfo *appinfo=self.apps[]; YYappInfo *appinfo=self.appinfo; UILabel *lab=[[UILabel alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(60, 450, 200, 20)]; [lab setBackgroundColor:[UIColor lightGrayColor]]; [lab setTextAlignment:NSTextAlignmentCenter]; [lab setText:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@成功下载",appinfo.name]]; //把lab添加到父视图(即view中) [self.superview addSubview:lab]; lab.alpha=1.0; [UIView animateWithDuration:2.0 animations:^{ lab.alpha=0; }completion:^(BOOL finished) { [lab removeFromSuperview]; }]; }
@end
优化后的主控制器部分
YYViewController.m文件代码
// // YYViewController.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import "YYViewController.h" #import "YYappInfo.h" #import "YYappInfoView.h"
@interface YYViewController () @property(nonatomic,strong)NSArray *apps; @end
@implementation YYViewController-(NSArray *)apps { if (!_apps) { NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"app.plist" ofType:nil]; NSArray * arrayM = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path]; NSMutableArray *appinfoarray=[NSMutableArray array]; for (NSDictionary *dict in arrayM) { [appinfoarray addObject:[YYappInfo appInfoWithDict:dict]]; } _apps = appinfoarray; } return _apps; }
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; NSLog(@"%d",self.apps.count); int totalloc = 3; CGFloat appviewW = 80; CGFloat appviewH = 90; CGFloat margin = (self.view.frame.size.width-totalloc*appviewW)/(totalloc+1); int count=self.apps.count; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { int row = i/totalloc; int loc = i%totalloc; CGFloat appviewX = margin + (margin + appviewW) * loc; CGFloat appviewY = margin + (margin + appviewH) * row; /*思路: 要达到的效果 appinfoview.appinfo=appinfo; 优化后即变成 appinfoview.appinfo=self.apps[i]; 要进行上面代码的操作,需要在视图中新增加一个appinfo类的属性,这样数据——》视图的转换即可以不需要在主控制器中完成,让程序结构一目了然 */ YYappInfo *appinfo=self.apps[i]; YYappInfoView *appinfoview=[YYappInfoView appInfoViewWithappInfo:appinfo]; //设置位置 appinfoview.frame=CGRectMake(appviewX, appviewY, appviewW, appviewH); //添加 [self.view addSubview:appinfoview]; } } @end
3.对2进一步优化(把数据处理部分拿到模型中去进行)
(1)思路:把字典转模型部分的数据处理操作,拿到模型中去处理,这样外界不需要再关心数据处理的内部细节。
(2)优化后的代码如下
YYappInfo.h文件中向外开放一个接口,返回一个处理好的数组。
// // YYappInfo.h // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface YYappInfo : NSObject @property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *name; @property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *icon; @property(nonatomic,strong)UIImage *img;
-(instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict; /**工厂方法*/ +(instancetype)appInfoWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict; +(NSArray *)appinfoarray; @end
YYappInfo.m文件中的数据处理
// // YYappInfo.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //
#import "YYappInfo.h" @interface YYappInfo() @end
@implementation YYappInfo
-(instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict
{
if (self=[super init]) {
self.name=dict[@"name"];
self.icon=dict[@"icon"];
}
return self;
}
+(instancetype)appInfoWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict
{
return [[self alloc]initWithDict:dict];
}
-(UIImage *)img
{
_img=[UIImage imageNamed:self.icon];
return _img;
}
//把数据处理部分拿到模型中来处理
+(NSArray *)appinfoarray
{
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle]pathForResource:@"app.plist" ofType:nil];
NSArray * arrayM = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSMutableArray *appinfoarray=[NSMutableArray array];
for (NSDictionary *dict in arrayM) {
[appinfoarray addObject:[YYappInfo appInfoWithDict:dict]];
}
return appinfoarray;
}
@end
主控制器中不再需要关心数据处理的内部细节
YYViewController.m文件现在只是负责模型和视图之间的协调工作了,怎么样?差不多了吧。
// // YYViewController.m // 12-视图改进(1) // // Created by apple on 14-5-25. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. //#import "YYViewController.h" #import "YYappInfo.h" #import "YYappInfoView.h"
@interface YYViewController () @property(nonatomic,strong)NSArray *apps; @end
@implementation YYViewController-(NSArray *)apps { if (!_apps) { _apps=[YYappInfo appinfoarray]; } return _apps; }
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; int totalloc = 3; CGFloat appviewW = 80; CGFloat appviewH = 90; CGFloat margin = (self.view.frame.size.width-totalloc*appviewW)/(totalloc+1); int count=self.apps.count; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { int row = i/totalloc; int loc = i%totalloc; CGFloat appviewX = margin + (margin + appviewW) * loc; CGFloat appviewY = margin + (margin + appviewH) * row; YYappInfo *appinfo=self.apps[i]; YYappInfoView *appinfoview=[YYappInfoView appInfoViewWithappInfo:appinfo]; appinfoview.frame=CGRectMake(appviewX, appviewY, appviewW, appviewH); [self.view addSubview:appinfoview]; } } @end
实现效果:

4.补充说明
View的封装思路
(1) 如果一个view内部的子控件比较多,一般会考虑自定义一个view,把它内部子控件的创建屏蔽起来,不让外界关心
(2) 外界可以传入对应的模型数据给view,view拿到模型数据后给内部的子控件设置对应的数据
三、mvc机制简单说明
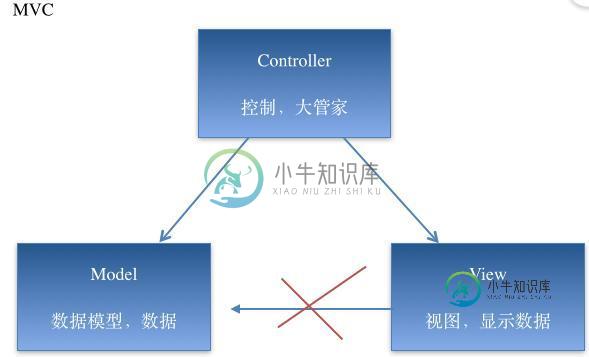
说明:
(1)在开发过程中,作为控制器处理的量级应该很轻,不该操心的不操心。协调好模型和视图就ok了,要学会当一个好老板。
(2)三个部分各司其职,数据模型只负责数据的处理,视图部分只负责把拿到的数据进行显示,两个部分都是被动的,等待着大管家控制器的调遣。
(3)在OC中,如果视图和数据模型之间有通道,那控制器是否处于失控状态呢?
-
本文向大家介绍Vue项目开发常见问题和解决方案总结,包括了Vue项目开发常见问题和解决方案总结的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Vue Cli 打包之后静态资源路径不对的解决方法 cli2版本: 将 config/index.js 里的 assetsPublicPath 的值改为 './' 。 cli3版本: 在根目录下新建 vue.config.js 文件,然后加上以下内容:(如果已经有
-
继续优化mvc结构 好吧,上一小节,给出了如何简单的把目录下的文件挂载到某个对象上,并发布npm上 照着这个思路,我们造了几个简单的库,用于挂载某个目录里的文件 mount-controllers mount-models mount-middlewares 1)mount-controllers var $ = require('mount-controllers')(__dirname).or
-
出于安全考虑,iOS系统把每个应用以及数据都放到一个沙盒(sandbox)里面,应用只能访问自己沙盒目录里面的文件、网络资源等(也有例外,比如系统通讯录、照相机、照片等能在用户授权的情况下被第三方应用访问)[1]。 请注意,使用沙盒的目的是为了防止被攻击的应用危害到系统或者其他应用,它并不能阻止应用本身被攻击,因此,开发者需要防御式的编程来避免应用被攻击。苹果官方是这样说的: Important:
-
本文向大家介绍Vue开发中常见的套路和技巧总结,包括了Vue开发中常见的套路和技巧总结的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 属性排放 管理请求加载状态 Proxy跨域 对developer和build的打包进行不同配置 大部分开发者都喜欢将Vue的config写在一个文件中,看起来是没有问题,但是随着环境的变化,项目优化,WebPack插件,等等具有针对性的配置进来后,就会显得稍微杂乱了,这个
-
本文向大家介绍提高iOS开发效率的小技巧与思路,包括了提高iOS开发效率的小技巧与思路的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 先用一张图展示学习iOS开发应该掌握的知识体系: 1.全图片作为背景的时候,可能遇到的问题。,滑回的时候,图片停留了一会才滑回去。 原因: 这种界面一般使用一般用imageView的第三种填充方式。 这种填充方式可以让图片不被压缩变形的前提下,尽可能去填充整个控件,但是设
-
本文向大家介绍提高iOS开发的小技巧和思路小结 (二),包括了提高iOS开发的小技巧和思路小结 (二)的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 之前跟大家分享过一篇《提高iOS开发的小技巧和思路》,但是里面整理的不够全面,通过最近这段时间的整理学习,又整理了一些小技巧和思路分享给大家,下面话不多说了,来看看详细的介绍吧。 一、如何让你的app在后台持续运行一段时间 iOS的app在按下hom

