在绘制的行上打印字符串(模拟等高线绘制标签)
等高线图演示显示了如何使用绘制在曲线上的标高值绘制曲线,请参见下文。
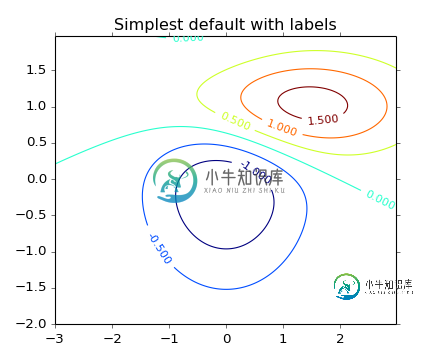
有没有一种方法可以对一个简单的线图做同样的事情,就像下面的代码得到的一样?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1.81,1.715,1.78,1.613,1.629,1.714,1.62,1.738,1.495,1.669,1.57,1.877,1.385]
y = [0.924,0.915,0.914,0.91,0.909,0.905,0.905,0.893,0.886,0.881,0.873,0.873,0.844]
# This is the string that should show somewhere over the plotted line.
line_string = 'name of line'
# plotting
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
共有2个答案
基于Jakob的代码,这里有一个函数,可以在数据空间中旋转文本,将标签放在给定的x或y数据坐标附近,还可以处理日志图。
def label_line(line, label_text, near_i=None, near_x=None, near_y=None, rotation_offset=0, offset=(0,0)):
"""call
l, = plt.loglog(x, y)
label_line(l, "text", near_x=0.32)
"""
def put_label(i):
"""put label at given index"""
i = min(i, len(x)-2)
dx = sx[i+1] - sx[i]
dy = sy[i+1] - sy[i]
rotation = np.rad2deg(math.atan2(dy, dx)) + rotation_offset
pos = [(x[i] + x[i+1])/2. + offset[0], (y[i] + y[i+1])/2 + offset[1]]
plt.text(pos[0], pos[1], label_text, size=9, rotation=rotation, color = line.get_color(),
ha="center", va="center", bbox = dict(ec='1',fc='1'))
x = line.get_xdata()
y = line.get_ydata()
ax = line.get_axes()
if ax.get_xscale() == 'log':
sx = np.log10(x) # screen space
else:
sx = x
if ax.get_yscale() == 'log':
sy = np.log10(y)
else:
sy = y
# find index
if near_i is not None:
i = near_i
if i < 0: # sanitize negative i
i = len(x) + i
put_label(i)
elif near_x is not None:
for i in range(len(x)-2):
if (x[i] < near_x and x[i+1] >= near_x) or (x[i+1] < near_x and x[i] >= near_x):
put_label(i)
elif near_y is not None:
for i in range(len(y)-2):
if (y[i] < near_y and y[i+1] >= near_y) or (y[i+1] < near_y and y[i] >= near_y):
put_label(i)
else:
raise ValueError("Need one of near_i, near_x, near_y")
您可以简单地添加一些文本(MPL库),如
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = [1.81,1.715,1.78,1.613,1.629,1.714,1.62,1.738,1.495,1.669,1.57,1.877,1.385]
y = [0.924,0.915,0.914,0.91,0.909,0.905,0.905,0.893,0.886,0.881,0.873,0.873,0.844]
# This is the string that should show somewhere over the plotted line.
line_string = 'name of line'
# plotting
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
l, = ax.plot(x,y)
pos = [(x[-2]+x[-1])/2., (y[-2]+y[-1])/2.]
# transform data points to screen space
xscreen = ax.transData.transform(zip(x[-2::],y[-2::]))
rot = np.rad2deg(np.arctan2(*np.abs(np.gradient(xscreen)[0][0][::-1])))
ltex = plt.text(pos[0], pos[1], line_string, size=9, rotation=rot, color = l.get_color(),
ha="center", va="center",bbox = dict(ec='1',fc='1'))
def updaterot(event):
"""Event to update the rotation of the labels"""
xs = ax.transData.transform(zip(x[-2::],y[-2::]))
rot = np.rad2deg(np.arctan2(*np.abs(np.gradient(xs)[0][0][::-1])))
ltex.set_rotation(rot)
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('button_release_event', updaterot)
plt.show()
注意,旋转是以度数和屏幕而不是数据空间为单位的。
由于我最近需要自动标签旋转,它更新缩放和平移,因此我更新了我的答案,以满足这些需求。现在标签旋转会在每次鼠标按钮释放时更新(缩放时不会触发单独的draw_event)。这种方法使用matplotlib转换来链接本教程中讨论的数据和屏幕空间。
-
我正在尝试使用swing制作一个rpg(是的,这是愚蠢的,我同意,但我这样做是为了学习,而不是实际的工作产品)。目前我正在研究每个角色的统计。 我有一个JPanel,我想画一条线。 左侧是一个JPanel,它有两个组件:表1和JLabel。右侧也是JPanel,它有自己的元素,但那是另一回事了。 我的问题是,我想创建一个只有一个图像的jpanel,该图像将是两行,与表中选定的元素相关。 但不幸的是
-
本文向大家介绍python绘制高斯曲线,包括了python绘制高斯曲线的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了python绘制高斯曲线的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 源码: 效果图: 以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持呐喊教程。
-
java中C代码的等价物是什么: 打印字符串值及其名称。
-
问题内容: 我正在用Piccolo编写一个交互式applet,并且需要在其中包含高斯曲线(又称正态分布图)。 我想象任何一种Java实现都足够,但是我找不到。理想情况下,我想传递一组值并将图表绘制在面板,图像对象或可以嵌入在applet中的任何对象中。 在让我自己动手编写代码之前,有人知道做这件事的有用代码吗? 欢迎使用其他语言的实现,只要它们易于移植到Java中即可。 问题答案: 不知道它是否有
-
绘制线 点击菜单栏或底下快捷工具栏中的“绘制线”按钮,按照弹出对话框进行线的绘制。 使用鼠标在地图上连续点击,双击完成线的绘制后弹出属性信息对话框,可以在“说明”栏中查看并修改对于该线的说明。 在“空间信息”栏中可以看到节点的坐标信息,双击一个节点的坐标信息后可修改该节点的坐标信息,也可在三维地球上选中节点直接移动修改。 在“样式”栏修改线的
-
绘制线 点击菜单栏或底下快捷工具栏中的“绘制线”按钮,按照弹出对话框进行线的绘制。 使用鼠标在地图上连续点击,双击完成线的绘制后弹出属性信息对话框,可以在“说明”栏中查看并修改对于该线的说明。 在“空间信息”栏中可以看到节点的坐标信息,双击一个节点的坐标信息后可修改该节点的坐标信息,也可在三维地球上选中节点直接移动修改。 在“样式”栏修改线的

