函数将二叉树转换为完整的二叉树?
下面给出了二叉树的实现。
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = None
self.left = None
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(7)
root.left.left.left = Node(9)
root.right.right = Node(1)
root.right.right.right = Node(6)
root.right.right.left = Node(4)
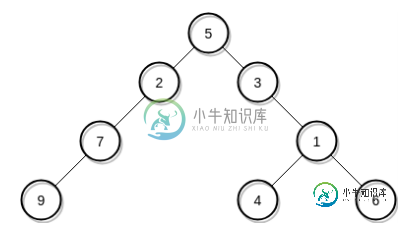
如图中所示,树不是完整的二叉树。如何编写一个函数,将上述二叉树转换为完整的二叉树,只需将字符串数据节点添加到没有子节点的节点,即可生成完整的二叉树。
我将手动在代码中添加节点,以获得如下结果树:
root.left.right = Node('a')
root.right.left = Node('a')
root.right.left.left = Node('a')
root.right.left.right = Node('a')
root.left.right.right = Node('a')
root.left.right.left = Node('a')
但是,如何编写一个函数,它将采取根节点和返回树,这是完整的二叉树。
共有2个答案
首先,获取树的高度。这将是完整树的高度。接下来,遍历树,对于每个节点,如果它的深度小于树的高度,并且缺少它的左子节点或右子节点(或两者),则添加缺少的内容,然后继续遍历。因此对于您的输入,该过程将执行
5 h=0
=> 2 h=1
=> 7 h=2
=> 9 h=3
=> 3 h=1
=> 1 h=2
=> 4 h=3
=> 6 h=3
max height seen was 3, so height of tree is 3
5 h < 3, has both children, nothing to add
=> 2 h < 3, missing right child, add 'a'
=> 7 h < 3, missing right child, add 'b'
=> 9 h = 3, nothing to add
=> b h = 3, nothing to add
=> a h < 3, missing left and right children, add 'c' and 'd'
=> c h = 3, nothing to add
=> d h = 3, nothing to add
=> 3 h < 3, missing left child, add 'e'
=> e h < 3, missing left and right children, add 'f' and 'g'
=> f h = 3, nothing to add
=> g h = 3, nothing to add
=> 1 h < 3, has both children, nothing to add
=> 4 h = 3, nothing to add
=> 6 h = 3, nothing to add
我们看到,这添加了与手动相同的节点(实际上可能遗漏了一个,7在图形中只有一个子节点)。我们将它们标记为a、b、c、d、e、f和g,但您可以编写代码,这样它就可以为它们提供相同的字符串。
您将需要创建一个可以为您提供树中最大深度的方法。从中,您可以添加一个方法来递归地将空节点添加到该深度:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.right = None
self.left = None
@property
def maxDepth(self): # compute maximum depth (i.e. levels under self)
depth = 0
if self.left: depth = self.left.maxDepth+1
if self.right: depth = max(depth,self.right.maxDepth+1)
return depth
def expandToDepth(self,depth=None): # add empty nodes to fill tree
if depth is None: depth = self.maxDepth
if not depth: return
if not self.left: self.left = Node(None)
if not self.right: self.right = Node(None)
self.left.expandToDepth(depth-1)
self.right.expandToDepth(depth-1)
def __repr__(self): # this is just to print the tree
nodeInfo = lambda n: (str(n.data or "?"),n.left,n.right)
return "\n".join(printBTree(self,nodeInfo,isTop=False))
输出:
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(7)
root.left.left.left = Node(9)
root.right.right = Node(1)
root.right.right.right = Node(6)
root.right.right.left = Node(4)
## BEFORE ##
print(root)
5
/ \
2 3
/ \
7 1
/ / \
9 4 6
root.expandToDepth()
## AFTER ##
print(root)
5
_____/ \_____
2 3
__/ \_ __/ \_
7 ? ? 1
/ \ / \ / \ / \
9 ? ? ? ? ? 4 6
printBTree()是我提供的一个函数,用于回答另一个问题:https://stackoverflow.com/a/49844237/5237560
这是它的副本(以防链接消失):
import functools as fn
def printBTree(node, nodeInfo=None, inverted=False, isTop=True):
# node value string and sub nodes
stringValue, leftNode, rightNode = nodeInfo(node)
stringValueWidth = len(stringValue)
# recurse to sub nodes to obtain line blocks on left and right
leftTextBlock = [] if not leftNode else printBTree(leftNode,nodeInfo,inverted,False)
rightTextBlock = [] if not rightNode else printBTree(rightNode,nodeInfo,inverted,False)
# count common and maximum number of sub node lines
commonLines = min(len(leftTextBlock),len(rightTextBlock))
subLevelLines = max(len(rightTextBlock),len(leftTextBlock))
# extend lines on shallower side to get same number of lines on both sides
leftSubLines = leftTextBlock + [""] * (subLevelLines - len(leftTextBlock))
rightSubLines = rightTextBlock + [""] * (subLevelLines - len(rightTextBlock))
# compute location of value or link bar for all left and right sub nodes
# * left node's value ends at line's width
# * right node's value starts after initial spaces
leftLineWidths = [ len(line) for line in leftSubLines ]
rightLineIndents = [ len(line)-len(line.lstrip(" ")) for line in rightSubLines ]
# top line value locations, will be used to determine position of current node & link bars
firstLeftWidth = (leftLineWidths + [0])[0]
firstRightIndent = (rightLineIndents + [0])[0]
# width of sub node link under node value (i.e. with slashes if any)
# aims to center link bars under the value if value is wide enough
#
# ValueLine: v vv vvvvvv vvvvv
# LinkLine: / \ / \ / \ / \
#
linkSpacing = min(stringValueWidth, 2 - stringValueWidth % 2)
leftLinkBar = 1 if leftNode else 0
rightLinkBar = 1 if rightNode else 0
minLinkWidth = leftLinkBar + linkSpacing + rightLinkBar
valueOffset = (stringValueWidth - linkSpacing) // 2
# find optimal position for right side top node
# * must allow room for link bars above and between left and right top nodes
# * must not overlap lower level nodes on any given line (allow gap of minSpacing)
# * can be offset to the left if lower subNodes of right node
# have no overlap with subNodes of left node
minSpacing = 2
rightNodePosition = fn.reduce(lambda r,i: max(r,i[0] + minSpacing + firstRightIndent - i[1]), \
zip(leftLineWidths,rightLineIndents[0:commonLines]), \
firstLeftWidth + minLinkWidth)
# extend basic link bars (slashes) with underlines to reach left and right
# top nodes.
#
# vvvvv
# __/ \__
# L R
#
linkExtraWidth = max(0, rightNodePosition - firstLeftWidth - minLinkWidth )
rightLinkExtra = linkExtraWidth // 2
leftLinkExtra = linkExtraWidth - rightLinkExtra
# build value line taking into account left indent and link bar extension (on left side)
valueIndent = max(0, firstLeftWidth + leftLinkExtra + leftLinkBar - valueOffset)
valueLine = " " * max(0,valueIndent) + stringValue
slash = "\\" if inverted else "/"
backslash = "/" if inverted else "\\"
uLine = "¯" if inverted else "_"
# build left side of link line
leftLink = "" if not leftNode else ( " " * firstLeftWidth + uLine * leftLinkExtra + slash)
# build right side of link line (includes blank spaces under top node value)
rightLinkOffset = linkSpacing + valueOffset * (1 - leftLinkBar)
rightLink = "" if not rightNode else ( " " * rightLinkOffset + backslash + uLine * rightLinkExtra )
# full link line (will be empty if there are no sub nodes)
linkLine = leftLink + rightLink
# will need to offset left side lines if right side sub nodes extend beyond left margin
# can happen if left subtree is shorter (in height) than right side subtree
leftIndentWidth = max(0,firstRightIndent - rightNodePosition)
leftIndent = " " * leftIndentWidth
indentedLeftLines = [ (leftIndent if line else "") + line for line in leftSubLines ]
# compute distance between left and right sublines based on their value position
# can be negative if leading spaces need to be removed from right side
mergeOffsets = [ len(line) for line in indentedLeftLines ]
mergeOffsets = [ leftIndentWidth + rightNodePosition - firstRightIndent - w for w in mergeOffsets ]
mergeOffsets = [ p if rightSubLines[i] else 0 for i,p in enumerate(mergeOffsets) ]
# combine left and right lines using computed offsets
# * indented left sub lines
# * spaces between left and right lines
# * right sub line with extra leading blanks removed.
mergedSubLines = zip(range(len(mergeOffsets)), mergeOffsets, indentedLeftLines)
mergedSubLines = [ (i,p,line + (" " * max(0,p)) ) for i,p,line in mergedSubLines ]
mergedSubLines = [ line + rightSubLines[i][max(0,-p):] for i,p,line in mergedSubLines ]
# Assemble final result combining
# * node value string
# * link line (if any)
# * merged lines from left and right sub trees (if any)
treeLines = [leftIndent + valueLine] + ( [] if not linkLine else [leftIndent + linkLine] ) + mergedSubLines
# invert final result if requested
treeLines = reversed(treeLines) if inverted and isTop else treeLines
# return intermediate tree lines or print final result
if isTop : print("\n".join(treeLines))
else : return treeLines
-
考虑二叉树,其中每个节点要么是叶,要么正好有两个子节点(左和右,我们认为不同)。在节点上有多少不同的树 例如: -3个节点-
-
问题内容: 我对二叉树有一些疑问: Wikipedia指出,当“完整的二叉树是其中所有级别(可能除了最后一个级别)均已完全填充且所有节点都位于最左侧”的二叉树时,该二叉树即已 完成 。最后的“越远越好”的段落是什么意思? 如果(1)它是空的,或者(2)它的左右子级是平衡的,并且左树的高度在以下高度的1之内,则格式正确的二叉树被称为“高度平衡”。正确的树,取自如何确定二叉树是否平衡?,这是正确的还是
-
我希望将二叉树表示为数组,以便数组在数组中表示为空的广度一阶。我不想使用数组列表,但很乐意使用链表结构。我发现数组的最大大小的大小将是2^n-1,其中n是以下情况下树的高度: 数组的最小大小(除了空树或没有子项的根 [大小为 0 和 3 相应])为 (2^n - 1) - 6,在这种情况下,6 可以计算为前一个级别的空位数乘以 2: 这些树是否可以表示为堆,其中位于索引0并且当前节点在索引i处的左
-
我如何转换使用以下代码,我的二叉树到一个简单的链表。这也许可以用递归来完成。 因此,如果根为NULL,也就是,如果函数没有收到有效的指针,则返回错误消息。 如果根是叶,这是,如果左子节点和右子节点都为NULL,您必须将其添加到叶节点列表中。
-
我将完整子树定义为所有级别都已满且最后一个级别左对齐的树,即所有节点都尽可能左对齐,我希望找到树中最大的完整子树。 一种方法是对每个节点作为根执行这里概述的方法,这将花费O(n^2)时间。 有更好的方法吗?
-
玩转二叉树 给定一棵二叉树的中序遍历和前序遍历,请你先将树做个镜面反转,再输出反转后的层序遍历的序列。所谓镜面反转,是指将所有非叶结点的左右孩子对换。这里假设键值都是互不相等的正整数。 输入格式: 输入第一行给出一个正整数N(≤30),是二叉树中结点的个数。第二行给出其中序遍历序列。第三行给出其前序遍历序列。数字间以空格分隔。 输出格式: 在一行中输出该树反转后的层序遍历的序列。数字间以1个空格分

