绘制scikit-learn(sklearn)SVM决策边界/曲面
我目前正在使用python的scikit库使用线性内核执行多类SVM。样本训练数据和测试数据如下:
型号数据:
x = [[20,32,45,33,32,44,0],[23,32,45,12,32,66,11],[16,32,45,12,32,44,23],[120,2,55,62,82,14,81],[30,222,115,12,42,64,91],[220,12,55,222,82,14,181],[30,222,315,12,222,64,111]]
y = [0,0,0,1,1,2,2]
我想绘制决策边界并可视化数据集。有人可以帮忙绘制此类数据吗?
上面给出的数据只是模拟数据,因此可以随时更改值。如果至少您可以建议要执行的步骤,这将很有帮助。提前致谢
问题答案:
您只需选择2个功能即可。 原因是您无法绘制7D图。选择2个要素后,仅将其用于决策面的可视化。
- (我还在这里写过一篇文章:[https]( https://towardsdatascience.com/support-vector-machines-
- svm-clearly-explained-a-python-tutorial-for-classification-
- problems-29c539f3ad8?source=friends_link&sk=80f72ab272550d76a0cc3730d7c8af35)
-
//towardsdatascience.com/support-vector-machines-svm-clearly-explained-a-
python-tutorial-for-classification-
problems-29c539f3ad8?source=friends_link&sk=80f72ab272550d76a0cc3730d7c8af35
)
现在,您要问的下一个问题: 如何选择这两个功能? 。好吧,有很多方法。您可以进行 单变量F值(功能排名)测试,
并查看哪些功能/变量最重要。然后,您可以将这些用于绘图。此外,例如,我们可以使用 PCA 将尺寸从7减少到2 。
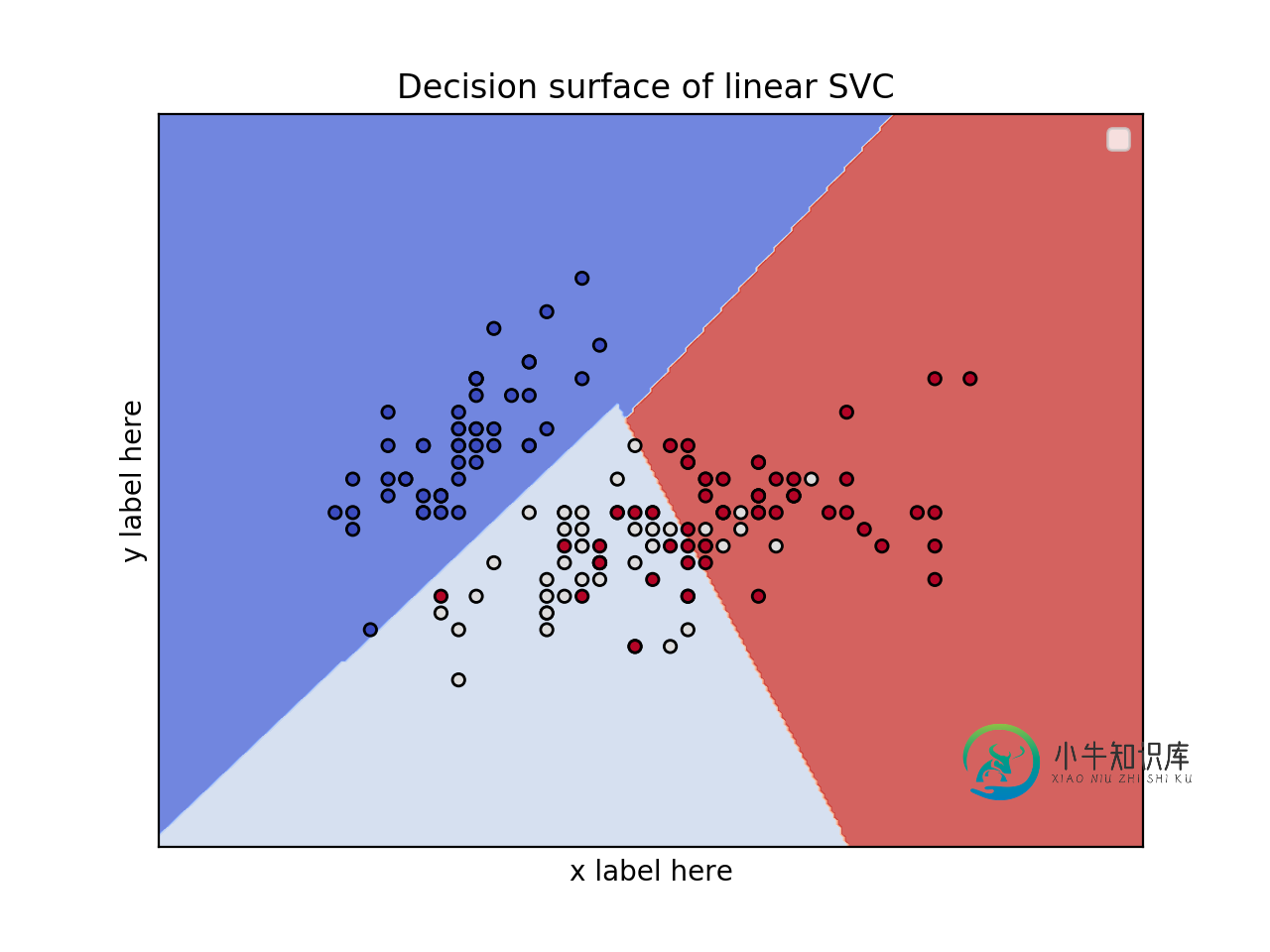
2个要素的2D图并使用虹膜数据集
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Select 2 features / variable for the 2D plot that we are going to create.
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
y = iris.target
def make_meshgrid(x, y, h=.02):
x_min, x_max = x.min() - 1, x.max() + 1
y_min, y_max = y.min() - 1, y.max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
return xx, yy
def plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, **params):
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
out = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, **params)
return out
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf = model.fit(X, y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# title for the plots
title = ('Decision surface of linear SVC ')
# Set-up grid for plotting.
X0, X1 = X[:, 0], X[:, 1]
xx, yy = make_meshgrid(X0, X1)
plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, alpha=0.8)
ax.scatter(X0, X1, c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
ax.set_ylabel('y label here')
ax.set_xlabel('x label here')
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(title)
ax.legend()
plt.show()
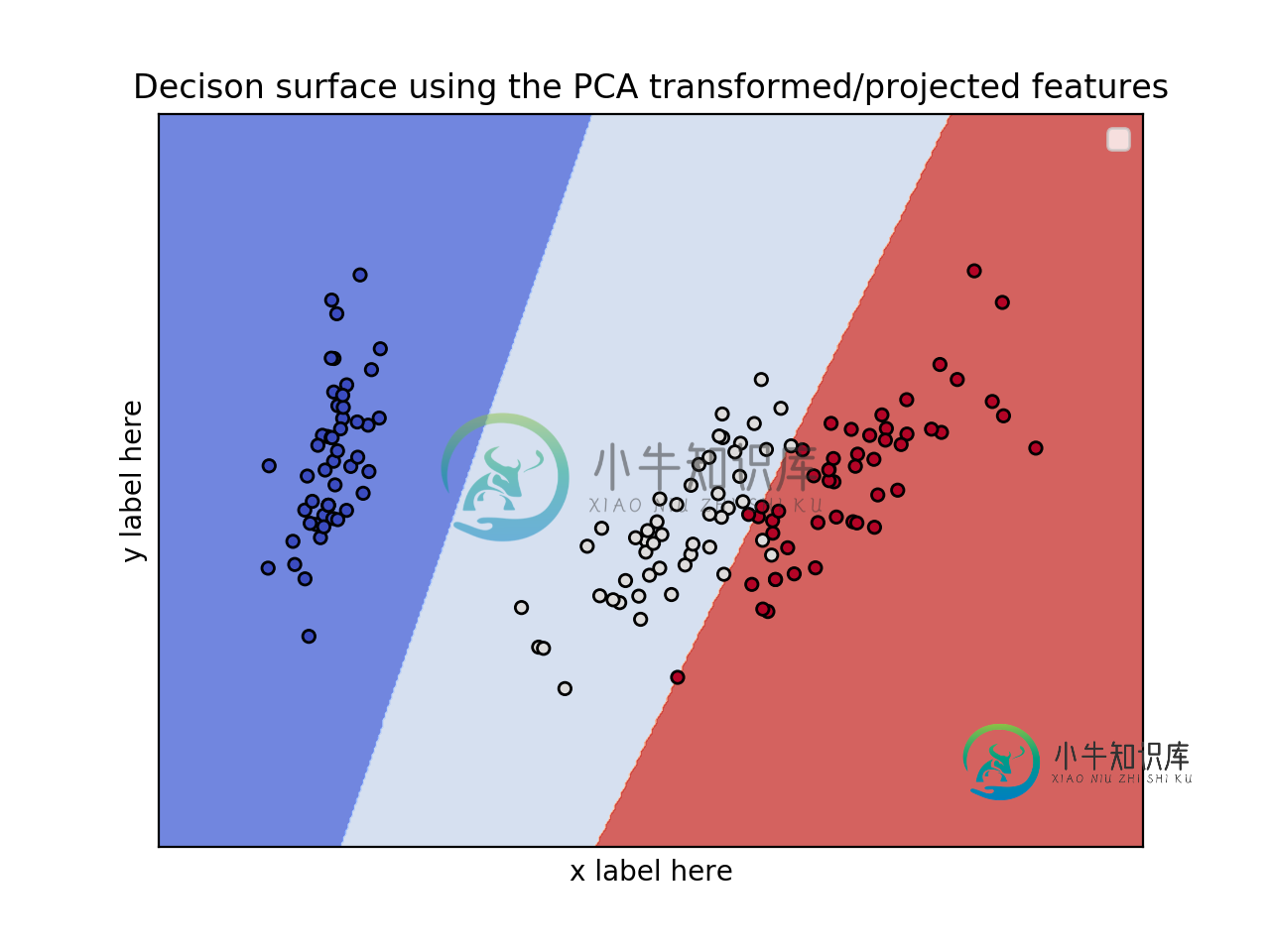
编辑:应用PCA以减少尺寸。
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
Xreduced = pca.fit_transform(X)
def make_meshgrid(x, y, h=.02):
x_min, x_max = x.min() - 1, x.max() + 1
y_min, y_max = y.min() - 1, y.max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
return xx, yy
def plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, **params):
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
out = ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, **params)
return out
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf = model.fit(Xreduced, y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# title for the plots
title = ('Decision surface of linear SVC ')
# Set-up grid for plotting.
X0, X1 = Xreduced[:, 0], Xreduced[:, 1]
xx, yy = make_meshgrid(X0, X1)
plot_contours(ax, clf, xx, yy, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, alpha=0.8)
ax.scatter(X0, X1, c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
ax.set_ylabel('PC2')
ax.set_xlabel('PC1')
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title('Decison surface using the PCA transformed/projected features')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
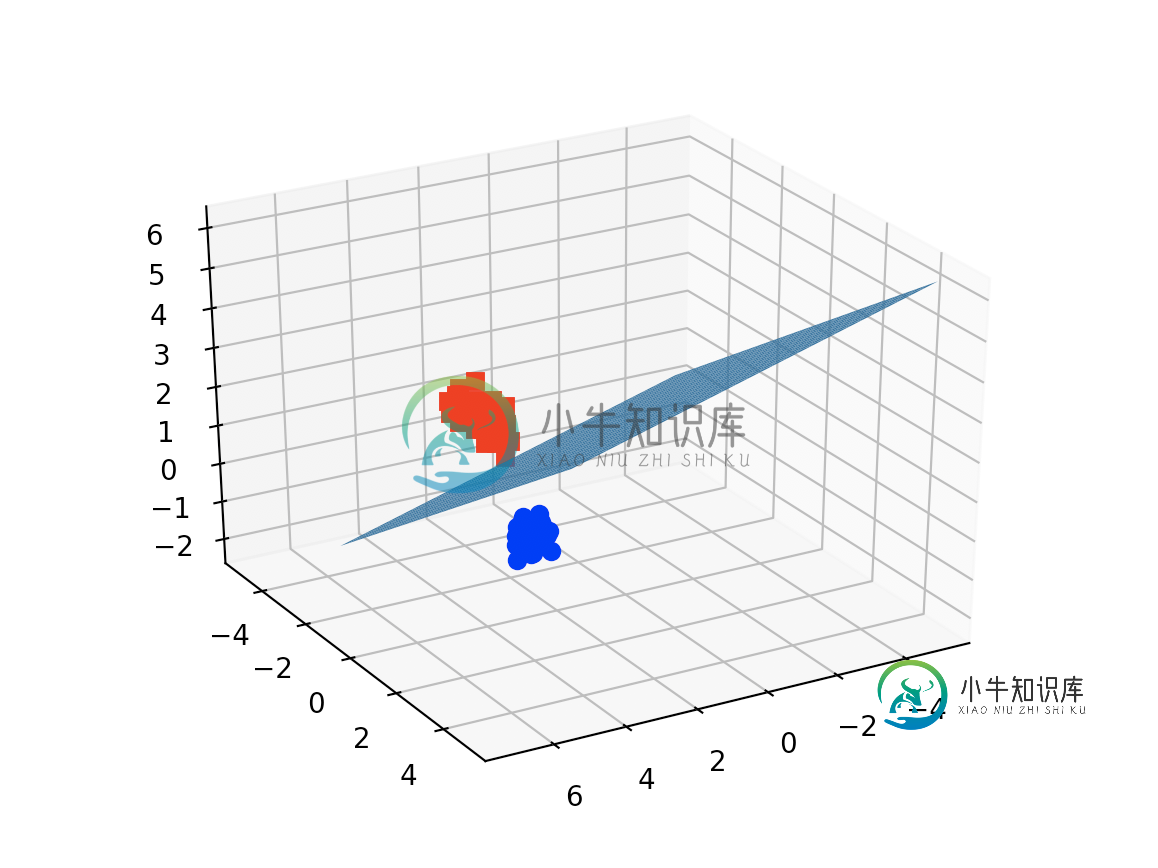
编辑1(2020年4月15日):
案例:3个特征的3D图并使用虹膜数据集
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm, datasets
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :3] # we only take the first three features.
Y = iris.target
#make it binary classification problem
X = X[np.logical_or(Y==0,Y==1)]
Y = Y[np.logical_or(Y==0,Y==1)]
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf = model.fit(X, Y)
# The equation of the separating plane is given by all x so that np.dot(svc.coef_[0], x) + b = 0.
# Solve for w3 (z)
z = html" target="_blank">lambda x,y: (-clf.intercept_[0]-clf.coef_[0][0]*x -clf.coef_[0][1]*y) / clf.coef_[0][2]
tmp = np.linspace(-5,5,30)
x,y = np.meshgrid(tmp,tmp)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot3D(X[Y==0,0], X[Y==0,1], X[Y==0,2],'ob')
ax.plot3D(X[Y==1,0], X[Y==1,1], X[Y==1,2],'sr')
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z(x,y))
ax.view_init(30, 60)
plt.show()
-
问题内容: 我对matplotlib非常陌生,并且正在从事一些简单的项目以熟悉它。我想知道如何绘制决策边界,决策边界是[w1,w2]形式的权重向量,它使用matplotlib将两个类(例如C1和C2)基本分开。 如果是这样,是否像从(0,0)到点(w1,w2)画一条线一样简单(因为W是权重“向量”),如果需要,如何像在两个方向上一样进行扩展? 现在我要做的是: 提前致谢。 问题答案: 决策边界通常
-
问题内容: 我正在尝试在Python中使用scikit-learn设计一个简单的决策树(我在Windows OS上将Anaconda的Ipython Notebook与Python 2.7.3结合使用),并将其可视化如下: 但是,出现以下错误: 我使用以下博客文章作为参考:Blogpost链接 以下stackoverflow问题似乎也不适合我:问题 有人可以帮助我如何在scikit-learn中可
-
问题内容: 我是否可以从决策树中经过训练的树中提取出基本的决策规则(或“决策路径”)作为文本列表? 就像是: 谢谢你的帮助。 问题答案: 我相信这个答案比这里的其他答案更正确: 这会打印出有效的Python函数。这是一个试图返回其输入的树的示例输出,该数字介于0和10之间。 这是我在其他答案中看到的一些绊脚石: 使用来决定一个节点是否为叶是不是一个好主意。如果它是阈值为-2的真实决策节点怎么办?相
-
问题内容: 我可以从决策树中经过训练的树中提取出基本的决策规则(或“决策路径”)作为文本列表吗? 就像是: 谢谢你的帮助。 问题答案: 我相信这个答案比这里的其他答案更正确: 这会打印出有效的Python函数。这是尝试返回其输入的树的示例输出,该数字介于0到10之间。 这是我在其他答案中看到的一些绊脚石: 使用tree_.threshold == -2来决定一个节点是否为叶是不是一个好主意。如果它
-
scikit-learn 是基于 Python 语言的机器学习工具。 简单高效的数据挖掘和数据分析工具 可供大家在各种环境中重复使用 建立在 NumPy ,SciPy 和 matplotlib 上 开源,可商业使用 - BSD许可证
-
这适用于必须使用SVM方法来提高模型精度的分配。 共有3部分,编写了下面的代码 但在此之后,问题如下 执行数字标准化。数据,并将转换后的数据存储在可变数字中。 提示:从sklearn.preprocessing.使用所需的实用程序再次,将digits_standardized分成两个集合名称X_train和X_test。此外,将digits.target分成两组Y_train和Y_test。 提示

