算术指令(Arithmetic Instructions)
INC指令
INC指令用于将操作数递增1。 它适用于单个操作数,可以在寄存器或内存中。
语法 (Syntax)
INC指令具有以下语法 -
INC destination
操作数destination可以是8位,16位或32位操作数。
例子 (Example)
INC EBX ; Increments 32-bit register
INC DL ; Increments 8-bit register
INC [count] ; Increments the count variable
DEC指令
DEC指令用于将操作数递减1。 它适用于单个操作数,可以在寄存器或内存中。
语法 (Syntax)
DEC指令具有以下语法 -
DEC destination
操作数destination可以是8位,16位或32位操作数。
例子 (Example)
segment .data
count dw 0
value db 15
segment .text
inc [count]
dec [value]
mov ebx, count
inc word [ebx]
mov esi, value
dec byte [esi]
ADD和SUB指令
ADD和SUB指令用于以字节,字和双字大小执行二进制数据的简单加/减,即分别用于加或减8位,16位或32位操作数。
语法 (Syntax)
ADD和SUB指令具有以下语法 -
ADD/SUB destination, source
ADD/SUB指令可以在 - 之间发生 -
- 注册注册
- 记忆要注册
- 注册到内存
- 注册恒定数据
- 内存到恒定数据
但是,与其他指令一样,使用ADD/SUB指令无法进行内存到内存操作。 ADD或SUB操作设置或清除溢出和进位标志。
例子 (Example)
以下示例将询问用户的两位数字,分别将数字存储在EAX和EBX寄存器中,添加值,将结果存储在内存位置“ res ”中,最后显示结果。
SYS_EXIT equ 1
SYS_READ equ 3
SYS_WRITE equ 4
STDIN equ 0
STDOUT equ 1
segment .data
msg1 db "Enter a digit ", 0xA,0xD
len1 equ $- msg1
msg2 db "Please enter a second digit", 0xA,0xD
len2 equ $- msg2
msg3 db "The sum is: "
len3 equ $- msg3
segment .bss
num1 resb 2
num2 resb 2
res resb 1
section .text
global _start ;must be declared for using gcc
_start: ;tell linker entry point
mov eax, SYS_WRITE
mov ebx, STDOUT
mov ecx, msg1
mov edx, len1
int 0x80
mov eax, SYS_READ
mov ebx, STDIN
mov ecx, num1
mov edx, 2
int 0x80
mov eax, SYS_WRITE
mov ebx, STDOUT
mov ecx, msg2
mov edx, len2
int 0x80
mov eax, SYS_READ
mov ebx, STDIN
mov ecx, num2
mov edx, 2
int 0x80
mov eax, SYS_WRITE
mov ebx, STDOUT
mov ecx, msg3
mov edx, len3
int 0x80
; moving the first number to eax register and second number to ebx
; and subtracting ascii '0' to convert it into a decimal number
mov eax, [num1]
sub eax, '0'
mov ebx, [num2]
sub ebx, '0'
; add eax and ebx
add eax, ebx
; add '0' to to convert the sum from decimal to ASCII
add eax, '0'
; storing the sum in memory location res
mov [res], eax
; print the sum
mov eax, SYS_WRITE
mov ebx, STDOUT
mov ecx, res
mov edx, 1
int 0x80
exit:
mov eax, SYS_EXIT
xor ebx, ebx
int 0x80
编译并执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
Enter a digit:
3
Please enter a second digit:
4
The sum is:
7
The program with hardcoded variables −
section .text
global _start ;must be declared for using gcc
_start: ;tell linker entry point
mov eax,'3'
sub eax, '0'
mov ebx, '4'
sub ebx, '0'
add eax, ebx
add eax, '0'
mov [sum], eax
mov ecx,msg
mov edx, len
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov ecx,sum
mov edx, 1
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
section .data
msg db "The sum is:", 0xA,0xD
len equ $ - msg
segment .bss
sum resb 1
编译并执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
The sum is:
7
MUL/IMUL指令
有两个用于乘以二进制数据的指令。 MUL(Multiply)指令处理无符号数据,IMUL(整数乘)处理带符号数据。 这两条指令都会影响进位和溢出标志。
语法 (Syntax)
MUL/IMUL指令的语法如下 -
MUL/IMUL multiplier
两种情况下的复数将位于累加器中,具体取决于被乘数和乘数的大小,并且生成的乘积也根据操作数的大小存储在两个寄存器中。 以下部分介绍了具有三种不同情况的MUL指令 -
| Sr.No. | 方案 |
|---|---|
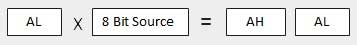
| 1 | When two bytes are multiplied − 被乘数位于AL寄存器中,乘数是存储器或另一个寄存器中的一个字节。 该产品在AX。 产品的高阶8位存储在AH中,低阶8位存储在AL中。
|
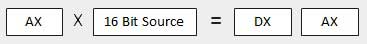
| 2 | When two one-word values are multiplied − 被乘数应位于AX寄存器中,乘数是存储器中的字或另一个寄存器。 例如,对于像MUL DX这样的指令,必须将乘数存储在DX中,将被乘数存储在AX中。 最终产品是双字,需要两个寄存器。 高阶(最左边)部分存储在DX中,低阶(最右边)部分存储在AX中。
|
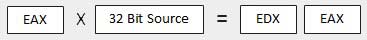
| 3 | When two doubleword values are multiplied − 当两个双字值相乘时,被乘数应为EAX,乘数为存储在存储器或另一个寄存器中的双字值。 生成的产品存储在EDX:EAX寄存器中,即高位32位存储在EDX寄存器中,低位32位存储在EAX寄存器中。
|
例子 (Example)
MOV AL, 10
MOV DL, 25
MUL DL
...
MOV DL, 0FFH ; DL= -1
MOV AL, 0BEH ; AL = -66
IMUL DL
例子 (Example)
以下示例将3与2相乘,并显示结果 -
section .text
global _start ;must be declared for using gcc
_start: ;tell linker entry point
mov al,'3'
sub al, '0'
mov bl, '2'
sub bl, '0'
mul bl
add al, '0'
mov [res], al
mov ecx,msg
mov edx, len
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov ecx,res
mov edx, 1
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
section .data
msg db "The result is:", 0xA,0xD
len equ $- msg
segment .bss
res resb 1
编译并执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
The result is:
6
DIV/IDIV指令
除法运算生成两个元素 - quotient和remainder 。 在乘法的情况下,不会发生溢出,因为使用双倍长度寄存器来保留产品。 但是,在分割的情况下,可能会发生溢出。 如果发生溢出,处理器会产生中断。
DIV(Divide)指令用于无符号数据,IDIV(整数除)用于签名数据。
语法 (Syntax)
DIV/IDIV指令的格式 -
DIV/IDIV divisor
股息在累加器中。 这两条指令都可以用于8位,16位或32位操作数。 该操作会影响所有六个状态标志。 以下部分介绍了具有不同操作数大小的三种划分案例 -
| Sr.No. | 方案 |
|---|---|
| 1 | When the divisor is 1 byte − 假设被除数在AX寄存器中(16位)。 除法后,商进入AL寄存器,余数进入AH寄存器。
|
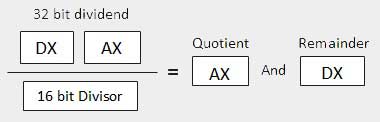
| 2 | When the divisor is 1 word − 假设被除数为32位,在DX:AX寄存器中。 高阶16位在DX中,低阶16位在AX中。 除法后,16位商进入AX寄存器,16位余数进入DX寄存器。
|
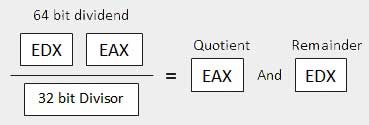
| 3 | When the divisor is doubleword − 假设被除数为64位,并且在EDX:EAX寄存器中。 高阶32位在EDX中,低阶32位在EAX中。 除法后,32位商进入EAX寄存器,32位余数进入EDX寄存器。
|
例子 (Example)
以下示例将8除以2. dividend 8存储在16-bit AX register , divisor 2存储在8-bit BL register 。
section .text
global _start ;must be declared for using gcc
_start: ;tell linker entry point
mov ax,'8'
sub ax, '0'
mov bl, '2'
sub bl, '0'
div bl
add ax, '0'
mov [res], ax
mov ecx,msg
mov edx, len
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov ecx,res
mov edx, 1
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
section .data
msg db "The result is:", 0xA,0xD
len equ $- msg
segment .bss
res resb 1
编译并执行上述代码时,会产生以下结果 -
The result is:
4