Field Options
字段是索引过程中最重要的单元。 它是包含要编制索引的内容的实际对象。 当我们添加一个字段时,Lucene使用字段选项在字段上提供了许多控件,字段选项说明了可搜索字段的数量。
我们将包含Field(s) Document(s)添加到IndexWriter ,其中IndexWriter用于更新或创建索引。
我们现在将向您展示一种逐步的方法,并使用一个基本示例帮助您了解各种Field Options。
各种现场选择
以下是各种领域选择 -
Index.ANALYZED - 在此,我们先分析,然后做索引。 这用于普通文本索引。 Analyzer会将字段的值分解为令牌流,并且每个令牌都可以单独搜索。
Index.NOT_ANALYZED - 在此,我们不进行分析,而是进行索引。 这用于完整的文本索引。 例如,人名,URL等。
Index.ANALYZED_NO_NORMS - 这是Index.ANALYZED的变体。 分析器会将字段的值分解为令牌流,并且每个令牌都可以单独搜索。 但是,NORM不会存储在索引中。 NORMS用于增强搜索,这通常会消耗大量内存。
Index.Index.NOT_ANALYZED_NO_NORMS - 这是Index.NOT_ANALYZED变体。 索引已完成,但NORMS未存储在索引中。
Index.NO - 字段值无法搜索。
使用现场选项
以下是可以使用现场选项的不同方式 -
创建从文本文件获取Lucene文档的方法。
创建各种类型的字段,这些字段是键值对,包含键作为名称和值作为要索引的内容。
设置要分析的字段与否。 在我们的例子中,只分析内容,因为它可以包含搜索操作中不需要的数据,例如a,am,are,an等。
将新创建的字段添加到文档对象并将其返回给调用方法。
private Document getDocument(File file) throws IOException {
Document document = new Document();
//index file contents
Field contentField = new Field(LuceneConstants.CONTENTS,
new FileReader(file));
//index file name
Field fileNameField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_NAME,
file.getName(),
Field.Store.YES,Field.Index.NOT_ANALYZED);
//index file path
Field filePathField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_PATH,
file.getCanonicalPath(),
Field.Store.YES,Field.Index.NOT_ANALYZED);
document.add(contentField);
document.add(fileNameField);
document.add(filePathField);
return document;
}
例子 Example Application
要测试索引过程,我们需要创建一个Lucene应用程序测试。
| 步 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在Lucene - First Application章节中解释,在cn.xnip.lucene包下创建一个名为LuceneFirstApplication的项目。 您还可以使用在EJB - First Application章节中创建的项目本章来理解索引过程。 |
| 2 | 按照Lucene - First Application章节中的说明创建LuceneConstants.java,TextFileFilter.java和LuceneConstants.java,TextFileFilter.java 。 保持其余文件不变。 |
| 3 | 创建LuceneTester.java ,如下所述。 |
| 4 | 清理并构建应用程序以确保业务逻辑按照要求运行。 |
LuceneConstants.java
此类用于提供跨示例应用程序使用的各种常量。
package cn.xnip.lucene;
public class LuceneConstants {
public static final String CONTENTS = "contents";
public static final String FILE_NAME = "filename";
public static final String FILE_PATH = "filepath";
public static final int MAX_SEARCH = 10;
}
TextFileFilter.java
此类用作.txt文件筛选器。
package cn.xnip.lucene;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class TextFileFilter implements FileFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".txt");
}
}
Indexer.java
此类用于索引原始数据,以便我们可以使用Lucene库对其进行搜索。
package cn.xnip.lucene;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.standard.StandardAnalyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Field;
import org.apache.lucene.index.CorruptIndexException;
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;
import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory;
import org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectory;
import org.apache.lucene.util.Version;
public class Indexer {
private IndexWriter writer;
public Indexer(String indexDirectoryPath) throws IOException {
//this directory will contain the indexes
Directory indexDirectory =
FSDirectory.open(new File(indexDirectoryPath));
//create the indexer
writer = new IndexWriter(indexDirectory,
new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_36),true,
IndexWriter.MaxFieldLength.UNLIMITED);
}
public void close() throws CorruptIndexException, IOException {
writer.close();
}
private Document getDocument(File file) throws IOException {
Document document = new Document();
//index file contents
Field contentField = new Field(LuceneConstants.CONTENTS,
new FileReader(file));
//index file name
Field fileNameField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_NAME,
file.getName(),
Field.Store.YES,Field.Index.NOT_ANALYZED);
//index file path
Field filePathField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_PATH,
file.getCanonicalPath(),
Field.Store.YES,Field.Index.NOT_ANALYZED);
document.add(contentField);
document.add(fileNameField);
document.add(filePathField);
return document;
}
private void indexFile(File file) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Indexing "+file.getCanonicalPath());
Document document = getDocument(file);
writer.addDocument(document);
}
public int createIndex(String dataDirPath, FileFilter filter)
throws IOException {
//get all files in the data directory
File[] files = new File(dataDirPath).listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if(!file.isDirectory()
&& !file.isHidden()
&& file.exists()
&& file.canRead()
&& filter.accept(file)
){
indexFile(file);
}
}
return writer.numDocs();
}
}
LuceneTester.java
该类用于测试Lucene库的索引功能。
package cn.xnip.lucene;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LuceneTester {
String indexDir = "E:\\Lucene\\Index";
String dataDir = "E:\\Lucene\\Data";
Indexer indexer;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LuceneTester tester;
try {
tester = new LuceneTester();
tester.createIndex();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void createIndex() throws IOException {
indexer = new Indexer(indexDir);
int numIndexed;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
numIndexed = indexer.createIndex(dataDir, new TextFileFilter());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
indexer.close();
System.out.println(numIndexed+" File indexed, time taken: "
+(endTime-startTime)+" ms");
}
}
数据和索引目录创建
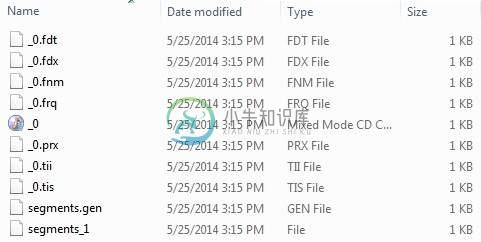
我们使用了来自record1.txt的10个文本文件到包含学生姓名和其他详细信息的record10.txt,并将它们放在目录E:\Lucene\Data中。。 索引目录路径应创建为E:\Lucene\Index 。 运行此程序后,您可以看到在该文件夹中创建的索引文件列表。
运行程序 (Running the Program)
完成源,原始数据,数据目录和索引目录的创建后,您可以编译并运行程序。 为此,请保持LuceneTester.Java文件选项卡处于活动状态,并使用Eclipse IDE中提供的“运行”选项或使用Ctrl + F11编译并运行LuceneTester应用程序。 如果您的应用程序成功运行,它将在Eclipse IDE的控制台中打印以下消息 -
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record1.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record10.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record2.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record3.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record4.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record5.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record6.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record7.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record8.txt
Indexing E:\Lucene\Data\record9.txt
10 File indexed, time taken: 109 ms
成功运行程序后,您的index directory中将包含以下内容 -