请求和响应(Requests & Response)
HTTP请求和HTTP响应在任何Web应用程序中都发挥着重要作用。 我们需要获取http请求的完整详细信息以便正确处理它。 处理完毕后,我们需要通过http响应将处理后的数据发送给客户端。
FuelPHP提供了出色的Request和Response类,分别用于读写HTTP请求和HTTP响应。 让我们在本章中了解Request和Response类。
Request
在典型的Web应用程序中,应用程序需要解析当前请求的详细信息。 Request类提供了简单的方法来解析应用程序要处理的当前请求。 Request还提供了一个通过充当http客户端来创建新请求的选项。
创建新请求使应用程序可以请求应用程序的其他部分或完全另一个应用程序并显示结果。 让我们学习如何解析本章中的传入请求,并学习如何在HMVC请求章节中创建新请求。
解析请求
Request类提供了三种获取http请求详细信息的方法。 它们如下,
active - 这是一个静态方法,它返回当前活动的http请求。
$currentRequest = Request::active();
param - 返回指定参数的值。 它包含两个参数。 如果参数在当前http请求中不可用,则第一个参数是参数名称,第二个参数是要返回的值。
$param = Request::active()->param('employee_name', 'none');
params - 除了将所有参数作为数组返回外,它与param相同。
$params = Request::active()->params();
例子 (Example)
让我们创建一个简单的表单并使用请求类处理表单。
Step 1 - 在员工控制器中创建新操作action_request 。
public function action_request() {
}
Step 2 - 调用请求方法以获取当前请求的所有参数。
public function action_request() {
$params = Request::active()->params();
}
Step 3 - 转储获取的参数数组。
public function action_request() {
$params = Request::active()->params();
echo dump($params);
}
Step 4 - 更改路由以在路由配置文件fuel/app/config/routes.php包含参数
'employee/request(/:name)?' => array('employee/request', 'name' => 'name'),
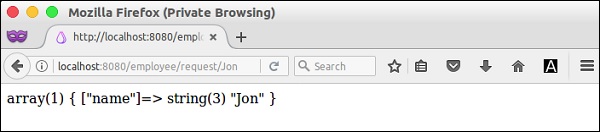
现在,请求新操作http://localhost:8080/employee/request/Jon,它将显示以下响应。
Response
Response类提供了创建http响应的选项。 默认情况下,我们不需要在大多数情况下直接使用响应类。 相反,我们使用View (我们将在下一章中学习)来创建http响应。 View隐藏了开发人员的http响应,并使用底层的Response类将响应发送到客户端。 在高级情况下,我们直接使用Response类并创建完整的http响应。
创建响应
响应由标题和正文组成。 主标题是http状态代码。 Http状态代码是HTTP协议中定义的标准代码,用于描述响应。 例如,状态代码200表示请求成功。
Response类提供了三个参数来创建http响应,
$body - http响应的正文
$status_code - http响应的状态代码
$headers - 作为数组的可选标头
$body = "Hi, FuelPHP";
$headers = array (
'Content-Type' => 'text/html',
);
$response = new Response($body, 200, $headers);
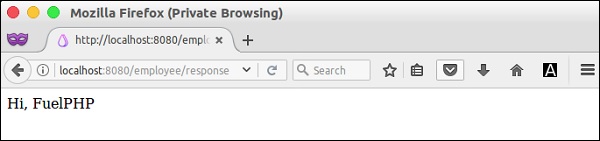
让我们在员工控制器中创建一个新动作action_response ,如下所示。
public function action_response() {
$body = "Hi, FuelPHP";
$headers = array ('Content-Type' => 'text/html',);
$response = new Response($body, 200, $headers);
return $response;
}
结果 (Result)
方法 (Methods)
Response类提供了许多操作http响应的方法。 它们如下,
forge - 它与响应类构造函数相同,如上所示。
return Response::forge("Hi, FuelPHP", 404);
redirect - 它提供重定向到URL而不是发送响应的选项。 它包含以下参数,
a.url - 目的地网址b。 方法 - 重定向方法。 location (默认)和refresh c 。 redirect_code - http状态代码。 默认值为302。
// use a URL
Response::redirect('http://some-domain/index', 'refresh');
// or use a relative URI
Response::redirect('employee/list');
redirect_back - 它类似于重定向方法,除了它重定向到上一页。 如果没有可用的后页,我们可以指定重定向页面。
// If there is no back page, go to the employee list page
Response::redirect_back('/employee/list', 'refresh');
set_status - 它提供了一个设置http状态代码的选项。
$response = new Response();
$response->set_status(404);
set_header - 它提供了一个设置http标头的选项。
$response = new Response();
$response->set_header('Content-Type', 'application/pdf');
// replace previous value using third arguments
$response->set_header('Content-Type', 'application/pdf', 'text/plain');
set_headers - 它与set_header相同,只是它提供了一个使用数组设置多个头的选项。
$response = new Response();
$response->set_headers (array
'Content-Type' => 'application/pdf',
'Pragma' => 'no-cache',
));
get_header - 它可以获取先前设置的标题详细信息。
$response = new Response();
$response->set_header('Pragma', 'no-cache');
// returns 'no-cache'
$header = $response->get_header('Pragma');
// returns array('Pragma' => 'no-cache')
$header = $response->get_header();
body - 它提供了一个设置http响应正文的选项。
$response = new Response();
$response->body('Hi, FuelPHP');
// returns 'Hi, FuelPHP'
$body = $response->body();
send_headers - 它将标send_headers送到请求的客户端。 FuelPHP使用此方法将响应发送到客户端。 通常,我们不需要使用此方法。
$response->send_headers();
send - 与send_headers相同,但在http响应中可能会限制标头。
// send the headers as well
$response->send(true);
// only send the body
$response->send(false);
$response->send();

