11 Pango II
在教程的这个部分,我们将继续探索Pango库。
Animated text
在下面的例子中,我们将在一个窗口中显示动态的文本。
Code:animation.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows animated text
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
import glib
import pango
import math
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
glib.timeout_add(160, self.on_timer)
self.count = 1
self.set_border_width(10)
self.set_title("ZetCode")
self.label = gtk.Label("ZetCode")
fontdesc = pango.FontDescription("Serif Bold 30")
self.label.modify_font(fontdesc)
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
vbox.add(self.label)
self.add(vbox)
self.set_size_request(300, 250)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.show_all()
def on_timer(self):
attr = pango.AttrList()
self.count = self.count + 1
for i in range(7):
r = pango.AttrRise(int(math.sin(self.count+i)*20)*pango.SCALE, i, i+1)
attr.insert(r)
self.label.set_attributes(attr)
return True
PyApp()
gtk.main()在上面的代码示例中,我们在标签部件中有一行文本。通过不断的更改它的Pango属性,这个文本就变成了动态的了。
self.label = gtk.Label("ZetCode")fontdesc = pango.FontDescription("Serif Bold 30")
self.label.modify_font(fontdesc)我们创建了一个标签,并且改变它的字体。为了更好的视觉效果,我们选择了较大的文本。
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 0) vbox.add(self.label)
我们将标签放置到垂直箱子中,这将使标签位于窗口的中间。
这个动画在on_timer()方法中被执行。
for i in range(7):
r = pango.AttrRise(int(math.sin(self.count+i)*20)*pango.SCALE, i, i+1)
attr.insert(r)在我们的文本中,我们有七个字母。我们为每个字母周期性地更改Pango的AttrRise属性。升降是基于三角正弦函数。文本的运动是沿着由正弦函数所绘成的笛卡尔曲线的。
当然也要注意到pango.SCALE常量。Pango有它自己的内部单元。它们不同于那些通常被widgets用来绘制图形或文本的单元。我们必须用这个常数来乘以我们的数字。

Figure:Animated Text
Using markup language
我们可以通过使用内置的标记语言来改变文本的属性。
Code:markup.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example uses markup language
# to change attributes of the text
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
import pango
quote = "<span foreground='blue' size='19000'>The only victory over love is flight</span>"
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Markup")
self.set_border_width(5)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
label = gtk.Label()
label.set_markup(quote)
vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
vbox.add(label)
self.add(vbox)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()
在代码示例中,我们有一个标签,我们通过标记语言来改变它的文本属性。
quote = "<span foreground='blue' size='19000'>The only victory over love is flight</span>"
这是包含有标记语言的文本。
label = gtk.Label() label.set_markup(quote)
我们创建了一个标签部件,并且为它设置了一个含有标记的文本。
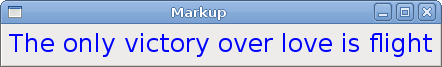
Figure:Using Markup
Pango layout
Pango的布局就是一个对象,它用来呈现一个段落包含属性的文本。
Code:layout.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# ZetCode PyGTK tutorial
#
# This example shows pango Layout
# in action
#
# author: jan bodnar
# website: zetcode.com
# last edited: February 2009
import gtk
import pango
lyrics = """Meet you downstairs in the bar and heard
your rolled up sleeves and your skull t-shirt
You say why did you do it with him today?
and sniff me out like I was Tanqueray
cause you're my fella, my guy
hand me your stella and fly
by the time I'm out the door
you tear men down like Roger Moore
I cheated myself
like I knew I would
I told ya, I was trouble
you know that I'm no good"""
class Area(gtk.DrawingArea):
def __init__(self):
super(Area, self).__init__()
self.modify_bg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, gtk.gdk.Color(16400, 16400, 16440))
self.connect("expose_event", self.expose)
def expose(self, widget, event):
gc = self.get_style().fg_gc[gtk.STATE_NORMAL]
font_desc = pango.FontDescription('Sans 10')
layout = self.create_pango_layout(lyrics)
width, height = self.get_size_request()
attr = pango.AttrList()
fg_color = pango.AttrForeground(60535, 60535, 60535, 0, -1)
attr.insert(fg_color)
layout.set_width(pango.SCALE * self.allocation.width)
layout.set_spacing(pango.SCALE * 3)
layout.set_alignment(pango.ALIGN_CENTER)
layout.set_font_description(font_desc)
layout.set_attributes(attr)
self.window.draw_layout(gc, 0, 5, layout)
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.set_title("You know I'm no Good")
self.add(Area())
self.set_size_request(300, 300)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
self.show_all()
PyApp()
gtk.main()在之前的例子中,我们在现存的部件中改变文本。现在,我们将用pango layout在DrawingArea部件上绘制文本。我们将用到GDK的绘制工具来绘制。
gc = self.get_style().fg_gc[gtk.STATE_NORMAL]
我们得到了DrawingArea部件的图形环境。
layout = self.create_pango_layout(lyrics)
这里创建了pango layout对象。
layout.set_width(pango.SCALE * self.allocation.width) layout.set_spacing(pango.SCALE * 3) layout.set_alignment(pango.ALIGN_CENTER) layout.set_font_description(font_desc) layout.set_attributes(attr)
我们更改布局的宽度、间隔、对齐、字体并且设置文本的属性。
self.window.draw_layout(gc, 0, 5, layout)
Layout被绘进窗口中。

Figure:Layout
在教程的这章中,我们用Pango库做了更深入的工作。

