物理内存和虚拟内存理论
在与 GDT 相关的章节中,我们知道分段物理内存地址使用的是段选择和计算偏移(Linux在X86上的虚拟内存管理)
在本章中,我们将实现内存的分页功能,其原理是将分段的线性地址转换成物理地址(分页表存储了虚拟(线性)地址到物理地址间的映射)。
为什么我们需要分页管理内存?
内存分页将允许我们的内核:
为避免歧义,保留部分原文
- use the hard-drive as a memory and not be limited by the machine ram memory limit
- to have a unique memory space for each process
- to allow and unallow memory space in a dynamic way
- 使用硬盘作为存储,且不受RAM内存的限制
- 每个进程使用独立的内存空间
- 控制是否以动态方式使用内存
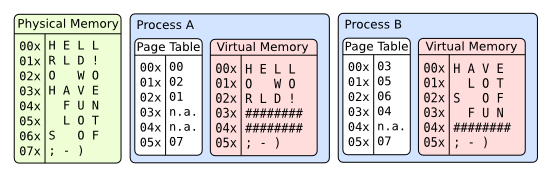
注:每个进程都以为自己拥有全部的内存空间,如果为32位的操作系统,则进程认为自己拥有4GB的执行空间,但实际并没有这么多。
在一个分页系统中,每个进程都可能在一个独有的4GB的空间范围内执行(并不是指4GB的实际内存空间),且不会对其他用户进程或内存进程的内存空间产生影响。这样就简化了系统对多任务的处理。
分页管理内存是怎样工作的?
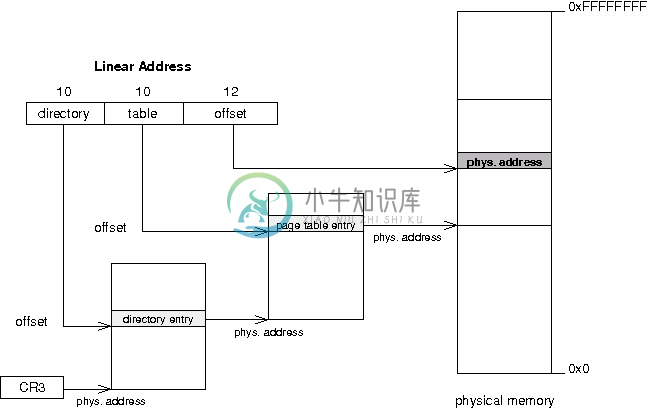
将线性地址转化为物理地址的几个步骤:
为避免歧义,保留部分原文
- The processor use the registry
CR3to know the physical address of the pages directory. - The first 10 bits of the linear address represent an offset (between 0 and 1023), pointing to an entry in the pages directory. This entry contains the physical address of a pages table.
- the next 10 bits of the linear address represent an offset, pointing to an entry in the pages table. This entry is pointing to a 4ko page.
- The last 12 bits of the linear address represent an offset (between 0 and 4095), which indicates the position in the 4ko page.
- 处理器从CR3寄存器中获取页目录的物理地址。(页目录中保存页面表)
- 线性地址的前10位代表一个偏移(0-1023),它指向页目录中的一个索引项。这个索引项包含一个页面表的物理地址。(每个活动的进程都有一个独立的页面表)
- 线性表接下来的10位偏移量,指向一个4ko大小的页(4ko即4k)。
- 最后12位(0-4095),标记一个4ko页的位置。
注:CR3 是页目录基址寄存器,保存页目录表的物理地址
格式化页表和页目录
下图页目录和页表各字段看起来一样,但在我们的OS中只会使用到灰色区域的字段。


为避免歧义,保留部分原文
P: indicate if the page or table is in physical memoryR/W: indicate if the page or table is accessible in writting (equals 1)U/S: equals 1 to allow access to non-preferred tasksA: indicate if the page or table was accessedD: (only for pages table) indicate if the page was writtenPS(only for pages directory) indicate the size of pages:- 0 = 4kb
- 1 = 4mb
p: 标记一个页或表是否在物理内存中R/W: 标记一个页或表是否正在写(以书面形式访问) (equals 1:=1则是)U/S: 标记为1,则允许访问非优选的任务A: 标记一个页或表是否被访问过D: (只针对页表) 标记也是否被写过PS(只针对页目录) 标记页大小:- 0 = 4kb
- 1 = 4mb
注意: 页目录与页表的地址,都要被写入20位(上图中12-31位),因为这些地址都是遵循4k对齐, 所以最后12位(0-12位)应该置0。
- 一个页目录或页表使用 1024*4 = 4096 bytes = 4k
- 一个页表可表示地址范围 1024 * 4k = 4 Mb
- 一个页目录可表示地址范围 1024 (1024 4k) = 4 Gb
怎样启动内存分页功能?
启动内存分页功能,我们只需要将 CR0 寄存器的第31位置1:
asm(" mov %%cr0, %%eax; \
or %1, %%eax; \
mov %%eax, %%cr0" \
:: "i"(0x80000000));
注:CR0 中包含了6个预定义标志,0位是保护允许位PE(Protedted Enable),用于启动保护模式,如果PE位置1,则保护模式启动(分页模式),如果PE=0,则在实模式下运行。
但是之前,我们至少需要一个页表来初始化我们的页目录,也就是说页目录中至少要有一个页表项。
Identity Mapping
With the identity mapping model, the page will apply only to the kernel as the first 4 MB of virtual memory coincide with the first 4 MB of physical memory:
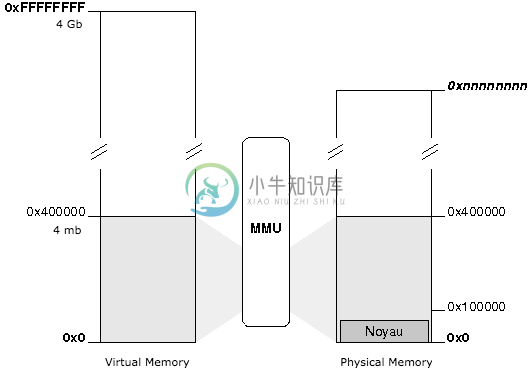
This model is simple: the first virtual memory page coincide to the first page in physical memory, the second page coincide to the second page on physical memory and so on ...

