第七天 线性表【上】
人活在社会上不可能孤立,比如跟美女有着千丝万缕的关系,有的是一对一,有的是一对多,有的是多对多。
哈哈,我们的数据也一样,存在这三种基本关系,用术语来说就是:
<1> 线性关系。
<2> 树形关系。
<3> 网状关系。
一: 线性表
1 概念:
线性表也就是关系户中最简单的一种关系,一对一。
如:学生学号的集合就是一个线性表。
2 特征:
① 有且只有一个“首元素“。
② 有且只有一个“末元素”。
③ 除“末元素”外,其余元素均有唯一的后继元素。
④ 除“首元素”外,其余元素均有唯一的前驱元素。
3 存储划分:
① 如果把线性表用“顺序存储”,那么就是“顺序表”。
② 如果把线性表用“链式存储”,那么就是“链表”。
4 常用操作:添加,删除,插入,查找,遍历,统计。
今天主要就说说“线性表”的“顺序存储”。
那么下面就简单的浅析一下这个操作的原理和复杂度。
<1> 初始化顺序表:
这个操作其实还是蛮简单的,设置length=0,也就是O(1)的时间。
<2> 求顺序表长度:
这个不解释,O(1)的时间。
<3> 添加节点:
因为是顺序表,所以添加的节点直接会放到数组的末尾,时间也是O(1)的。
<4> 插入节点:
这个还是有点小麻烦的,主要也就是说分两种情况:
①:当插入节点在数组的最后,那么这个“插入”其实就是”添加“操作,时间当然是O(1)。
②:当插入节点在数组的开头,那就悲催了,被插入节点的后续元素都要向后移动一位,
也就让整个数组一阵痉挛,效率低下可想而知,时间复杂度退化为O(n)。
<5> 删除节点:
这个跟“插入”的道理是一样的,也要分两个情况,
①:当删除的元素在数组的最后,不用移位,谢天谢地,时间为O(1)。
②: 当删除的元素在数组的开头,删除节点处的元素都要统统向前移位,同样也是一阵痉挛,
时间复杂度也退化为O(n)。
<6> 按序号查找节点:
大家都知道,顺序表的存储地址是连续的,所以第N个元素地址公式为:(N-1)X 数据存储长度。
哈哈,这就是顺序表得瑟的地方,查找的时间复杂度为O(1)。
<7> 按关键字查找:
嗯,这个在日常开发中用的最多的,那么就避免不了将key的值在我们的list中查找,前期也说过,
最快的查找是O(1),当然他是用空间来换取时间的,最慢的查找是O(n),那么这里我们就一个for
循环搞定,时间复杂度为O(n)。
说了这么多,目的就是预先评估算法的执行效率,给我们带来一手的参考资料,做到真正的运筹帷幄,决胜千里之外。
这也是我们学习算法的目的,到时候不会让我们说tnd,程序歇菜了,我也歇菜了。
好,现在是上代码时间。
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 using System.Linq;
4 using System.Text;
5
6 namespace SeqList
7 {
8 public class Program
9 {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SeqList seq = new SeqList();
SeqListType<Student> list = new SeqListType<Student>();
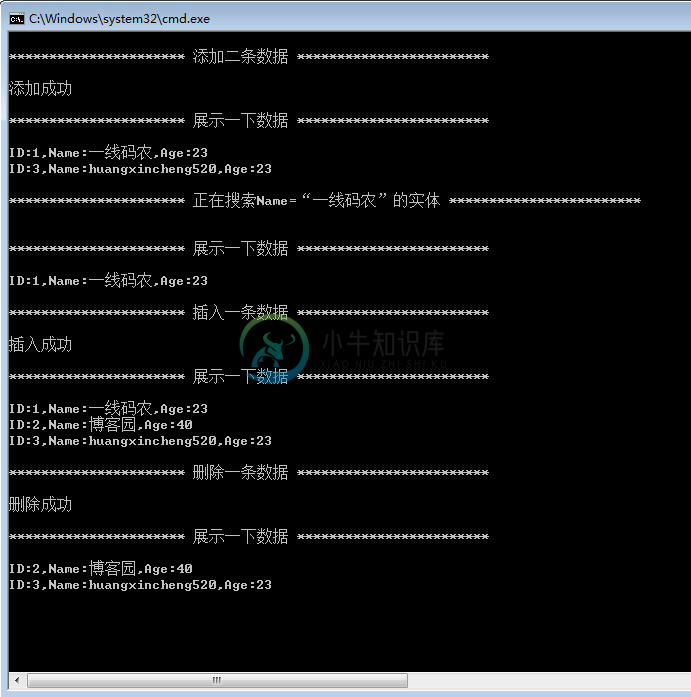
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 添加二条数据 ************************\n");
seq.SeqListAdd<Student>(list, new Student() { ID = "1", Name = "一线码农", Age = 23 });
seq.SeqListAdd<Student>(list, new Student() { ID = "3", Name = "huangxincheng520", Age = 23 });
Console.WriteLine("添加成功");
//展示数据
Display(list);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 正在搜索Name=“一线码农”的实体 ************************\n");
var student = seq.SeqListFindByKey<Student, string>(list, "一线码农", s => s.Name);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 展示一下数据 ************************\n");
if (student != null)
Console.WriteLine("ID:" + student.ID + ",Name:" + student.Name + ",Age:" + student.Age);
else
Console.WriteLine("对不起,数据未能检索到。");
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 插入一条数据 ************************\n");
seq.SeqListInsert(list, 1, new Student() { ID = "2", Name = "博客园", Age = 40 });
Console.WriteLine("插入成功");
//展示一下
Display(list);
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 删除一条数据 ************************\n");
seq.SeqListDelete(list, 0);
Console.WriteLine("删除成功");
//展示一下数据
Display(list);
Console.Read();
}
///<summary>
/// 展示输出结果
///</summary>
static void Display(SeqListType<Student> list)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n********************** 展示一下数据 ************************\n");
if (list == null || list.ListLen == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("呜呜,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.ListLen; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("ID:" + list.ListData[i].ID + ",Name:" + list.ListData[i].Name + ",Age:" + list.ListData[i].Age);
}
}
}
#region 学生的数据结构
///<summary>
/// 学生的数据结构
///</summary>
public class Student
{
public string ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
#endregion
#region 定义一个顺序表的存储结构
///<summary>
/// 定义一个顺序表的存储结构
///</summary>
public class SeqListType<T>
{
private const int maxSize = 100;
public int MaxSize { get { return maxSize; } }
//数据为100个存储空间
public T[] ListData = new T[maxSize];
public int ListLen { get; set; }
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的相关操作
///<summary>
///顺序表的相关操作
///</summary>
public class SeqList
{
#region 顺序表初始化
///<summary>
/// 顺序表初始化
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
public void SeqListInit<T>(SeqListType<T> t)
{
t.ListLen = 0;
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的长度
///<summary>
/// 顺序表的长度
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public int SeqListLen<T>(SeqListType<T> t)
{
return t.ListLen;
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的添加
///<summary>
///顺序表的添加
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public bool SeqListAdd<T>(SeqListType<T> t, T data)
{
//防止数组溢出
if (t.ListLen == t.MaxSize)
return false;
t.ListData[t.ListLen++] = data;
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的插入操作
///<summary>
/// 顺序表的插入操作
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<param name="n"></param>
///<param name="data"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public bool SeqListInsert<T>(SeqListType<T> t, int n, T data)
{
//首先判断n是否合法
if (n < 0 || n > t.MaxSize - 1)
return false;
//说明数组已满,不能进行插入操作
if (t.ListLen == t.MaxSize)
return false;
//需要将插入点的数组数字依次向后移动
for (int i = t.ListLen - 1; i >= n; i--)
{
t.ListData[i + 1] = t.ListData[i];
}
//最后将data插入到腾出来的位置
t.ListData[n] = data;
t.ListLen++;
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的删除操作
///<summary>
/// 顺序表的删除操作
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<param name="n"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public bool SeqListDelete<T>(SeqListType<T> t, int n)
{
//判断删除位置是否非法
if (n < 0 || n > t.ListLen - 1)
return false;
//判断数组是否已满
if (t.ListLen == t.MaxSize)
return false;
//将n处后的元素向前移位
for (int i = n; i < t.ListLen; i++)
t.ListData[i] = t.ListData[i + 1];
//去掉数组最后一个元素
--t.ListLen;
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的按序号查找
///<summary>
/// 顺序表的按序号查找
///</summary>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<param name="n"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public T SeqListFindByNum<T>(SeqListType<T> t, int n)
{
if (n < 0 || n > t.ListLen - 1)
return default(T);
return t.ListData[n];
}
#endregion
#region 顺序表的关键字查找
///<summary>
/// 顺序表的关键字查找
///</summary>
///<typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
///<typeparam name="W"></typeparam>
///<param name="t"></param>
///<param name="key"></param>
///<param name="where"></param>
///<returns></returns>
public T SeqListFindByKey<T, W>(SeqListType<T> t, string key, Func<T, W> where) where W : IComparable
{
for (int i = 0; i < t.ListLen; i++)
{
if (where(t.ListData[i]).CompareTo(key) == 0)
{
return t.ListData[i];
}
}
return default(T);
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
}运行结果: